Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nojima, Hitomi*; Kaida, Atsushi*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Uo, Motohiro*; Yoshimura, Ryoichi*; Arazi, L.*; Miura, Masahiko*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.11468_1 - 11468_13, 2024/05
Diffusing alpha-emitters radiation therapy (Alpha-DaRT) is a unique radiotherapy that uses seeds emitting alpha particles placed in solid tumors to kill cancer cells surrounding the seeds. Although the DNA damage response is an important cellular response that determines cell death after radiation; however, how DNA damage response occurs during Alpha-DaRT treatment has not yet been explored. In this study, we measured the spatiotemporal characteristics of the DNA damage response, including the number of DNA double-strand breaks and G2 arrest, during Alpha-DaRT treatment by cell experiments using HeLa cells expressing the Fucci cell cycle visualization system. As a result, we found a strong correlation between the number of alpha particles detected by solid-state track detector CR-39 and  -H2AX staining, a marker for detecting DNA damage, and that the area of G2-arrested cells spread over a wider area up to 24 hours. In addition, time-lapse observations revealed that cell cycle dynamics change depending on the distance from the seed. The experimental model in this study revealed for the first time the spatiotemporal information of the DNA damage response around the seed during Alpha-DaRT treatment.
-H2AX staining, a marker for detecting DNA damage, and that the area of G2-arrested cells spread over a wider area up to 24 hours. In addition, time-lapse observations revealed that cell cycle dynamics change depending on the distance from the seed. The experimental model in this study revealed for the first time the spatiotemporal information of the DNA damage response around the seed during Alpha-DaRT treatment.
Terasaka, Yuta; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Uritani, Akira*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Sato, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 7(4), p.042002_1 - 042002_7, 2021/10
For the application in the measurement of the high dose rate hot spots inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) buildings, we propose a novel one-dimensional radiation distribution sensing method using an optical fiber sensor based on wavelength spectrum unfolding. The proposed method estimates the incident position of radiation to the fiber by the unfolding of the wavelength spectrum output from the fiber edge using the fact that the attenuation length of light along the fiber depends on the wavelength. Because this method measures the integrated light intensity, this method can avoid the problem of counting loss and signal pile-up, which occurs in the radiation detector with pulse counting mode under high dose rate field. Through basic experiments using the ultraviolet light source and  Sr/
Sr/ Y radioactive point source, basic properties of source position detection were confirmed.
Y radioactive point source, basic properties of source position detection were confirmed.
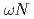 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.57(Physics, Nuclear)Terasaka, Yuta; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Uritani, Akira*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Sato, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo; Wakaida, Ikuo
Proceedings of International Youth Nuclear Congress 2020 (IYNC 2020) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/05
Mukaida, Kyoko; Kato, Atsushi; Kamiya, Masayoshi; Ishii, Katsunori
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2019/05
The levelized cost of electricity is one of key indicator to evaluate economic competitiveness of energy systems. This report estimated the levelized cost of SFR system considering additional safety measures identified after the 1F incident and social cost, using major calculation tools: G4-ECONS and the calculation tool developed by the Governmental WG in Japan (CEWG-tool). The calculation results of G4-ECONS showed that the additional safety measures raise 160% of levelized cost in the case of the safety enhanced SFR system with 1500 MWe of twin looped cooling system. As a result of calculation with 3% discount rate and social cost, the levelized cost of the safety enhanced SFR system with 1200 MWe of Single looped cooling system was estimated 84 mills/kWh by CEWG-tool. This result is almost equal to the estimated levelized cost of similar standard LWR system, and it was indicated the economic competitiveness of the future SFR system.
Kato, Atsushi; Mukaida, Kyoko
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2019/05
Improvement of economic competitiveness is a part of key requirement in the project. By adopting innovative technologies to reduce plant commodities, JSFR could achieve economic competitiveness compared with LWR. After the Fukushima-Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plants accident, safety enhancement measures were added on LWR in Japan mainly against external hazards. In parallel, Safety Design Criteria and Guidelines (SDC/SDG) for SFR were constructed in the framework of Generation IV international forum. Design studies of JSFR were carried out responding to GIF SDC/SDG and lessons learn from the Fukushima accident. This reports an impact of recent safety design enhancements on JSFR construction cost. Safety design enhancement adopted in JSFR.
Mukaida, Kyoko; Kato, Atsushi; Kamiya, Masayoshi; Ishii, Katsunori
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 61(1), p.40 - 47, 2019/01
, 61(1), p.40 - 47, 2019/01
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has proceeded on the research and development (R&D) of fast neutron rector fuel cycle with a system which has economic competitiveness in contrast with light water reactor systems as one of development objectives, from the start of its development. This report shows the evaluation results of generation cost of fast reactor fuel cycle in light of additional safety measure cost and social cost, based on the design of fast reactor and related fuel cycle facilities which considered in FaCT phase I.
Mukaida, Kyoko; Kato, Atsushi; Shiotani, Hiroki; Hayafune, Hiroki; Ono, Kiyoshi
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 324, p.35 - 44, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)An economic calculation model based on detailed mass-flow (the JAEA model) was developed for the comprehensive evaluation of an advanced loop-type sodium-cooled fast reactor cycle system (SFR) designed in the FaCT project. The JAEA model enables calculation of the processing amount and its composition in each facility by simulating mass-flow, and has function to evaluate economics based on the processing amount. In this report, to identify the difference in evaluation methods between the JAEA model and an internationally-authorized code, and verify its calculation functions, the generation cost of SFR system was evaluated using the JAEA model and the G4-ECONS. Consequently, it was clarified that the JAEA model is influenced to higher degree by the discount rate. When the present value was not taken into account, the results of both methods were quite similar, but it was found that the sensitivity of the load factor is relatively larger the G4-ECONS than in the JAEA model.
Nagano, Takuya*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kaida, Atsushi*; Nojima, Hitomi*; Furuta, Takuya; Sato, Kaoru; Yoshimura, Ryoichi*; Miura, Masahiko*
no journal, ,
A dental prosthesis such as a metal crown exists in radiation field when performing head and neck cancer radiotherapy. In our previous studies, we have evaluated the sensitizing effect ratio (SER) of the radiobiological effects around metal crowns by in vitro analysis. However, it is uncertain how much SER is actually expected in complex geometry in clinical practice. Here, we simulated the treatment plan using a head phantom with a metal crown, and evaluated the dose distributions around the metal crown in a realistic patient system by simulation. The simulation results using PHITS agree well with the SER values obtained in vitro. It has been known that localized mucositis occurs around metal crowns during radiotherapy, and this outcome is expected to provide a precise understanding of the mechanism on inflammation in tissues around metals.
Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Ouchi, Atsushi*; Mizusako, Fumiki*; Eto, Yoshinori*; Torimaru, Tadahiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shiotani, Hiroki; Kawasaki, Hirotsugu; Kato, Atsushi; Mukaida, Kyoko; Ono, Kiyoshi; Heta, Masanori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mukaida, Kyoko; Shiotani, Hiroki; Kato, Atsushi; Kawasaki, Hirotsugu; Ono, Kiyoshi; Yasumatsu, Naoto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kato, Atsushi; Mukaida, Kyoko; Ohtaki, Akira; Shiotani, Hiroki; Ono, Kiyoshi; Yasumatsu, Naoto*; Kubota, Sadae*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo; Ouchi, Atsushi*; Mizusako, Fumiki*; Eto, Yoshinori*; Torimaru, Tadahiko*
no journal, ,
For measurement of the fuel debris from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, we analyzed the LIBS spectrum of the mixed simulated fuel debris of U, Zr and Fe, using the least-squares method. We present the results of the calibration curve and analysis spectrum.
Nagano, Takuya*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kaida, Atsushi*; Nojima, Hitomi*; Yoshimura, Ryoichi*; Miura, Masahiko*
no journal, ,
In radiotherapy, metals placed close to oral tumors are often irradiated together. To date, physical calculations and dosimetry have confirmed dose enhancement around metals; however, the biological effects remain unclear. In this study, using gold as a dental material and lead which is a high atomic number similar to gold, we investigated the biological effects of tumor cells placed close to metals after therapeutic X-rays. As a result of the cell experiment, the sensitizing effect ratios of the lead plate with 2 mm and 3 mm thicknesses at 1% survival endpoint were 1.41 and 1.27, respectively, and the ratio for the 2-mm gold plate was 1.44. Meanwhile, the PHITS simulation shows that the dose enhancement ratio with and without the metal plate was approximately 1.11, which was equivalent to the measured sensitization effect ratio. In the future, we will measure the DNA damage responses for various metal thicknesses and further elucidate the mechanism of the sensitizing effects from standpoints of a hybrid approach combined with PHITS simulation.
Terasaka, Yuta; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Uritani, Akira*; Yamazaki, Atsushi*; Sato, Yuki; Torii, Tatsuo; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
We are developing a one-dimensional radiation distribution sensing method using optical fiber to measure the distribution of hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) buildings. As a new radiation distribution sensing technique applicable to high dose rate environments, a wavelength-resolved analysis method was developed. This method measures the emission wavelength spectrum derived from the interaction between the optical fiber and radiation on one side of the fiber and estimates the radiation incident position to the fiber reversely using the fact that the attenuation length of light along the fiber depends on the wavelength. In the presentation, we report the results of the principle verification of this method.
Shizume, Yuki*; Takata, Atsushi*; Nabae, Hiroyuki*; Suzumori, Koichi*; Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Kikura, Hiroshige*; Takahashi, Hideharu*; Endo, Gen*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Karino, Takahiro; Wakaida, Ikuo; Ouchi, Atsushi*; Miura, Yusuke*; Eto, Yoshinori*; Sakamoto, Kan*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English