Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Kamaya, Masayuki*; Yamada, Teruaki*; Akita, Koichi
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 83(852), p.17-00072_1 - 17-00072_7, 2017/07
In order to assess the fatigue damage of austenitic stainless steels by electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) method more simply and easily, it should be more preferable to use a commercially available general-purpose EBSD analysis software rather than to employ an in-house developed EBSD analysis programme. In the present study, EBSD measurement was performed for Type 316 austenitic stainless steels subjected to cyclic loading, and the applicability of the EBSD parameter relevant to the pattern quality, which could be obtained by the commercial software, to the fatigue damage assessment was discussed by comparing the other EBSD parameter of the averaged local misorientation (Mave), which could be calculated by the in-house developed programme. As a result, the EBSD parameter relevant to the pattern quality, which signified the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the histogram distribution of the image quality (IQ), was saturated at the beginning stage of the fatigue cycles, while Mave was increased monotonically with the cycles. This suggested that the FWHM of IQ could be useful to detect the initial stage of the fatigue damage, while Mave was suitable for the quantitative evaluation of the fatigue damage. XRD measurement was also carried out for the same samples employed in the EBSD measurement, and the XRD data was compared with the EBSD data to discuss the crystallographic mechanism of the change in the FWHM of IQ. As a result, it was found that the FWHM of the (111) XRD peak correlated well with the FWHM of IQ. Because the (111) plane in fcc metal such as austenitic stainless steel was most preferable for slip system, this implied that the change in the distribution of the pattern quality generated by the fatigue loading could be due to the slip deformation.
Nagai, Masaki*; Lu, K.; Kamaya, Masayuki*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2016 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfarensu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.481 - 483, 2016/10
In nuclear power plants, a number of cracks attributed to stress corrosion cracking (SCC) have been detected in welds made with nickel alloy weld metals. One of the characteristics of these cracks is that crack aspect ratio 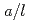 is greater than 0.5, where a is the crack depth and
is greater than 0.5, where a is the crack depth and  is the crack length. When a crack is detected in components of nuclear power plants during in-service inspection, flaw evaluation is conducted according to the requirement of codes such as JSME Rules on Fitness-for-Service for Nuclear Power Plants. Here, the stress intensity factor plays an important role for predicting crack growth behavior due to fatigue and/or SCC. Although several solutions of the stress intensity factor are already given in the JSME code, no solutions are available for the cracks with
is the crack length. When a crack is detected in components of nuclear power plants during in-service inspection, flaw evaluation is conducted according to the requirement of codes such as JSME Rules on Fitness-for-Service for Nuclear Power Plants. Here, the stress intensity factor plays an important role for predicting crack growth behavior due to fatigue and/or SCC. Although several solutions of the stress intensity factor are already given in the JSME code, no solutions are available for the cracks with 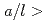 0.5. According to the current code, surface cracks with
0.5. According to the current code, surface cracks with 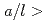 0.5 are characterized as semi-circular shape
0.5 are characterized as semi-circular shape 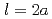 . To evaluate these cracks in a rational manner, several solutions have been proposed for cracks with
. To evaluate these cracks in a rational manner, several solutions have been proposed for cracks with 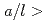 0.5. In this paper, comprehensive comparison was made between solutions for cracks
0.5. In this paper, comprehensive comparison was made between solutions for cracks 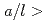 0.5, and benchmark analysis on SCC crack growth was performed.
0.5, and benchmark analysis on SCC crack growth was performed.
Hojo, Kiminobu*; Hayashi, Shotaro*; Nishi, Wataru*; Kamaya, Masayuki*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Masaki, Koichi*; Nagai, Masaki*; Okamoto, Toshiki*; Takada, Yasukazu*; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 3(4), p.16-00083_1 - 16-00083_16, 2016/08
Performance demonstration certification of non-destructive inspection for cast stainless steel (CASS) has been planned but the target flaw depth to be detected has not been determined yet in Japan. The target flaw size is closely connected to the allowable flaw size which is determined by flaw evaluation of the rules on fitness-for-service. For rational mitigation of the acceptable flaw size, application of probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is one of the useful countermeasures compared with deterministic approach. In this paper, benchmark problems for a CASS pipe were proposed with intention applying and verifying PFM codes. As the fracture modes, fatigue crack extension, plastic collapse and ductile crack initiation were assumed. Six organizations participated in the benchmark analysis and failure probabilities from them were compared. As a result the failure probability of each problem showed good agreement and the code for application of CASS issue has been verified.
Kamaya, Masayuki*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 76(3), p.386 - 401, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:77.85(Mechanics)In stress corrosion cracking of stainless steel, two different schemes of analysis of crack growth should be employed for the crack initiation phase and crack growth phase. However, this distinction is not clear-cut in the crack initiation phase, because initiation of crack tends to occur at the tip of a pre-existing crack and it can be regarded as crackgrowth. The contribution of this type of initiation dominant growth to crack growth was evaluated by a Monte Carlo simulation, and it was shown that the contribution of IDG to crack growth was large for small cracks.
Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Kamaya, Masayuki*; Akita, Koichi; Yamada, Teruaki*; Shimasaki, Tomonori*; Tanigawa, Ryohei*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English