Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kwon, H.*; Pietrasiak, E.*; Ohara, Takashi; Nakao, Akiko*; Chae, B.*; Hwang, C.-C.*; Jung, D.*; Hwang, I.-C.*; Ko, Y. H.*; Kim, K.*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(9), p.6403 - 6409, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Jung, W.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hicks, K.*; Hwang, S.*; Ichikawa, Yudai; Kim, S.*; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Tanida, Kiyoshi
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 27, p.011007_1 - 011007_6, 2019/11
Jung, K.; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2017-008, 26 Pages, 2017/08
We are developing an analytical method using laser ablation absorption spectroscopy (LAAS) to analyze radioactive waste mixed with zirconium, uranium and so on. It is essential to evaluate the characteristics of the plume formed by the objective particles for LAAS analysis. Therefore, in this study, titanium and hafnium whose chemical properties are similar to those of Zr were chosen as analytical object. And the difference in expanding behavior of the plume due to the weight of the particles was investigated. As a result of changing the height of the probe beam and applying the optical time-of-flight method to the plume, it was found that the influence of the background gas is larger for Ti than Hf. The meaning of the resonance absorption signal of the waste sample mixed with nuclear fuel materials and nuclear reactor materials was understood by this study and basic knowledge to optimize experimental conditions were also obtained.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Jung, K.; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Khumaeni, A.*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 134, p.42 - 51, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:91.41(Spectroscopy)Spectroscopic properties of atomic species of plutonium were investigated by combining laser ablation and resonance absorption techniques for the analysis of a plutonium oxide sample. For 17 transitions of Pu atoms and ions, the absorbance, isotope shift, and hyperfine splitting were determined via Voigt profile fitting of the recorded absorption spectra. Three transitions were selected as candidates for analytical use. Using these transitions, we investigated the analytical performance that was attainable and determined a correlation coefficient R2 between the absorbance and plutonium concentration of 0.9999, a limit of detection of 30-130 ppm, and a relative standard deviation of approximately 6% for an abundance of  Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Iwata, Yoshihiro*; Jung, K.*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
For the radioactivity evaluation regarding to the accident of TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, time-consuming and skills-required sample pretreatments for  Sr analysis (radiometric or ICP-MS analyses) is serious issue. We are developing a ultra-sensitive and rapid analytical technique for
Sr analysis (radiometric or ICP-MS analyses) is serious issue. We are developing a ultra-sensitive and rapid analytical technique for  Sr by combining resonance ionization spectroscopy, in which only the atoms of specific isotope can be ionized using the slight difference in level energy, and ion trap technique, in which only the ions of specific isotope can be trapped for a long duration to observe them with high sensitivity. In this study, we applied a continuous-wave isolated-core excitation technique (cw-ICE) for the first time to search for highly efficient and isotope-selective ionization schemes, especially for the Rydberg series converging to the 5
Sr by combining resonance ionization spectroscopy, in which only the atoms of specific isotope can be ionized using the slight difference in level energy, and ion trap technique, in which only the ions of specific isotope can be trapped for a long duration to observe them with high sensitivity. In this study, we applied a continuous-wave isolated-core excitation technique (cw-ICE) for the first time to search for highly efficient and isotope-selective ionization schemes, especially for the Rydberg series converging to the 5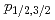 ionic levels, of which information is quite scarce. As a result, we have revealed a detailed level-structure of autoionizing 5
ionic levels, of which information is quite scarce. As a result, we have revealed a detailed level-structure of autoionizing 5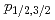 (nl) series of Sr atoms.
(nl) series of Sr atoms.
Jung, K.; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyabe, Masabumi; Jung, K.; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
Remote isotopic analysis for highly radioactive fuel debris containing various actinides, fission products and the other reactor materials is expected to be needed for the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan. This is because the information on the amount of fissile materials in the debris is of great importance for the purpose of safeguard verification and prevention of re-criticality accident. However, to decrease radiation dose to the analytical workers handling the debris, traditional analytical techniques such as radiometric and radiochemical methods are inadequate and an alternative technique is needed. For this reason, we are developing remote spectroscopic techniques (LIBS and LAAS) for debris analysis using laser ablation process. Laser ablation absorption spectroscopy (LAAS) is the technique by combining resonance absorption spectroscopy and laser ablation. In this technique for nuclear fuel materials, one uses the probe laser whose frequency is tuned to the resonance line of the specific isotope of U or Pu and determines the isotopic abundance from the measured absorbance. For realization of highly sensitive and isotope-selective analysis, it is necessary to optimize experimental conditions to decrease kinetic energy of the ablated species and the number of ionic species so as to reduce Doppler and Stark effects. For this optimization, we have studied the temporal and spatial variations in the density distribution under various background gas conditions. Using the optimum conditions, we have measured isotope-selective absorption spectra of U and Pu and evaluated several analytical performances of LAAS.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Jung, K.; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
In order to analyze isotopic composition of fuel debris generated in melted reactor core, a remote analytical method is developed based on laser ablation technique. In this method, the interaction between ablated and gas species affects time evolution of the plume structure, which also affects on analytical performance. Thus we investigate time evolution of ablated and gas species using resonance fluorescence and absorption techniques. As a result, it was found that the interaction between gas and ablated species leads complicated three dimensional structure. In particular, in the case of atmospheric air condition, it was found that many particulates and clusters are produced at the contact layer between gas and plume, and the neutral atoms stays near the center of the clusters. These findings is of great importance for future development of various laser-ablation-based analytical techniques.