Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Nishijima, Masahiko*; Kamada, Yasuhiro*
Corrosion, 79(8), p.818 - 830, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)7xxx aluminum alloys are representative high-strength aluminum alloys; however, mechanical property degradation due to hydrogen hinders further strengthening. We propose the dispersion of Mn-based second-phase particles as a novel technique for preventing 7xxx aluminum alloy hydrogen embrittlement. In this study, the deformation and fracture behaviors of high hydrogen 7xxx alloys containing 0.0% Mn and 0.6% Mn are observed in situ using synchrotron radiation X-ray tomography. The obtained macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement is quantitatively analyzed based on hydrogen partitioning in alloys. Adding 0.6% Mn, generating second-phase particles with high hydrogen trapping abilities, significantly suppresses hydrogen-induced quasicleavage fracture.
 -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of nuclear facilities being decommissioned has been increasing worldwide, in particular following the accident of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011. In these nuclear facilities, proper management of radioactive materials is required. Then, A  -ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr
-ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr scintillators with a dimension of
scintillators with a dimension of 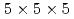
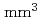 was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the
was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the  -ray exposure study under
-ray exposure study under  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields. Under the
Co radiation fields. Under the  Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2
Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0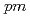 0.03%, and 9.0
0.03%, and 9.0 0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioningKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:89.29(Instruments & Instrumentation)An increasing number of nuclear facilities have been decommissioned worldwide following the 2011 accident of the TEPCO' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. During the decommissioning, radioactive materials have to be retrieved under proper management. In this study, a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm was manufactured to perform
5 mm was manufactured to perform  -ray spectroscopy under intense
-ray spectroscopy under intense  -ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform
-ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform  -ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a
-ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a  Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a
Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a  Co radiation field, which suggested to realize
Co radiation field, which suggested to realize  -ray assessment of
-ray assessment of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
 gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 971, p.164118_1 - 164118_8, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:66.68(Instruments & Instrumentation)Urano, Hajime; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095006_1 - 095006_7, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)H-modes operated at higher 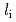 with the current ramp down have shown higher energy confinement with higher density in JT-60U. The
with the current ramp down have shown higher energy confinement with higher density in JT-60U. The  -factor evaluated for the core plasma depends strongly on
-factor evaluated for the core plasma depends strongly on 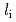 with the relation of
with the relation of 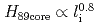 for the case without sawtooth activities. Center peaked profiles of electron density and electron temperature are obtained in high
for the case without sawtooth activities. Center peaked profiles of electron density and electron temperature are obtained in high 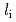 H-modes. The pedestal pressure is not significantly changed. The enhanced energy confinement in high
H-modes. The pedestal pressure is not significantly changed. The enhanced energy confinement in high 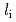 H-modes is attributed to the core improvement with the peaked profiles of electron density and temperature. The electron heat diffusivity is reduced at the plasma core in high
H-modes is attributed to the core improvement with the peaked profiles of electron density and temperature. The electron heat diffusivity is reduced at the plasma core in high 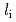 case, resulting in the center peaked
case, resulting in the center peaked 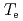 profile while the
profile while the 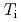 profiles are approximately unchanged.
profiles are approximately unchanged.
Urano, Hajime; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Dependence of the H-mode confinement and pedestal structure on the plasma current is investigated. Higher energy confinement is obtained in higher 
 H-mode. The profiles of the core
H-mode. The profiles of the core 
 and
and 
 are tends to be peaked. The H-factor for the core plasma depends strongly on
are tends to be peaked. The H-factor for the core plasma depends strongly on 
 . Higher energy confinement obtained at higher
. Higher energy confinement obtained at higher 
 is attributed to the core confinement improvement. The edge pedestal pressure is not significantly changed by core current density profile. In both
is attributed to the core confinement improvement. The edge pedestal pressure is not significantly changed by core current density profile. In both 
 ramp and
ramp and 
 scan experiments, the core energy confinement is improved by the increased core
scan experiments, the core energy confinement is improved by the increased core 
 value. The effect of magnetic shear on the confinement should be investigated in next step study.
value. The effect of magnetic shear on the confinement should be investigated in next step study.
 magnetic measurements under neutron radiation in Fe metal and low carbon steel
magnetic measurements under neutron radiation in Fe metal and low carbon steelTakahashi, Seiki*; Kikuchi, Hiroaki*; Ara, Katsuyuki*; Ebine, Noriya; Kamada, Yasuhiro*; Kobayashi, Satoru*; Suzuki, Masahide
Journal of Applied Physics, 100(2), p.023902_1 - 023902_6, 2006/07
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:75.26(Physics, Applied)Magnetic minor hysteresis loops of low carbon steel and Fe metal have been measured during neutron radiation at 563 K in a nuclear reactor. For investigation of nucleation mechanism of copper precipitates and dislocation loops, special attention was paid to minor-loop coefficients, which are deduced from simple relations between minor-loop parameters and are very sensitive to lattice defects. We found that with increasing neutron fluence, the minor-loop coefficients of low carbon steel sharply increase and show a maximum at the fluence of 1 10
10 cm
cm , followed by a slow decrease. The appearance of the maximum suggests the presence of two mechanisms of internal stress; while copper precipitates and dislocation loops in the matrix make the internal stress increase, those grown in the vicinity of dislocations compensate the internal stress of dislocations. On the other hand, the minor-loop coefficients show a monotonic increase with neutron fluence in Fe metal.
, followed by a slow decrease. The appearance of the maximum suggests the presence of two mechanisms of internal stress; while copper precipitates and dislocation loops in the matrix make the internal stress increase, those grown in the vicinity of dislocations compensate the internal stress of dislocations. On the other hand, the minor-loop coefficients show a monotonic increase with neutron fluence in Fe metal.
Urano, Hajime; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
no journal, ,
H-modes operated at higher 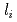 with the current ramp down have shown higher energy confinement with higher density in JT-60U. The H-factor evaluated for the core plasma depends strongly on
with the current ramp down have shown higher energy confinement with higher density in JT-60U. The H-factor evaluated for the core plasma depends strongly on 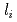 with the relation of
with the relation of 
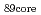
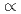


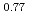 for the case without sawtooth activities. Center peaked profiles of electron density and electron temperature are obtained in high
for the case without sawtooth activities. Center peaked profiles of electron density and electron temperature are obtained in high 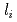 H-modes. While the peripheral current density profiles are largely modified by the current ramp, the pedestal pressure is not significantly changed. The enhanced energy confinement in high
H-modes. While the peripheral current density profiles are largely modified by the current ramp, the pedestal pressure is not significantly changed. The enhanced energy confinement in high 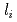 H-modes is attributed to the core improvement with the peaked profiles of electron density and electron temperature while no explicit difference in pedestal profile is observed. The electron heat diffusivity is reduced at the plasma core in high
H-modes is attributed to the core improvement with the peaked profiles of electron density and electron temperature while no explicit difference in pedestal profile is observed. The electron heat diffusivity is reduced at the plasma core in high 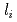 case, resulting in the center peaked
case, resulting in the center peaked 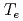 profile while the
profile while the 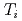 profiles are approximately unchanged.
profiles are approximately unchanged.
 gamma-ray spectrometer toward the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
gamma-ray spectrometer toward the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Foong, W. S.*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
 -ray spectrometric system for the decommissioning of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
-ray spectrometric system for the decommissioning of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The retrieval of the nuclear fuel debris, which is the substance including melted nuclear fuel and structural materials, will be started from fiscal 2021. Then, as a non-destructive analysis technology of the nuclear fuel debris, a  -ray spectroscopy system is being developed to measure high energy
-ray spectroscopy system is being developed to measure high energy  rays due to
rays due to  Eu and nuclear reactions under high dose rate, which was composed of a CeBr
Eu and nuclear reactions under high dose rate, which was composed of a CeBr cubic, photomultiplier tube, and fast signal processing unit. This presentation reports that the exposure study of the detector system was performed for a
cubic, photomultiplier tube, and fast signal processing unit. This presentation reports that the exposure study of the detector system was performed for a  Co field at the dose rates of up to 750 mSv/h, and the detector response was investigated at each dose rate.
Co field at the dose rates of up to 750 mSv/h, and the detector response was investigated at each dose rate.
 -ray spectrometry system specific to high dose-rate radiation fields for the retrieval of nuclear fuel debris in Tokyo Electrical Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
-ray spectrometry system specific to high dose-rate radiation fields for the retrieval of nuclear fuel debris in Tokyo Electrical Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The retrieval of nuclear fuel debris will be started at Tokyo Electrical Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Because of high dose-rate fields on the surface of nuclear fuel debris and these inhomogeneous elements, non-destructive analysis is required during the retrieval. Here, it is presented that a  -ray spectrometry system specific to high dose-rate fields was developed and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometry system specific to high dose-rate fields was developed and its performance under intense  -ray fields was evaluated for the retrieval of nuclear fuel debris.
-ray fields was evaluated for the retrieval of nuclear fuel debris.
Wakai, Eiichi; Noto, Hiroyuki*; Shibayama, Tamaki*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishida, Taku*; Sato, Koichi*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; Takahashi, Toshiharu*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
In recent years, it has been reported that high-entropy alloys (HEA) have high strength but good ductility, and they are being researched and developed by cutting-edge research institutions around the world with the aim of finding various applications in progress. In this study, we considered several Fe-based, W-based, and Ti-based HEAs, excluding Co and Ni elements, in order to aim for use in high radiation fields and considering low-activation properties. These materials mainly have a bcc crystal structure and were fabricated using a melting method and their material properties were evaluated. As a result, it was found that Fe-based HEA has properties that exceed the hardness of pure W and has excellent irradiation resistance. In addition, a Ti-based HEA that can be subjected to high-temperature forging and high-temperature rolling has been found, and evaluation of the optimal heat treatment temperature is progressing. The hardness of W-based HEA increased through Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) treatment, and it was found to have the world's highest hardness among HEA materials.