Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Jiang, X.*; Hattori, Takanori; Xu, X.*; Li, M.*; Yu, C.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(3), p.977 - 982, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.86(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)As a promising environment-friendly alternative to current vapor-compression refrigeration, solid-state refrigeration based on the barocaloric effect has been attracting world wide attention. Generally, both phases in which a barocaloric effect occurs are present at ambient pressure. Here, instead, we demonstrate that KPF exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
 clusters in dilute neutron-rich matter
clusters in dilute neutron-rich matterTanaka, Junki*; Yang, Z.*; Typel, S.*; Adachi, Satoshi*; Bai, S.*; van Beek, P.*; Beaumel, D.*; Fujikawa, Yuki*; Han, J.*; Heil, S.*; et al.
Science, 371(6526), p.260 - 264, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:99.12(Multidisciplinary Sciences)By employing quasi-free  -cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of
-cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of  clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between
clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between  -cluster formation and the neutron skin.
-cluster formation and the neutron skin.
 decay of
decay of 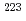 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:79.42(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Onuki, Toshihiko; Jiang, M.*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Yu, Q.; Tanaka, Kazuya; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Xia, X.*; Yange, K.*; et al.
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 163, p.1 - 13, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:57.4(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The association of Ce(III) with the microbial cell surface and the formation of Ce phosphate nano-particles are responsible for suppressing the oxidation of Ce(III) to Ce(IV) in the mixtures.
 fungal cells; A pH-dependent contribution of phosphoryl functional group
fungal cells; A pH-dependent contribution of phosphoryl functional groupJiang, M. Y.*; Onuki, Toshihiko; Yamasaki, Shinya; Tanaka, Kazuya*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 295(3), p.2283 - 2287, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.73(Chemistry, Analytical)The adsorption of Ytterbium on the cells of yeast  has been studied by batch type experiment by changing solution pH. The Yb adsorption species on the yeast cell wall of the
has been studied by batch type experiment by changing solution pH. The Yb adsorption species on the yeast cell wall of the  was determined by extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy combined with a linear combination analysis at various pHs. The results indicated that the contribution of Yb-phosphoryl species was constant between pH 3 and 5, strongly suggesting that most of the Yb was associated with undeprotonated phosphoryl functional groups.
was determined by extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopy combined with a linear combination analysis at various pHs. The results indicated that the contribution of Yb-phosphoryl species was constant between pH 3 and 5, strongly suggesting that most of the Yb was associated with undeprotonated phosphoryl functional groups.

Jiang, M. Y.*; Onuki, Toshihiko; Tanaka, Kazuya*; Kozai, Naofumi; Kamiishi, Eigo; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 93, p.30 - 46, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:63.8(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We have investigated the post-adsorption process of ytterbium (Yb) phosphate nano-particle formation by  . We have elucidated the nano particle formation by TEM and EXAFS analyses, that adsorbed Yb reacts on the cell surface with the released pohosphate from inside the cell.
. We have elucidated the nano particle formation by TEM and EXAFS analyses, that adsorbed Yb reacts on the cell surface with the released pohosphate from inside the cell.
Kozai, Naofumi; Onuki, Toshihiko; Arisaka, Makoto; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Yamasaki, Shinya; Jiang, M.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(5), p.473 - 478, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:97.82(Nuclear Science & Technology)Chemical states of radioactive Cs in the contaminated soils by Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident has been characterized by the desorption experiments using appropriate reagents solutions and size fractionation of the contaminated soils. Approximately 70% of radioactive Cs in the residual fraction were associated with the size fractions larger than the elutriated one, even though mica-like minerals were contained in the elutriated one. These results strongly suggest that radioactive Cs was irreversibly associated with soil components other than mica like minerals in the contaminated soil.

Jiang, M.; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi; Tanaka, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kamiishi, Eigo*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
Chemical Geology, 277(1-2), p.61 - 69, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:66.93(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We have investigated the mechanism underlying Ce sequestration by yeast  after exposure to Ce(III) solution at pH 3, 4, or 5. We found that needle-shaped Ce(III) phosphate nanocrystallites with a monazite structure formed on the yeast cells by exposure to Ce(III) for 42 h, even though the initial solutions did not contain any P species. These results suggest that the sorbed Ce on the cell surfaces reacted with P released from inside the yeast cell, resulting in the formation of Ce(III) phosphate nanocrystallites.
after exposure to Ce(III) solution at pH 3, 4, or 5. We found that needle-shaped Ce(III) phosphate nanocrystallites with a monazite structure formed on the yeast cells by exposure to Ce(III) for 42 h, even though the initial solutions did not contain any P species. These results suggest that the sorbed Ce on the cell surfaces reacted with P released from inside the yeast cell, resulting in the formation of Ce(III) phosphate nanocrystallites.
 Rf
RfQian, J.*; Heinz, A.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; Peterson, D.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Ahmad, I.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 79(6), p.064319_1 - 064319_13, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:83.95(Physics, Nuclear) -,
-,  -, and conversion electron spectroscopy experiments for
-, and conversion electron spectroscopy experiments for  Rf have been performed using Fragment Mass Analyzer at Argonne National Laboratory. A new isomer with a half-life of 160
Rf have been performed using Fragment Mass Analyzer at Argonne National Laboratory. A new isomer with a half-life of 160  s has been discovered in
s has been discovered in  Rf, and it is interpreted as a three-quasiparticle high-
Rf, and it is interpreted as a three-quasiparticle high- isomer. Neutron configurations of one-quasiparticle states in
isomer. Neutron configurations of one-quasiparticle states in 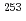 No, the
No, the  -decay daughter of
-decay daughter of  Rf, have been assigned on the basis of
Rf, have been assigned on the basis of  -decay hindrance factors. Excitation energies of the 1/2
-decay hindrance factors. Excitation energies of the 1/2 [620] states in
[620] states in  =151 isotones indicate that the deformed shell gap at
=151 isotones indicate that the deformed shell gap at  =152 increases with the atomic number.
=152 increases with the atomic number.
Jiang, M.; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi; Tanaka, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
We investigated association of Ce with yeast S. cerevisiae at pH of 3, 4, and 5. SEM analysis showed that nano-sized Ce bearing minerals were developed on the cell surface. TEM and SAED analyses showed that the Ce- bearing mineral is monazite.

Onuki, Toshihiko; Jiang, M.; Kamiishi, Eigo*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Suzuki, Yoshinori*
no journal, ,
We have investigated the association of heavy REE of Yb with yeast 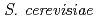 after exposure at pH of 3, 4 or 5. A variety of analytical techniques including FESEM-EDS, TEM, ICP-AES, XAFS have been employed to investigate the sequestration mechanism of Yb by yeast as a function of exposure time. Ytterbium concentrations in solutions decrease as the exposure time increases. FESEM, TEM, and XAFS analyses revealed that nano-sized blocky Yb phosphate with amorphous phase formed on the yeast cells surface after 24 h. These results suggest that the sorbed Yb on the cell surfaces reacted with P released from inside of the yeast cell, resulting in the formation of amorphous Yb phosphate.
after exposure at pH of 3, 4 or 5. A variety of analytical techniques including FESEM-EDS, TEM, ICP-AES, XAFS have been employed to investigate the sequestration mechanism of Yb by yeast as a function of exposure time. Ytterbium concentrations in solutions decrease as the exposure time increases. FESEM, TEM, and XAFS analyses revealed that nano-sized blocky Yb phosphate with amorphous phase formed on the yeast cells surface after 24 h. These results suggest that the sorbed Yb on the cell surfaces reacted with P released from inside of the yeast cell, resulting in the formation of amorphous Yb phosphate.
Kozai, Naofumi; Jiang, M.; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Kuwabata, Susumu*; Onuki, Toshihiko
no journal, ,
We have observed biogenic nano-particles developed on cell surface of microorganism coated with ionic liquid by SEM. In the sample preparation, the microbial cells were coated with hydrophilic and hydrophobic ionic liquids. The biogenic nano-particles were clearly observed by SEM, when the sample were coated with hydrophilic ionic liquid. On the contrary, the cells were collapsed during SEM observation, when the sample were coated with hydrophobic ionic liquid. These results showed that the coating with hydrophilic ionic liquid is effective for analyzing nano-particles developed on microbial cell surface by SEM.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Jiang, M.*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Onuki, Toshihiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Onuki, Toshihiko; Tanaka, Kazuya; Jiang, M.; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
The interaction of heavy elements involving actinides with microorganisms has been studied by experiments. Here, we report the nanoscale mineralization process of REE phosphate on microbial cell surfaces and sorption of REE by biogenic Mn oxide. We found that dissolved Ce was accumulated on the cell surface, and precipitated as nanoscale phosphate mineral, even though no P was added in the solution. The analyses of nanoscale phosphate mineral indicate that the sorbed Ce on the cell surfaces reacted with P released from inside the yeast cell, resulting in the formation of Ce(III) phosphate nanocrystallites of monazite. The biogenic Mn oxide (plus microbial cells) showed large a positive Ce anomaly in acid solution. With increasing pH, the positive Ce anomaly became less pronounced. Furthermore, negative Ce anomalies were observed at a pH of more than 6.5. This anomaly change was caused by organic matters released by bacteria.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi; Jiang, M.; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Effect of microorganisms on the solubility of trivalent actinides have been studied by using Ce(III) or Eu(III) as alternatives. Precipitation of CePO or EuPO
or EuPO on the cell surface by SEM analysis. The chemical components of the solution were higher than those estimated by thermodynamic data. These results suggest that some organic materials secreted from microorganisms are associated with Ce and Eu.
on the cell surface by SEM analysis. The chemical components of the solution were higher than those estimated by thermodynamic data. These results suggest that some organic materials secreted from microorganisms are associated with Ce and Eu.
Jiang, M.; Onuki, Toshihiko; Tanaka, Kazuya*; Kamiishi, Eigo; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Formation process of samarium phosphate mineralization on the cell surface of microorganisms has been studied. The rate of nano-particles formation on the cells of yeast was lower than that of soil bacteria, suggesting that thicker cell wall of yeast than soil bacteria gave lower release rate of phosphate ions from inside of cells.
Jiang, M.; Onuki, Toshihiko; Tanaka, Kazuya*; Kozai, Naofumi; Kamiishi, Eigo; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
The objective of the present study is to further understand the post-adsorption process of middle REE (Sm) and heavy REE (Yb) biomineralization by several representative microbes for the long-term exposure. Based on the FESEM and TEM analyses, nano-sized Sm phosphate crystallites with monazite structure formed on these three kinds of microbial cells surfaces and nano-sized Yb phosphate with amorphous phase formed on yeast cells surfaces. The EXAFS data indicated that the chemical states of accumulated Sm and Yb on cells surfaces changed from the mixture of both phosphate and carboxyl sites at 30 min to phosphate precipitates phase at 5 days, suggesting the REE-phosphate mineralization as a major post-adsorption process.
Jiang, M.; Onuki, Toshihiko; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Post adsorption of REE by microorganisms has been studied by long-term exposure experiments. In the experiments using Yb, concentration of Yb decreased with increasing time. SEm and TEM analyses showed development of nano-particles including Yb and P on the cells surface. XAFS analysis cralified that Yb was initially adsorbed on the functional groups of cells surface, followed by formation of phosphate mineralization.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Jiang, M.*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Tanaka, Kazuya*
no journal, ,
We found that Sm(III) phosphate minerals were formed on the cells surface of gram negative bacterium after exposure of Sm(III) solution with the resting cells. TEM-SAED analysis showed that Sm-monazite was developed directly from the surface of cells. Sm(III) ions were first adsorbed by the functional groups of cells surface, followed by the chemical states change by the reaction with phosphate ions released from inside the yeast cells.