Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Koide, Yoshihiko; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Wanner, M.*; Barabaschi, P.*; Cucchiaro, A.*; Davis, S.*; Decool, P.*; Di Pietro, E.*; Disset, G.*; Genini, L.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(8), p.086001_1 - 086001_7, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:83.12(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The most distinctive feature of the superconducting magnet system for JT-60SA is the optimized coil structure in terms of the space utilization as well as the highly accurate coil manufacturing, thus meeting the requirements for the steady-state tokamak research: A conceptually new outer inter-coil structure separated from the casing is introduced to the toroidal field coils to realize their slender shape, allowing large-bore diagnostic ports for detailed plasma measurements. A method to minimize the manufacturing error of the equilibrium-field coils has been established, aiming at the precise plasma shape/position control. A compact butt-joint has been successfully developed for the Central Solenoid, which allows an optimized utilization of the limited space for the Central Solenoid to extend the duration of the plasma pulse.
Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Arai, Takashi; Hasegawa, Koichi; Hoshi, Ryo; Kamiya, Koji; Kawashima, Hisato; Kubo, Hirotaka; Masaki, Kei; Saeki, Hisashi; Sakurai, Shinji; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.705 - 710, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Shinohara, Koji; Honda, Mitsuru; Takizuka, Tomonori; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 52(11), p.114013_1 - 114013_9, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.66(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Effects of local toroidal field (TF) ripple due to test blanket modules (TBMs) for ITER on radial transport of thermal ions are investigated using fully three-dimensional magnetic field orbit following Monte Carlo (F3D-OFMC) code. The simulation under ITER plasma condition indicates that the additional losses caused by the localized TF ripple due to TBMs linearly increase with number of TBMs. When the amplitude of local TF ripple in one TBM port is increased, on the other hand, the additional losses increase quickly. A comparison of the number of lost particles suggests that a condition with three TBM ports corresponds to 1.7 times of ripple amplitude at one TBM port.
Urano, Hajime; Saibene, G.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Parail, V.*; de Vries, P.*; Sartori, R.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kamiya, Kensaku; Loarte, A.*; L nnroth, J.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(11), p.113004_1 - 113004_10, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:40.87(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The effect of TF ripple on the edge pedestal characteristics are examined in JET and JT-60U. By the installation of ferritic inserts, TF ripple was reduced from 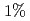 to
to 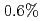 in JT-60U. In JET, TF ripple was varied from
in JT-60U. In JET, TF ripple was varied from 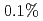 to
to 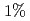 by feeding different currents to TF coils. The pedestal pressure was similar with reduced ripple in JT-60U. In JET, no clear difference of the pedestal characteristics was also observed. The edge toroidal rotation clearly decreased in counter direction by increased TF ripple. However, in JT-60U, the ELM frequency decreased by
by feeding different currents to TF coils. The pedestal pressure was similar with reduced ripple in JT-60U. In JET, no clear difference of the pedestal characteristics was also observed. The edge toroidal rotation clearly decreased in counter direction by increased TF ripple. However, in JT-60U, the ELM frequency decreased by 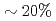 and the increased ELM loss power by
and the increased ELM loss power by 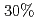 with reduced ripple. In JET, ELM frequency increases only slightly with increased TF ripple. From this inter-machine experiment, TF ripple less than
with reduced ripple. In JET, ELM frequency increases only slightly with increased TF ripple. From this inter-machine experiment, TF ripple less than 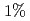 does not strongly affect the pedestal pressure. The effect of TF ripple on pedestal characteristics at lower collisionality close to ITER should be investigated as a next step study.
does not strongly affect the pedestal pressure. The effect of TF ripple on pedestal characteristics at lower collisionality close to ITER should be investigated as a next step study.
Kamada, Yutaka; Barabaschi, P.*; Ishida, Shinichi; Ide, Shunsuke; Lackner, K.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Bolzonella, T.*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Matsunaga, Go; Yoshida, Maiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(7), p.073011_1 - 073011_11, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:92.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Kamiya, Kensaku; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Matsunaga, Go; Kojima, Atsushi; Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Ida, Katsumi*; Kurki-Suonio, T.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(5), p.053009_1 - 053009_3, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.28(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We revisited to measure the edge impurity ion dynamic with new CXRS in the hot ion H-mode regime at the high magnetic field having two steps transition where a jump of Ti gradient precedes a jump of impurity Vp. Two discrete phases with different magnitude of Er in the H-phase have been observed. One is the intermediate H-phase having a large Ti gradients without significant Vp of impurity species with moderate magnitude of Er, and the other is the complete H-phase characterized by a large Er.
 plasmas
plasmasMatsunaga, Go; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Takechi, Manabu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Yoshida, Maiko; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
 -mode edge
-mode edgeKamiya, Kensaku; Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Matsunaga, Go; Kojima, Atsushi; Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Kamada, Yutaka
Physical Review Letters, 105(4), p.045004_1 - 045004_4, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:79.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Oyama, Naoyuki; Kojima, Atsushi; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Horton, L. D.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamiya, Kensaku; Urano, Hajime; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 50(6), p.064014_1 - 064014_10, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:67.96(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The effect of the edge collisionality on ELM characteristics has been investigated in the grassy ELM regime on JT-60U. Both in high and low  regimes (
regimes (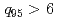 and
and 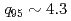 ), ELM amplitude becomes higher in plasmas with high edge collisionality. This collisionality dependence is opposite to the dependence observed in type I ELM regime, where the ELM amplitude decreases with increasing the edge collisionality. This collisionality dependence is favorable for next step devices such as ITER.
), ELM amplitude becomes higher in plasmas with high edge collisionality. This collisionality dependence is opposite to the dependence observed in type I ELM regime, where the ELM amplitude decreases with increasing the edge collisionality. This collisionality dependence is favorable for next step devices such as ITER.
Kojima, Atsushi; Kamiya, Kensaku; Fujita, Takaaki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Iguchi, Harukazu*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 5, p.015_1 - 015_7, 2010/04
A lithium beam probe (LiBP) has been developed for the measurement of electron density profiles with high spatial and temporal resolutions in JT-60U. Using an electron beam heating ion source with a capability of 10 mA extraction, a 5.5 mA beam has been injected to the plasmas. Using the LiBP, time evolutions of pedestal density profiles during type I and grassy edge localized modes (ELMs) have been obtained for the first time. After a type I ELM crash, the drop of the line-integrated density measured by an interferometer delays by 2 ms later than that of the pedestal density. Comparing the line-integrated density to the line integration of the edge density profile measured by the LiBP, it is found that the recovery from the type I ELM crash is correlated with the reduction of core plasma density. Compared with the type I ELM, grassy ELMs have smaller density crashes than that of type I ELMs, which is mainly derived from the narrower ELM affected area.
Kojima, Atsushi; Oyama, Naoyuki; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Kamada, Yutaka; Urano, Hajime; Kamiya, Kensaku; Fujita, Takaaki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Aiba, Nobuyuki; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 49(11), p.115008_1 - 115008_8, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:61.58(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In order to understand the physics of the ELM trigger and determining the ELM size, the fast ELM dynamics of type I and grassy ELMs have been studied in JT-60U, using new fast diagnostics with high spatial and temporal resolutions. The evolution of the ion pressure profile in the pedestal region is evaluated for the first time by detailed edge profile measurements. Type I ELMs observed in co-rotating plasmas exhibited larger and wider ELM affected area than ctr-rotating plasmas. Just before type I ELM crash, the pedestal ion pressure and its maximum gradient in co-rotating plasmas are 20% and 12% higher than those in ctr-rotating plasmas, respectively. It is found that the radial extent of the ion pressure gradient at the pedestal region in co-rotating plasmas is 14% wider than that in ctr-rotating plasmas. The experimental results suggest that the ELM size is determined by the structure of the plasma pressure in the whole pedestal region.
Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Matsunaga, Go; Oyama, Naoyuki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Isayama, Akihiko; Shinohara, Koji; Yoshida, Maiko; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095017_1 - 095017_8, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:73.96(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper reports the recent development of reversed shear plasmas with a high bootstrap current fraction towards reactor relevant regime, especially lower 
 regime. By utilizing large volume configuration close to the conductive wall for wall stabilization, the beta limit of the reversed shear plasmas is significantly improved. As a result, high confinement reversed shear plasmas with high bootstrap current fraction exceeding no-wall beta limit are obtained in reactor relevant regime, where
regime. By utilizing large volume configuration close to the conductive wall for wall stabilization, the beta limit of the reversed shear plasmas is significantly improved. As a result, high confinement reversed shear plasmas with high bootstrap current fraction exceeding no-wall beta limit are obtained in reactor relevant regime, where 
 of 2.7,
of 2.7, 
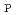 of 2.3 is achieved with reversed
of 2.3 is achieved with reversed  profile with
profile with 
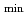 of 2.3, and then HH
of 2.3, and then HH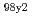 of 1.7,
of 1.7, 
 /
/
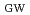 of 0.87 and
of 0.87 and 
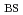 of 0.9 are also obtained at
of 0.9 are also obtained at 
 of 5.3.
of 5.3.
Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nagaoka, Kenichi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Osakabe, Masaki*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095024_1 - 095024_9, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:71.94(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dynamics of ion internal transport barrier (ITB) formation and impurity transport both in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and JT-60U tokamak are described. Significant differences between heliotron and tokamak plasmas are observed. The location of the ITB moves outward during the ITB formation regardless of the sign of magnetic shear in JT-60U and the ITB becomes more localized in the plasma with negative magnetic shear. In LHD, the low Te/Ti ratio ( 1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
 plasmas in the JT-60U tokamak
plasmas in the JT-60U tokamakMatsunaga, Go; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Isayama, Akihiko; Takechi, Manabu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Oyama, Naoyuki; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(4), p.045001_1 - 045001_4, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:84.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Urano, Hajime; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Kojima, Atsushi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 36th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2009/07
In JT-60U, the physics basis and control of the H-mode pedestal have been studied. Frequency of type-I ELMs becomes higher with increasing counter toroidal rotation. Fast recovery of density pedestal was observed after the ELM crash. ELM perturbation profile of density and temperature extends inward with co-NBI. In grassy ELM regime, ELM frequency increases with counter-toroidal rotation independently of 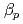 . The amplitude of grassy ELM decreases as edge collisionality decreases. QH-mode was obtained at nearly zero or slightly co-toroidal rotation at the plasma edge. Scaling of pedestal width was examined by using hydrogen/deuterium discharges. It was found that dependence of pedestal width on the Larmor radius is weak.
. The amplitude of grassy ELM decreases as edge collisionality decreases. QH-mode was obtained at nearly zero or slightly co-toroidal rotation at the plasma edge. Scaling of pedestal width was examined by using hydrogen/deuterium discharges. It was found that dependence of pedestal width on the Larmor radius is weak.
Shinohara, Koji; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; L nnroth, J.*; Saibene, G.*; Parail, V.*; Kamada, Yutaka
nnroth, J.*; Saibene, G.*; Parail, V.*; Kamada, Yutaka
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(1), p.24 - 32, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:83.13(Nuclear Science & Technology) plasmas
plasmasMatsunaga, Go; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Takechi, Manabu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Isayama, Akihiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Asakura, Nobuyuki; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Toi, Kazuo*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(7), p.465 - 467, 2008/07
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Toi, Kazuo*; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Takizuka, Tomonori; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(1), p.70 - 72, 2008/01
no abstracts in English
Oyama, Naoyuki; Saibene, G.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kamiya, Kensaku; Loarte, A.*; L nnroth, J.*; Parail, V.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Salmi, A.*; Sartori, R.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; Parail, V.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Salmi, A.*; Sartori, R.*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 123, p.012015_1 - 012015_13, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:90.3(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The effect of the toroidal field ripple and the edge toroidal rotation on H-mode and pedestal performance as well as ELM characteristics are investigated both in JET and JT-60U. In JT-60U, the amplitude of TF ripple was reduced from 1.2 % to 0.5 % after the installation of ferritic steel tiles. In JET, the ripple amplitude can actively be varied. In both devices, edge rotation in the same direction to the plasma current was reduced with increasing the ripple amplitude. Even at the same amplitude of 0.5 %, the achievable edge rotation in JT-60U was still lower than that in JET. A series of power and density scans performed at several ripple amplitude indicated that plasmas with smaller ripple amplitude and/or larger co-rotation are favorable to achieve higher pedestal pressure and plasma confinement in both devices. As for ELM characteristics, larger co-rotation seems to increase the ELM energy loss together with the reduction of the ELM frequency.