Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray fields
-ray fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Kamada, Kei*; Ishii, Junya*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Manabe, Seiya*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Harano, Hideki*; Kato, Masahiro*; Shimazoe, Kenji*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 19(11), p.P11019_1 - P11019_16, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kamada, Masaki*; Yoshida, Takuma*; Sugita, Tsukasa*; Okumura, Keisuke
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(2), p.83 - 86, 2024/02
, 66(2), p.83 - 86, 2024/02
no abstracts in English
 -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of nuclear facilities being decommissioned has been increasing worldwide, in particular following the accident of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011. In these nuclear facilities, proper management of radioactive materials is required. Then, A  -ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr
-ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr scintillators with a dimension of
scintillators with a dimension of 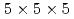
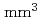 was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the
was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the  -ray exposure study under
-ray exposure study under  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields. Under the
Co radiation fields. Under the  Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2
Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0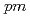 0.03%, and 9.0
0.03%, and 9.0 0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioningKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:84.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)An increasing number of nuclear facilities have been decommissioned worldwide following the 2011 accident of the TEPCO' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. During the decommissioning, radioactive materials have to be retrieved under proper management. In this study, a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm was manufactured to perform
5 mm was manufactured to perform  -ray spectroscopy under intense
-ray spectroscopy under intense  -ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform
-ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform  -ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a
-ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a  Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a
Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a  Co radiation field, which suggested to realize
Co radiation field, which suggested to realize  -ray assessment of
-ray assessment of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
 measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
 Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O scintillators by gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy
scintillators by gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopyFujimori, Kosuke*; Kitaura, Mamoru*; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Fujimoto, Masaki*; Zen, H.*; Watanabe, Shinta*; Kamada, Kei*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Kato, Masahiro*; Hosaka, Masahito*; et al.
Applied Physics Express, 13(8), p.085505_1 - 085505_4, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.86(Physics, Applied)To clarify the existence of cation vacancies in Ce-doped Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O (Ce:GAGG) scintillators, we performed gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (GiPALS). GiPAL spectra of GAGG and Ce:GAGG comprised two exponential decay components, which were assigned to positron annihilation at bulk and defect states. By an analogy with Ce:Y
(Ce:GAGG) scintillators, we performed gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (GiPALS). GiPAL spectra of GAGG and Ce:GAGG comprised two exponential decay components, which were assigned to positron annihilation at bulk and defect states. By an analogy with Ce:Y Al
Al O
O , the defect-related component was attributed to Al/Ga-O divacancy complexes. This component was weaker for Ce, Mg:GAGG, which correlated with the suppression of shallow electron traps responsible for phosphorescence. Oxygen vacancies were charge compensators for Al/Ga vacancies. The lifetime of the defect-related component was significantly changed by Mg co-doping. This was understood by considering aggregates of Mg
, the defect-related component was attributed to Al/Ga-O divacancy complexes. This component was weaker for Ce, Mg:GAGG, which correlated with the suppression of shallow electron traps responsible for phosphorescence. Oxygen vacancies were charge compensators for Al/Ga vacancies. The lifetime of the defect-related component was significantly changed by Mg co-doping. This was understood by considering aggregates of Mg ions at Al/Ga sites with oxygen vacancies, which resulted in the formation of vacancy clusters.
ions at Al/Ga sites with oxygen vacancies, which resulted in the formation of vacancy clusters.
 gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 971, p.164118_1 - 164118_8, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:60.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nancekievill, M.*; Espinosa, J.*; Watson, S.*; Lennox, B.*; Jones, A.*; Joyce, M. J.*; Katakura, Junichi*; Okumura, Keisuke; Kamada, So*; Kato, Michio*; et al.
Sensors (Internet), 19(20), p.4602_1 - 4602_16, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:44.74(Chemistry, Analytical)In order to contribute to fuel debris search at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, we developed a system to search for submerged fuel debris by mounting a sonar on the remotely operated vehicle (ROV). The system can obtain 3D images of submerged fuel debris in real time by using the positioning system, depth sensor, and collected sonar data. As a demonstration test, a simulated fuel debris was installed at the bottom of the water tank facility at the Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development, and a 3D image was successfully obtained.
Okumura, Keisuke; Riyana, E. S.; Sato, Wakaei*; Maeda, Hirobumi*; Katakura, Junichi*; Kamada, So*; Joyce, M. J.*; Lennox, B.*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.108 - 112, 2019/01
In order to establish the prediction method of the dose rate distribution in the primary containment vessel (PCV) of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, a series of calculations were carried out in the following way; (1) burnup calculation to obtain fuel composition at the time of accident, (2) activation calculation for the structural materials including impurities, (3) estimation of Cs contamination in PCV based on the result of severe accident analysis by IRID, (4) decay calculation of radioactive nuclides, (5) photon transport calculation to obtain dose rate distribution. After that, Cs concentration around the dry-well of 1F was modified to be consistent with locally measured dose rates in the PCV-investigation by IRID.
Kamada, So*; Kato, Michio*; Nishimura, Kazuya*; Nancekievill, M.*; Watson, S.*; Lennox, B.*; Jones, A.*; Joyce, M. J.*; Okumura, Keisuke; Katakura, Junichi*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.199 - 202, 2019/01
As a technology development to investigate the distribution of submerged fuel debris in the primary containment vessel (PCV) of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, we are conducting development experiments of sonar system to be mounted in a compact ROV. The experiments were conducted in two types of water tanks with different depths, simulating the PCV, using sonar with different sizes, ultrasonic frequencies, and beam scanning method, and simulated fuel debris. As a result, we characterized the shape discrimination performance of the simulated debris, and the noise due to multi-path in narrow closed space.
Nancekievill, M.*; Jones, A. R.*; Joyce, M. J.*; Lennox, B.*; Watson, S.*; Katakura, Junichi*; Okumura, Keisuke; Kamada, So*; Kato, Michio*; Nishimura, Kazuya*
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 65(9), p.2565 - 2572, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:91.67(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In order to contribute to the development of technology to search fuel debris submerged in water inside the primary containment vessel of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, we are developing a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) system equipped with a compact radiation detector and sonar. A cerium bromide (CeBr ) scintillator detector for dose rate monitoring and
) scintillator detector for dose rate monitoring and  ray spectroscopy was integrated into ROV and experimentally validated with a
ray spectroscopy was integrated into ROV and experimentally validated with a  Cs source, both in the conditions of laboratory and submerged. In addition, the ROV combined with the IMAGENEX 831L sonar could characterize the shape and size of a simulated fuel debris at the bottom of the water pool facility.
Cs source, both in the conditions of laboratory and submerged. In addition, the ROV combined with the IMAGENEX 831L sonar could characterize the shape and size of a simulated fuel debris at the bottom of the water pool facility.
Nancekievill, M.*; Jones, A. R.*; Joyce, M. J.*; Lennox, B.*; Watson, S.*; Katakura, Junichi*; Okumura, Keisuke; Kamada, So*; Kato, Michio*; Nishimura, Kazuya*
Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Advancements in Nuclear Instrumentation Measurement Methods and their Applications (ANIMMA 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2017/06
We are developping a submersible ROV system, coupled with radiation detectors aimed at mapping the interior of the reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. To map the  -ray intensity environment a cerium bromide (CeBr
-ray intensity environment a cerium bromide (CeBr ) inorganic scintillator detector sensitive to
) inorganic scintillator detector sensitive to  -rays has been incorporated into the ROV to measure
-rays has been incorporated into the ROV to measure  -ray intensity and identify radioactive isotopes. The ROV is a cylindrical shape with a diameter of about 150 mm, and it have two end caps of five pumps each allowing control of the ROV in 5 degree of freedom. It is possible to directly replace the CeBr
-ray intensity and identify radioactive isotopes. The ROV is a cylindrical shape with a diameter of about 150 mm, and it have two end caps of five pumps each allowing control of the ROV in 5 degree of freedom. It is possible to directly replace the CeBr detector with a single crystal chemical vapour deposition (CVD) neutron detector with a
detector with a single crystal chemical vapour deposition (CVD) neutron detector with a  Li convertor foil that is capable of mapping the thermal neutron flux.
Li convertor foil that is capable of mapping the thermal neutron flux.
 (Al,Ga)
(Al,Ga) O
O scintillator Compton camera mounted on an unmanned helicopter
scintillator Compton camera mounted on an unmanned helicopterShikaze, Yoshiaki; Nishizawa, Yukiyasu; Sanada, Yukihisa; Torii, Tatsuo; Jiang, J.*; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Yoshino, Masao*; Ito, Shigeki*; Endo, Takanori*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(12), p.1907 - 1918, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:96.07(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Compton camera was improved for use with the unmanned helicopter. Increase of the scintillator array from 4 4 to 8
4 to 8 8 and expanse of the distance between the two layers contributed to the improvements of detection efficiency and angular resolution, respectively. Measurements were performed over the riverbed of the Ukedo river of Namie town in Fukushima Prefecture. By programming of flight path and speed, the areas of 65 m
8 and expanse of the distance between the two layers contributed to the improvements of detection efficiency and angular resolution, respectively. Measurements were performed over the riverbed of the Ukedo river of Namie town in Fukushima Prefecture. By programming of flight path and speed, the areas of 65 m  60 m and 65 m
60 m and 65 m  180 m were measured during about 20 and 30 minutes, respectively. By the analysis the air dose rate maps at 1 m height were obtained precisely with the angular resolution corresponding to the position resolution of about 10 m from 10 m height. Hovering flights were executed over the hot spot areas for 10-20 minutes at 5-20 m height. By using the reconstruction software the
180 m were measured during about 20 and 30 minutes, respectively. By the analysis the air dose rate maps at 1 m height were obtained precisely with the angular resolution corresponding to the position resolution of about 10 m from 10 m height. Hovering flights were executed over the hot spot areas for 10-20 minutes at 5-20 m height. By using the reconstruction software the  -ray images including the hot spots were obtained with the angular resolution same as that evaluated in the laboratory (about 10
-ray images including the hot spots were obtained with the angular resolution same as that evaluated in the laboratory (about 10 ).
).
Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Arai, Takashi; Hasegawa, Koichi; Hoshi, Ryo; Kamiya, Koji; Kawashima, Hisato; Kubo, Hirotaka; Masaki, Kei; Saeki, Hisashi; Sakurai, Shinji; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.705 - 710, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:61.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shibata, Keiichi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Nakagawa, Tsuneo*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Ichihara, Akira; Kunieda, Satoshi; Chiba, Satoshi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Otsuka, Naohiko*; Osawa, Takaaki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(1), p.1 - 30, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:1751 Percentile:99.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)The fourth version of Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library has been produced. In the new library, much emphasis is placed on the improvements of fission product and minor actinoid data. Two nuclear model codes were developed to evaluate the cross sections of fission products and minor actinoids. Coupled-channel optical model parameters, which can be applied to wide mass and energy regions, were obtained for nuclear model calculations. Thermal cross sections of actinoids were determined by considering recent experimental data or by the systematics of neighboring nuclei. A simultaneous evaluation was performed for the fission cross sections of important uranium and plutonium isotopes above 10 keV. The data on FP were re-evaluated, and new evaluations were performed for 30 nuclides. The data on light elements and structural materials were partly re-evaluated. The new library was released as JENDL-4.0 in May 2010.
Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Arai, Takashi; Kawashima, Hisato; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Hoshi, Ryo; Kobayashi, Kaoru; Sawai, Hiroaki; Masaki, Kei; Sakurai, Shinji; Shibama, Yusuke; et al.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.9, p.276 - 281, 2010/08
The JT-60 SA project is a combined project of JA-EU satellite tokamak program under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement and JA domestic program. Major components of JT-60SA for assembly are vacuum vessel (VV), superconducting coils (TF coils, EF coils and CS coil), in-vessel components such as divertor, thermal shield and cryostat. An assembly frame (with the dedicated cranes), which is located around the tokamak, is adopted to carry out effectively the assembly of tokamak components in the tokamak hall, independently of the facility cranes in the building. The assembly frame also provides assembly tools and jigs with jacks to support temporarily the components as well as to adjust the components at right positions. In this paper, the assembly scenario and scequence of the major components such as VV and TFC and the concept of the assembly frame including special jigs and fixtures are discussed.
Kamada, So*; Shibata, Keiichi; Ichihara, Akira; Kunieda, Satoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(4), p.329 - 339, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:51.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron nuclear data on 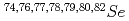 have been calculated for the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4. Simultaneously calculated are the total, elastic and inelastic scattering, (n,p), (n,d), (n,t), (n,
have been calculated for the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4. Simultaneously calculated are the total, elastic and inelastic scattering, (n,p), (n,d), (n,t), (n,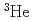 ), (n,
), (n, ), (n,np), (n,nd), (n,n
), (n,np), (n,nd), (n,n ), (n,2n), (n,3n) reaction cross sections, the angular distributions of emitted particles, and the energy distributions of emitted particles and
), (n,2n), (n,3n) reaction cross sections, the angular distributions of emitted particles, and the energy distributions of emitted particles and  -rays. The statistical model was applied to calculate these quantities. Coupled-channel optical model parameters were used for neutrons. Preequilibrium and direct-reaction processes were taken into account in addition to the compound process. The present calculations are consistent with available experimental data. The calculated results are compiled into JENDL-4.
-rays. The statistical model was applied to calculate these quantities. Coupled-channel optical model parameters were used for neutrons. Preequilibrium and direct-reaction processes were taken into account in addition to the compound process. The present calculations are consistent with available experimental data. The calculated results are compiled into JENDL-4.
Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nagaoka, Kenichi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Osakabe, Masaki*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095024_1 - 095024_9, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:73.08(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dynamics of ion internal transport barrier (ITB) formation and impurity transport both in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and JT-60U tokamak are described. Significant differences between heliotron and tokamak plasmas are observed. The location of the ITB moves outward during the ITB formation regardless of the sign of magnetic shear in JT-60U and the ITB becomes more localized in the plasma with negative magnetic shear. In LHD, the low Te/Ti ratio ( 1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Nishiyama, Tomokazu; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Masaki, Kei; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(7), p.075012_1 - 075012_11, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:35.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Characteristics of internal transport barrier (ITB) have been investigated under reactor relevant condition with edge fuelling and electron heating in JT-60U weak shear plasmas. High confinement was sustained at high density with edge fuelling by shallow pellet injection or supersonic molecular beam injection (SMBI). The ion temperature (T ) in the central region inside the ITB decreased due to cold pulse propagation even with edge fuelling. By optimizing the injection frequency and the penetration depth, the decreased central T
) in the central region inside the ITB decreased due to cold pulse propagation even with edge fuelling. By optimizing the injection frequency and the penetration depth, the decreased central T was recovered and good ITB was sustained with enhanced pedestal pressure. The T
was recovered and good ITB was sustained with enhanced pedestal pressure. The T -ITB also degraded significantly with electron cyclotron heating (ECH), when stiffness feature was strong in the electron temperature (T
-ITB also degraded significantly with electron cyclotron heating (ECH), when stiffness feature was strong in the electron temperature (T ) profile. The ion thermal diffusivity in the ITB region increased with the electron thermal diffusivity, indicating existence of clear relation between ion and electron thermal transport. On the other hand, T
) profile. The ion thermal diffusivity in the ITB region increased with the electron thermal diffusivity, indicating existence of clear relation between ion and electron thermal transport. On the other hand, T -ITB unchanged or even grew, when stiffness feature was weak in the T
-ITB unchanged or even grew, when stiffness feature was weak in the T profile. Density fluctuation level at ITB seemed to be unchanged during ECH, however, correlation length became longer in the T
profile. Density fluctuation level at ITB seemed to be unchanged during ECH, however, correlation length became longer in the T -ITB degradation case and shorter in the T
-ITB degradation case and shorter in the T -ITB unchanging case.
-ITB unchanging case.
Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Takao; Higashijima, Satoru; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.795 - 803, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:71.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English