Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 4 of others*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Lee, M.-S.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Yamashita, Takayuki*; Harjo, S.; Hyun, Y.-T.*; Jeong, Y.*; Jun, T.-S.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.3719_1 - 3719_10, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:71.60(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Co
Co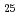 Ni
Ni Al
Al Ti
Ti Mo
Mo medium-entropy alloy; In situ neutron diffraction analysis
medium-entropy alloy; In situ neutron diffraction analysisKwon, H.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gong, W.; Jeong, S. G.*; Kim, E. S.*; Sathiyamoorthi, P.*; Kato, Hidemi*; Kim, H. S.*
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 23(1), p.579 - 586, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:64.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kim, S.*; Lee, B.*; Reeder, J. T.*; Seo, S. H.*; Lee, S.-U.*; Hourlier-Fargette, A.*; Shin, J.*; Sekine, Yurina; Jeong, H.*; Oh, Y. S.*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(45), p.27906 - 27915, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:109 Percentile:94.20(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In this study, we present a wireless, battery-free, skin-interfaced microfluidic system that combines lateral flow immunoassay for sweat cortisol assay, fluorometric imaging of glucose and ascorbic acid (vitamin C) assays, and digital tracking of sweat rate using electrodes that measure skin galvanic response. Systematic benchtop testing and on-body field studies on human subjects exercising in a gym environment highlight the key multifunctional features of this platform in tracking the biochemical correlates of physical stress.
Schury, P.*; Wada, Michiharu*; Ito, Yuta*; Kaji, Daiya*; Arai, Fumiya*; MacCormick, M.*; Murray, I.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Jeong, S.*; Kimura, Sota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(1), p.011305_1 - 011305_6, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:94.99(Physics, Nuclear)Using a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph located after a gas cell coupled with the gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS-II, the masses of several  -decaying heavy nuclei were directly and precisely measured. The nuclei were produced via fusion-evaporation reactions and separated from projectilelike and targetlike particles using GARIS-II before being stopped in a helium-filled gas cell. Time-of-flight spectra for three isobar chains,
-decaying heavy nuclei were directly and precisely measured. The nuclei were produced via fusion-evaporation reactions and separated from projectilelike and targetlike particles using GARIS-II before being stopped in a helium-filled gas cell. Time-of-flight spectra for three isobar chains,  Fr-
Fr- Rn-
Rn- At-
At- Po,
Po,  Fr-
Fr-  Rn-
Rn- At-
At- Po-
Po- Bi, and
Bi, and  Fr-
Fr- Rn-
Rn- At, were observed. Precision atomic mass values were determined for
At, were observed. Precision atomic mass values were determined for 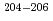 Fr,
Fr, 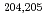 Rn, and
Rn, and 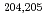 At. Identifications of
At. Identifications of  Bi,
Bi,  Po,
Po,  Rn, and
Rn, and  At were made with N
At were made with N 10 detected ions, representing the next step toward use of mass spectrometry to identify exceedingly low-yield species such as superheavy element ions.
10 detected ions, representing the next step toward use of mass spectrometry to identify exceedingly low-yield species such as superheavy element ions.

Oh, J.*; Le, M. D.*; Nahm, H.-H.*; Sim, H.*; Jeong, J.*; Perring, T. G.*; Woo, H.*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Yamani, Z.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 7, p.13146_1 - 13146_6, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:68 Percentile:87.80(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnons and phonons are fundamental quasiparticles in a solid and can be coupled together to form a hybrid quasi-particle. However, detailed experimental studies on the underlying Hamiltonian of this particle are rare for actual materials. Moreover, the anharmonicity of such magnetoelastic excitations remains largely unexplored, although it is essential for a proper understanding of their diverse thermodynamic behaviour and intrinsic zero-temperature decay. Here we show that in non-collinear antiferromagnets, a strong magnon phonon coupling can significantly enhance the anharmonicity, resulting in the creation of magnetoelastic excitations and their spontaneous decay. By measuring the spin waves over the full Brillouin zone and carrying out anharmonic spin wave calculations using a Hamiltonian with an explicit magnon phonon coupling, we have identified a hybrid magnetoelastic mode in (Y,Lu)MnO and quantified its decay rate and the exchange-striction coupling termrequired to produce it.
and quantified its decay rate and the exchange-striction coupling termrequired to produce it.
Jeong, J. H.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Joung, M.*; Kim, H. J.*; Park, S. I.*; Han, W. S.*; Kim, J. S.*; Yang, H. L.*; Kwak, J. G.*; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(5), p.380 - 387, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.44(Nuclear Science & Technology)Jeong, S. H.*; Chang, D. H.*; Kim, T. S.*; In, S. R.*; Lee, K. W.*; Jin, J. T.*; Chang, D. S.*; Oh, B. H.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, J. S.*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(2), p.02B102_1 - 02B102_3, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:70.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)The first NB (neutral beam) injection system of the KSTAR tokamak was partially completed in 2010 with only 1/3 of its full design capability, and NB heating experiments were carried out during the 2010 KSTAR operation campaign. The ion source is composed of a JAEA bucket plasma generator and a KAERI large multi-aperture accelerator assembly. Before the beam injection experiments, characteristics of the ion source were investigated. A minimum beam divergence angle was 0.8  . The ion species ratio was D
. The ion species ratio was D :D
:D
 :D
:D
 =75:20:5. The arc efficiency is more than 1.0 A/kW. In the 2010 KSTAR campaign, the deuterium NB power of 0.7-1.5 MW was successfully injected into the KSTAR plasma with the beam energy of 70-90 keV. L-H transitions were observed within a wide range of beam powers relative to a threshold value. In every deuterium NB injection, a burst of D-D neutrons was recorded, and increases in the ion temperature and the plasma stored energy were found.
=75:20:5. The arc efficiency is more than 1.0 A/kW. In the 2010 KSTAR campaign, the deuterium NB power of 0.7-1.5 MW was successfully injected into the KSTAR plasma with the beam energy of 70-90 keV. L-H transitions were observed within a wide range of beam powers relative to a threshold value. In every deuterium NB injection, a burst of D-D neutrons was recorded, and increases in the ion temperature and the plasma stored energy were found.
Chang, D. H.*; Jeong, S. H.*; Jin, J. T.*; Chang, D. S.*; Kim, T. S.*; Lee, K. W.*; In, S. R.*; Oh, B. H.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, J. S.*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.275 - 280, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A long pulse ion source (LPIS) for the neutral beam injector (NBI) has been developed for the Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) superconducting tokamak. The arc discharge characteristics of the ion source were investigated on the first KSTAR neutral beam injector (NBI-1). The ion source consists of a magnetic bucket plasma generator with multi-pole cusp fields and a set of prototype tetrode accelerators with circular apertures. Stable and efficient arc plasmas up to an arc power of 70 kW have been produced by using a constant power-mode operation of the arc power supply. The reliable operation region of the arc discharges has been investigated for various filament heating voltages, arc powers, and amounts of injected deuterium gas.
Chang, D. H.*; Jeong, S. H.*; Kim, T. S.*; Lee, K. W.*; In, S. R.*; Jin, J. T.*; Chang, D. S.*; Oh, B. H.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, J. S.*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(6), p.066302_1 - 066302_7, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:45.23(Physics, Applied)A stable ion beam extraction of the LPIS-1 was achieved up to 85 kV/32 A for a 5 s pulse length and 80 kV/25 A for a 14 s pulse length. An optimum beam perveance of 1.15  perv was observed at an acceleration voltage of 60 kV. Neutralization efficiency was measured by a water-flow calorimetry (WFC) method using a calorimeter and the operation of a bending magnet. The full-energy species of ion beams were detected by using the diagnostic method of optical multichannel analyzer (OMA). An arc efficiency of the LPIS was 0.6-1.1 A/kW depending on the operating conditions of arc discharge. A neutral beam power of 1.0 MW must be sufficiently injected into the KSTAR plasmas from the LPIS-1 at a beam energy of 80 keV.
perv was observed at an acceleration voltage of 60 kV. Neutralization efficiency was measured by a water-flow calorimetry (WFC) method using a calorimeter and the operation of a bending magnet. The full-energy species of ion beams were detected by using the diagnostic method of optical multichannel analyzer (OMA). An arc efficiency of the LPIS was 0.6-1.1 A/kW depending on the operating conditions of arc discharge. A neutral beam power of 1.0 MW must be sufficiently injected into the KSTAR plasmas from the LPIS-1 at a beam energy of 80 keV.
Bae, Y. S.*; Park, Y. M.*; Kim, J. S.*; Han, W. S.*; Kwak, S. W.*; Chang, Y. B.*; Park, H. T.*; Song, N. H.*; Chang, D. H.*; Jeong, S. H.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/03
The neutral beam injection (NBI) system is designed to provide the ion heating and current drive for the high performance operation and long pulse operation of the Korean Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR). The KSTAR NBI consists of two beam lines. Each beam line contains three ion sources of which one ion source has been designed to deliver more than 2.5 MW of deuterium neutral beam power with maximum 120-keV beam energy. Consequently, the final goal of the KSTAR NBI system aims to inject more than 14 MW of deuterium beam power with the two beam lines. According to the planned NBI system, the first NBI system is to demonstrate the beam injection from one ion source into the KSTAR tokamak plasma in 2010 campaign including the system commissioning of each components and subsystems. In this paper, the construction and the commissioning of the first NBI system with one ion source is presented.
Bae, Y. S.*; Na, Y. S.*; Oh, Y. K.*; Kwon, M.*; Bak, J. S.*; Lee, G. S.*; Jeong, J. H.*; Park, S. I.*; Cho, M. H.*; Namkung, W.*; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 52(2), p.321 - 333, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:81.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)An 84-GHz, 500-kW gyrotron system have been installed at KSTAR, and the initial test of the gyrotron has been carried out with 20  sec-pulse and an output RF power of 500 kW. The launcher system having with a highly flexible steering mirror was fabricated and would inject 500-kW rf power into the KSTAR plasma. KSTAR will employ 170-GHz EC current drive (CD) in ITER-relevant experiments such as the suppression of the neoclassical tearing modes and the creation of an electron internal transport barrier. A JAEA 170-GHz, 1-MW gyrotron on loan in accordance with a Korea-Japan fusion collaboration agreement, and it will be used for the 170-GHz, 1-MW ECCD system in 2010. This paper describes the current status of the installation and initial conditioning tests of the 84-GHz gyrotron system as well as the development plan of the 170-GHz ECH and CD system. Also, this paper discusses the CD efficiency and the steering range of the second-harmonic X-mode injection.
sec-pulse and an output RF power of 500 kW. The launcher system having with a highly flexible steering mirror was fabricated and would inject 500-kW rf power into the KSTAR plasma. KSTAR will employ 170-GHz EC current drive (CD) in ITER-relevant experiments such as the suppression of the neoclassical tearing modes and the creation of an electron internal transport barrier. A JAEA 170-GHz, 1-MW gyrotron on loan in accordance with a Korea-Japan fusion collaboration agreement, and it will be used for the 170-GHz, 1-MW ECCD system in 2010. This paper describes the current status of the installation and initial conditioning tests of the 84-GHz gyrotron system as well as the development plan of the 170-GHz ECH and CD system. Also, this paper discusses the CD efficiency and the steering range of the second-harmonic X-mode injection.
Orimo, Satoshi; Yogo, Akifumi; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Mori, Michiaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Li, Z.*; Ma, J.-L.; Daido, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Shu*; et al.
no journal, ,
Laser drive ion acceleration generated by thin foil irradiation high intensity laser and it is applications. An intense p-pol. laser was irradiated by the 45 degree incident angle on 3 10
10 Wcm
Wcm at 5 microns thickness copper tape target. The proton of a maximum of more 2MeV was generated, and a space spread and the propagation characteristic for energy of the were measured using CR39 with a range filter. Moreover, demonstration of simultaneous imaging by the proton beam and X-rays was measured.
at 5 microns thickness copper tape target. The proton of a maximum of more 2MeV was generated, and a space spread and the propagation characteristic for energy of the were measured using CR39 with a range filter. Moreover, demonstration of simultaneous imaging by the proton beam and X-rays was measured.
Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Akino, Noboru; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Oh, B. H.*; Jeong, S. H.*; Chang, D. H.*; Lee, K. W.*; Bae, Y. S.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Takai, Mamiko; Mori, Michiaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Daido, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Shu*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English