Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kaburagi, Masaaki; Miyamoto, Yuta; Mori, Norimasa; Iwai, Hiroki; Tezuka, Masashi; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*; Tagawa, Akihiro; Takasaki, Koji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.308 - 316, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) -ray fields
-ray fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Kamada, Kei*; Ishii, Junya*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Manabe, Seiya*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Harano, Hideki*; Kato, Masahiro*; Shimazoe, Kenji*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 19(11), p.P11019_1 - P11019_16, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation) -ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a
-ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a  -ray field
-ray fieldKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Terasaka, Yuta; Tomita, Hideki*; Yoshihashi, Sachiko*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Uritani, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1046, p.167636_1 - 167636_8, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:88.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)We focus on the thickness and property controls of inorganic scintillators used for thermal neutron detection in intense  -ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20
-ray fields without considering pulse shape discrimination techniques. GS20 (a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF
(a lithium glass) and LiCaAlF :Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a
:Ce(LiCAF:Ce) cintillators with thicknesses of 0.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively, have been employed. Pulse signals generated by photomultiplier tubes, to which the scintillators were coupled, were inserted into a digital pulse processing unit with 1 Gsps, and the areas of waveforms were integrated for 360 ns. In a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron detection for GS20
-ray field, the neutron detection for GS20 with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a
with a 0.5-mm thickness was possible at dose rates of up to 0.919 Gy/h; however, for LiCAF:Ce, neutron detection was possible at 0.473 Gy/h, and it failed at 0.709 Gy/h. Threfore, in a  Co
Co  -ray field, the neutron/
-ray field, the neutron/ -ray discrimination of GS20
-ray discrimination of GS20 was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
was better than that of LiCAF:Ce due to its better energy resolution and higher detection efficiency.
Shiba, Tomooki; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Nomi, Takayoshi; Suzuki, Risa; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Takada, Akira*; Nagatani, Taketeru; Okumura, Keisuke
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/10
Nauchi, Yasushi*; Nomi, Takayoshi; Suzuki, Risa; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Shiba, Tomooki; Takada, Akira*; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Okumura, Keisuke
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
 Co radiation source under an intense
Co radiation source under an intense  Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr
Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fields
spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.983 - 992, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:28.39(Nuclear Science & Technology) -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of nuclear facilities being decommissioned has been increasing worldwide, in particular following the accident of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011. In these nuclear facilities, proper management of radioactive materials is required. Then, A  -ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr
-ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr scintillators with a dimension of
scintillators with a dimension of 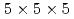
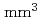 was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the
was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the  -ray exposure study under
-ray exposure study under  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields. Under the
Co radiation fields. Under the  Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2
Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0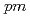 0.03%, and 9.0
0.03%, and 9.0 0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioningKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:84.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)An increasing number of nuclear facilities have been decommissioned worldwide following the 2011 accident of the TEPCO' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. During the decommissioning, radioactive materials have to be retrieved under proper management. In this study, a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm was manufactured to perform
5 mm was manufactured to perform  -ray spectroscopy under intense
-ray spectroscopy under intense  -ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform
-ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform  -ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a
-ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a  Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a
Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a  Co radiation field, which suggested to realize
Co radiation field, which suggested to realize  -ray assessment of
-ray assessment of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
 gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 971, p.164118_1 - 164118_8, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:60.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kaburagi, Masaaki; Torii, Tatsuo; Ogawa, Toru
JAEA-Review 2019-031, 251 Pages, 2020/01
There is high expectation for advanced remote technology and robotics to reduce the radiation exposure for workers in harsh nuclear environments such as the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). However, the radiation tolerance of state-of-the-art key components, sensors and electronic devices, for remote operation is still limited. In order to extend the application of robotics in nuclear energy, it is pertinent to develop "Radiation hardness" of components and "Radiation smartness" in operation procedures. Furthermore, developments of "Radiation measurement" and "Technology to recognize the location and to grasp the surrounding environment", including the radiation imaging of the high dose-rate fields inside the FDNPS and the detection of nuclear fuel debris, are necessary for the future nuclear fuel debris retrieval. This Fukushima Research Conference aims to share the future vision for advancing the remote technology among experts from diverse fields.
Sato, Yuki; Terasaka, Yuta; Miyamura, Hiroko; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Tanifuji, Yuta; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Torii, Tatsuo
Reactor Dosimetry; 16th International Symposium on Reactor Dosimetry (ISRD-16) (ASTM STP 1608), p.428 - 436, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kaburagi, Masaaki; Sato, Yuki; Yoshihara, Yuri*; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Torii, Tatsuo
Reactor Dosimetry; 16th International Symposium on Reactor Dosimetry (ISRD-16) (ASTM STP 1608), p.405 - 414, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Yuki; Tanifuji, Yuta; Terasaka, Yuta; Usami, Hiroshi; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Utsugi, Wataru*; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki*; Takahira, Shiro*; Torii, Tatsuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(9), p.965 - 970, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:96.83(Nuclear Science & Technology) -ray imager mounted on a multicopter drone
-ray imager mounted on a multicopter droneSato, Yuki; Ozawa, Shingo*; Terasaka, Yuta; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Tanifuji, Yuta; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Miyamura, Hiroko; Izumi, Ryo*; Suzuki, Toshikazu*; Torii, Tatsuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(1), p.90 - 96, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:97.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Yuki; Terasaka, Yuta; Ozawa, Shingo*; Miyamura, Hiroko; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Tanifuji, Yuta; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Torii, Tatsuo
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(11), p.C11007_1 - C11007_8, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:68.62(Instruments & Instrumentation) -ray imager mounted on a remotely operated machine
-ray imager mounted on a remotely operated machineSato, Yuki; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Ozawa, Shingo*; Izumi, Ryo*; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Tanifuji, Yuta; Terasaka, Yuta; Miyamura, Hiroko; Kawamura, Takuma; Suzuki, Toshikazu*; et al.
IFAC-PapersOnLine, 50(1), p.1062 - 1066, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:70.76(Automation & Control Systems)Kaburagi, Masaaki; Yamada, Hironao*; Miyakawa, Takeshi*; Morikawa, Ryota*; Takasu, Masako*; Kato, Takamitsu*; Uesaka, Mitsuru*
Polymer Journal, 48(2), p.189 - 195, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.93(Polymer Science)We performed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of telomeric single-stranded DNA and POT1 for 100 ns. The distance between 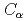 (POT1) and O5' (telomeric ssDNA) is calculated to verify the binding system for 100 ns MD. We then calculated the distance between the bases of telomeric DNA ends and the root mean square deviation and gyration radius in single and binding states. We compared the root mean square fluctuations between single and binding states and calculated the number of hydrogen bonds between POT1 and telomeric DNA. There are many hydrogen bonds between Gln94 and the first guanine of the closest TTAGGG sequence in telomeric single-stranded DNA. These Gln94 and the guanine have a large difference in root mean square fluctuation between single and binding states. We found that Gln94 and guanine are important components of the binding system, and they are related to its stability.
(POT1) and O5' (telomeric ssDNA) is calculated to verify the binding system for 100 ns MD. We then calculated the distance between the bases of telomeric DNA ends and the root mean square deviation and gyration radius in single and binding states. We compared the root mean square fluctuations between single and binding states and calculated the number of hydrogen bonds between POT1 and telomeric DNA. There are many hydrogen bonds between Gln94 and the first guanine of the closest TTAGGG sequence in telomeric single-stranded DNA. These Gln94 and the guanine have a large difference in root mean square fluctuation between single and binding states. We found that Gln94 and guanine are important components of the binding system, and they are related to its stability.
冠城 雅晃
島添 健次*
The present invention carries out highly accurate assay of a sample, even under high-dose radiation, by analyzing an energy spectrum obtained by a radiation detector. In this radiation analysis method, first, the spectrum (actual spectrum) of a sample is measured by a radiation detector (sample measurement step: S1). In this step, two or more types of scintillators having different sizes are used and two or more types of shielding substances having different thicknesses are used to obtain an actual spectrum for each condition (setting condition). Next, measurement similar to that described above is carried out with respect to a reference radiation source (reference radiation source measurement step: S2). Next, a background nuclide-derived component, which is a component derived from a background nuclide (137Cs) in the actual spectrum, is inferred from the reference spectrum obtained in the reference radiation source measurement step (S2) (background nuclide-derived component inference step: S3). ・・・
冠城 雅晃
島添 健次*
The present invention carries out highly accurate assay of a sample, even under high-dose radiation, by analyzing an energy spectrum obtained by a radiation detector. In this radiation analysis method, first, the spectrum (actual spectrum) of a sample is measured by a radiation detector (sample measurement step: S1). In this step, two or more types of scintillators having different sizes are used and two or more types of shielding substances having different thicknesses are used to obtain an actual spectrum for each condition (setting condition). Next, measurement similar to that described above is carried out with respect to a reference radiation source (reference radiation source measurement step: S2). Next, a background nuclide-derived component, which is a component derived from a background nuclide (137Cs) in the actual spectrum, is inferred from the reference spectrum obtained in the reference radiation source measurement step (S2) (background nuclide-derived component inference step: S3). ・・・
冠城 雅晃
島添 健次*
The present invention carries out highly accurate assay of a sample, even under high-dose radiation, by analyzing an energy spectrum obtained by a radiation detector. In this radiation analysis method, first, the spectrum (actual spectrum) of a sample is measured by a radiation detector (sample measurement step: S1). In this step, two or more types of scintillators having different sizes are used and two or more types of shielding substances having different thicknesses are used to obtain an actual spectrum for each condition (setting condition). Next, measurement similar to that described above is carried out with respect to a reference radiation source (reference radiation source measurement step: S2). Next, a background nuclide-derived component, which is a component derived from a background nuclide (137Cs) in the actual spectrum, is inferred from the reference spectrum obtained in the reference radiation source measurement step (S2) (background nuclide-derived component inference step: S3). ・・・