Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 /4H-SiC(0001) interface and its correlation with electrical properties
/4H-SiC(0001) interface and its correlation with electrical propertiesWatanabe, Heiji*; Hosoi, Takuji*; Kirino, Takashi*; Kagei, Yusuke*; Uenishi, Yusuke*; Chanthaphan, A.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Shimura, Takayoshi*
Applied Physics Letters, 99(2), p.021907_1 - 021907_3, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:124 Percentile:95.48(Physics, Applied) /4H-SiC interfaces and its modulation induced by intrinsic and extrinsic interface charge transfer
/4H-SiC interfaces and its modulation induced by intrinsic and extrinsic interface charge transferWatanabe, Heiji*; Kirino, Takashi*; Kagei, Yusuke*; Harries, J.; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Mitani, Shuhei*; Nakano, Yuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
Materials Science Forum, 679-680, p.386 - 389, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:99.52(Engineering, Multidisciplinary) gate dielectrics
gate dielectricsHosoi, Takuji*; Okamoto, Gaku*; Kutsuki, Katsuhiro*; Kagei, Yusuke*; Harries, J.; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Oyo Butsuri Gakkai Hakumaku, Hyomen Butsuri Bunkakai, Shirikon Tekunoroji Bunkakai Kyosai Tokubetsu Kenkyukai Kenkyu Hokoku, p.145 - 148, 2010/01
We developed high quality high- /Ge gate stacks with reduced leakage current and superior interface quality, which was fabricated by direct deposition of ZrO
/Ge gate stacks with reduced leakage current and superior interface quality, which was fabricated by direct deposition of ZrO on Ge substrate and thermal oxidation. Synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that thermal oxidation at 823 K caused not only an intermixing between ZrO
on Ge substrate and thermal oxidation. Synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that thermal oxidation at 823 K caused not only an intermixing between ZrO and Ge but also the formation of GeO
and Ge but also the formation of GeO at the interlayer. We obtained an equivalent oxide thickness (EOT) of 1.9 nm, and an interface state density of 10
at the interlayer. We obtained an equivalent oxide thickness (EOT) of 1.9 nm, and an interface state density of 10 cm
cm eV
eV for Au/ZrO
for Au/ZrO /Ge capacitors. Furthermore, we found that the A1
/Ge capacitors. Furthermore, we found that the A1 0
0 capping on the Zr0
capping on the Zr0 1ayer is effective for decreasing EOT. The interface state density as low as 5.3
1ayer is effective for decreasing EOT. The interface state density as low as 5.3 10
10 cm
cm eV
eV was obtained for the Al
was obtained for the Al O
O /ZrO
/ZrO /Ge stack with 30 min oxidation. The EOT could be reduced to l.6 nm by 10 min oxidation. The leakage current was two orders of magnitude lower than the conventional poly-Si/SiO
/Ge stack with 30 min oxidation. The EOT could be reduced to l.6 nm by 10 min oxidation. The leakage current was two orders of magnitude lower than the conventional poly-Si/SiO /Si stack.
/Si stack.
 /SiC interfaces formed by thermal oxidation of plasma nitrided SiC surfaces
/SiC interfaces formed by thermal oxidation of plasma nitrided SiC surfacesKagei, Yusuke*; Kosono, Kohei*; Kutsuki, Katsuhiro*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
no journal, ,
Impact of high-density plasma nitridation of 4H-SiC(0001) surface on thermally grown SiO /SiC interface structure was investigated using synchrotron radiation X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. Surface nitridation was confirmed from Si2p and N1s spectra. Both Si sub-oxide and Si sub-nitride states at SiO
/SiC interface structure was investigated using synchrotron radiation X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. Surface nitridation was confirmed from Si2p and N1s spectra. Both Si sub-oxide and Si sub-nitride states at SiO /SiC interface was evaluated through deconvolution of Si2p spectra. We found that the amount of Si sub-oxide states increased with the oxidation time. However, the formation of Si sub-oxides was effectively suppressed by the surface nitridation treatment prior to oxidation. Since an interface state density of Al/SiO
/SiC interface was evaluated through deconvolution of Si2p spectra. We found that the amount of Si sub-oxide states increased with the oxidation time. However, the formation of Si sub-oxides was effectively suppressed by the surface nitridation treatment prior to oxidation. Since an interface state density of Al/SiO /SiC MOS capacitor was approximately halved by the surface nitridation treatment, a generation of interface defects was considered to be caused by the Si sub-oxides formation.
/SiC MOS capacitor was approximately halved by the surface nitridation treatment, a generation of interface defects was considered to be caused by the Si sub-oxides formation.
 O
O /ZrO
/ZrO /GeO
/GeO layered gate dielectrics
layered gate dielectricsOkamoto, Gaku*; Kutsuki, Katsuhiro*; Kagei, Yusuke*; Harries, J.; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
no journal, ,
Structure analyses and electrical characteristic tests have been conducted for a high-k/Ge stuck of Al O
O /ZrO
/ZrO /GeO
/GeO /Ge structure. A ZrGeO layer and intermediate oxidation number states for Ge have been confirmed in photoemission spectra in addition to a chemically-shifted Ge
/Ge structure. A ZrGeO layer and intermediate oxidation number states for Ge have been confirmed in photoemission spectra in addition to a chemically-shifted Ge component suggesting the growth of GeO
component suggesting the growth of GeO interface layer. An Au electrode was capped on this dielectic substrate to make an Au/Al
interface layer. An Au electrode was capped on this dielectic substrate to make an Au/Al O
O /ZrO
/ZrO /GeO
/GeO /Ge capacitor. C-V measurements were conducted for the capacitor. Hysteresis was so small of 21 mV and frequency dispersion was also small. Interface state density near a mid gap, estimated by a low temperature conductance method, was 5.3
/Ge capacitor. C-V measurements were conducted for the capacitor. Hysteresis was so small of 21 mV and frequency dispersion was also small. Interface state density near a mid gap, estimated by a low temperature conductance method, was 5.3 10
10 cm
cm eV
eV . As a conclusion, we succeeded to make a high-k/Ge stuck which has excellent interface characteristics.
. As a conclusion, we succeeded to make a high-k/Ge stuck which has excellent interface characteristics.
 /SiC interfaces formed by thermal oxidation of 4H-SiC(000
/SiC interfaces formed by thermal oxidation of 4H-SiC(000 ) surfaces
) surfacesKirino, Takashi*; Kagei, Yusuke*; Okamoto, Gaku*; Harries, J.; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Mitani, Shuhei*; Nakano, Yuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to study the origin of degradation for interface chracteristics and reliability of SiC(0001)C surfaces, chemical bonding states at SiO /SiC interfaces made on (000
/SiC interfaces made on (000 )
)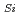 and (000
and (000 )
)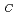 surfaces have been analyzed by using a synchrotron radiation XPS method. Si2p
surfaces have been analyzed by using a synchrotron radiation XPS method. Si2p components were extracted from Si2p photoemission peaks. Sub-oxidea components were observed in addition to the SiC substrate and the oxide layer. In the interface of the oxide layer formed on the (000
components were extracted from Si2p photoemission peaks. Sub-oxidea components were observed in addition to the SiC substrate and the oxide layer. In the interface of the oxide layer formed on the (000 )
)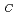 surface, Si
surface, Si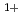 component was small, higher oxidation number components were larger, and total amount od sub-oxides was larger comparing to that of the (000
component was small, higher oxidation number components were larger, and total amount od sub-oxides was larger comparing to that of the (000 )
)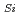 surface. A binding energy for oxide formed on the (000
surface. A binding energy for oxide formed on the (000 )
)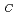 surface was shifted to 0.22 eV higher side comparing to that of the (000
surface was shifted to 0.22 eV higher side comparing to that of the (000 )
)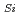 surface. It indicates that band off-set of conduction band is small in the SiO
surface. It indicates that band off-set of conduction band is small in the SiO /SiC interface.
/SiC interface.
 /4H-SiC conduction band offset by SR-XPS
/4H-SiC conduction band offset by SR-XPSKirino, Takashi*; Kagei, Yusuke*; Okamoto, Gaku*; Harries, J.; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Mitani, Shuhei*; Nakano, Yuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
It has been reported that hydrogen incorporation into thermally grown SiO /4H-SiC structures not only improves the interface quality, but also degrades the gate oxide reliability depending on SiC surface orientation. In this study, energy band diagrams of thermally grown SiO
/4H-SiC structures not only improves the interface quality, but also degrades the gate oxide reliability depending on SiC surface orientation. In this study, energy band diagrams of thermally grown SiO /4H-SiC(0001) and SiO
/4H-SiC(0001) and SiO /4H-SiC(000-1) structures with and without high-temperature hydrogen annealing were evaluated by synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The SiO
/4H-SiC(000-1) structures with and without high-temperature hydrogen annealing were evaluated by synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The SiO band gap and valence band offset at SiO
band gap and valence band offset at SiO /SiC interface were extracted from O 1s energy loss spectra and valence band spectra, respectively. The obtained energy band diagrams revealed that conduction band offsets at SiO
/SiC interface were extracted from O 1s energy loss spectra and valence band spectra, respectively. The obtained energy band diagrams revealed that conduction band offsets at SiO /SiC interfaces were decreased after the hydrogen annealing especially for 4H-SiC(000-1) substrates. This is one possible reason for the reliability degradation of 4H-SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor devices by hydrogen incorporation.
/SiC interfaces were decreased after the hydrogen annealing especially for 4H-SiC(000-1) substrates. This is one possible reason for the reliability degradation of 4H-SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor devices by hydrogen incorporation.
 /4H-SiC formed by thermal oxidation
/4H-SiC formed by thermal oxidationWatanabe, Heiji*; Kirino, Takashi*; Kagei, Yusuke*; Harries, J.; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Mitani, Shuhei*; Nakano, Yuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
Channel registibity of SiC-MOSFETs becomes larger with decreasing carrier mobility due to defects in the SiO /SiC interface. Although channel mobility is larger than that of 4H-SiC(0001)Si face in the MOSFET fabricated on the 4H-SiC(000-1)C face, degradation of reliability for an oxide layer is remarkable. Valence band off-set and interface level density of the SiO
/SiC interface. Although channel mobility is larger than that of 4H-SiC(0001)Si face in the MOSFET fabricated on the 4H-SiC(000-1)C face, degradation of reliability for an oxide layer is remarkable. Valence band off-set and interface level density of the SiO /SiC interface are different from the former 4H-SiC(0001)Si face. Physical origins for these characters has not known yet. Thus, in order to make clear the origin of reliability degradation and interface characteristics of (000-1)C face, the energy band structure and chemical bonding states of the SiO
/SiC interface are different from the former 4H-SiC(0001)Si face. Physical origins for these characters has not known yet. Thus, in order to make clear the origin of reliability degradation and interface characteristics of (000-1)C face, the energy band structure and chemical bonding states of the SiO /SiC interface formed by thermal oxidation.
/SiC interface formed by thermal oxidation.
 /4H-SiC interfaces and its modulation induced by post-oxidation treatments
/4H-SiC interfaces and its modulation induced by post-oxidation treatmentsKirino, Takashi*; Kagei, Yusuke*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Mitani, Shuhei*; Nakano, Yuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
no journal, ,
 stacked dielectrics
stacked dielectricsWatanabe, Heiji*; Kagei, Yusuke*; Kosono, Kohei*; Kirino, Takashi*; Watanabe, Yu*; Mitani, Shuhei*; Nakano, Yuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; et al.
no journal, ,
SiC-MOSFET's are expected for normally-off-type high performance power devices. Electrical defects due to residual inpurities such as carbon are in the interface of thermally-oxidized SiC-MOS's so that channel mobility is degraded preferentially. Although upgrade of reliability of a gate insulator is necessary for practical use, insulator degradation mechanisms have not well known yet. We are studying high quality MOS interface made by plasma nitridation techniques, upgrade of reliability and insulation by a stuck structure of a high-k insulator (AlON) layer and an SiO underlayer. Recent research results on those subjects are reported in this talk.
underlayer. Recent research results on those subjects are reported in this talk.
 /4H-SiC interface
/4H-SiC interfaceKirino, Takashi*; Kagei, Yusuke*; Okamoto, Gaku*; Harries, J.; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Mitani, Shuhei*; Nakano, Yuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
Device ability of SiC-MOSFET's expected from physical data has not been achieved because channel resistance increases by mobility degradation due to Si0 /SiC interface defects. Although high channel mobility is obtained in the MOSFET's made on a 4H-SiC(000-1)c face compared to them on a 4H-SiC(0001)Si face, reliability of an oxide film is preferential in the MOSFET's on a 4H-SiC(000-1)c face. Conduction band off-set of SiO
/SiC interface defects. Although high channel mobility is obtained in the MOSFET's made on a 4H-SiC(000-1)c face compared to them on a 4H-SiC(0001)Si face, reliability of an oxide film is preferential in the MOSFET's on a 4H-SiC(000-1)c face. Conduction band off-set of SiO /SiC interface and energy distribution of the interface level density are known to be different between MOSFET's on a 4H-SiC(000-1)c face and a 4H-SiC(0001)Si face. Physical origins for them are not known yet. In order to make clear the reasons for degradation of interface characteristics and reliability in the MOSFET's made on an SiC(000-1)c face, we evaluated chemical bonding states and energy band structures of SiO
/SiC interface and energy distribution of the interface level density are known to be different between MOSFET's on a 4H-SiC(000-1)c face and a 4H-SiC(0001)Si face. Physical origins for them are not known yet. In order to make clear the reasons for degradation of interface characteristics and reliability in the MOSFET's made on an SiC(000-1)c face, we evaluated chemical bonding states and energy band structures of SiO /SiC interfaces formed on an SiC(0001)Si face and an SiC(000-1)c face using synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy.
/SiC interfaces formed on an SiC(0001)Si face and an SiC(000-1)c face using synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy.