Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Faenov, A. Y.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; Koga, J. K.; Mori, Michiaki; Kawase, Keigo*; et al.
RAL-TR-2015-025, P. 22, 2015/00
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 16(9), p.093003_1 - 093003_30, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:80.89(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Takahiro*; Iwasaki, Atsushi*; Owada, Shigeki*; Yamanouchi, Kaoru*; Takahashi, Eiji*; Midorikawa, Katsumi*; Aoyama, Makoto; Yamakawa, Koichi; Togashi, Tadashi*; Fukami, Kenji*; et al.
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 46(16), p.164006_1 - 164006_6, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:18.94(Optics)By introducing 13th- (61.7 nm) and 15th-order harmonics (53.4 nm) of femtosecond laser pulses at 800 nm into an undulator of SCSS (SPring-8 Compact SASE Source) test accelerator at RIKEN, these harmonic pulses were amplified by a factor of more than 10 with a high contrast ratio through the interaction between accelerated electron bunches and the harmonic pulses. From numerical simulations of the amplification processes of high-order harmonic pulses in the undulator, optimum conditions of the electron bunch duration interacting with the high-order harmonic pulses were investigated for generating full-coherent and intense pulses in the extreme ultraviolet wavelength region.
with a high contrast ratio through the interaction between accelerated electron bunches and the harmonic pulses. From numerical simulations of the amplification processes of high-order harmonic pulses in the undulator, optimum conditions of the electron bunch duration interacting with the high-order harmonic pulses were investigated for generating full-coherent and intense pulses in the extreme ultraviolet wavelength region.
Kando, Masaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Hayashi, Yukio; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kawase, Keigo*; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Fukuda, Yuji; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Okada, Hajime; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.159 - 166, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.13(Physics, Applied)Esirkepov, T. Z.; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.172 - 180, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.13(Physics, Applied)The bow wave induced mechanism of high-order harmonics generation was discovered using simulations and catastrophe theory. This mechanism feasibility was successfully demonstrated in 3D and 2D PIC simulations. The mechanism and the simulations explained high-order harmonics in the XUV spectral region seen in recent experiments with terawatt lasers. Development of new XUV light and X-ray source based on the high-order harmonics generation mechanism is proposed.
Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T.; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.167 - 171, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:46.34(Physics, Applied)Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Gallegos, P.*; Ahmed, H.*; Ragozin, E. N.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T.; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 108(13), p.135004_1 - 135004_5, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:69 Percentile:90.63(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We demonstrate a new high-order harmonic generation mechanism reaching the "water window" spectral region in experiments with multi-terawatt femtosecond lasers irradiating gas jets. A few hundred harmonic orders are resolved, giving  J/sr pulses. Harmonics are collectively emitted by an oscillating electron spike formed at the joint of the boundaries of a cavity and bow wave created by a relativistically self-focusing laser in underdense plasma. The spike sharpness and stability are explained by catastrophe theory. The mechanism is corroborated by particle-in-cell simulations.
J/sr pulses. Harmonics are collectively emitted by an oscillating electron spike formed at the joint of the boundaries of a cavity and bow wave created by a relativistically self-focusing laser in underdense plasma. The spike sharpness and stability are explained by catastrophe theory. The mechanism is corroborated by particle-in-cell simulations.
Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kando, Masaki; Daito, Izuru; Kameshima, Takashi*; Kawase, Keigo*; Chen, L. M.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Koga, J. K.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(6), p.066401_1 - 066401_3, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.75(Physics, Applied)Kawase, Keigo; Kando, Masaki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Daito, Izuru; Kondo, Shuji; Homma, Takayuki; Kameshima, Takashi*; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Chen, L. M.*; Fukuda, Yuji; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 637(1, Suppl.), p.S141 - S144, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.56(Instruments & Instrumentation)We report the present status of the sub-MeV X-ray generation via Compton backscattering by using 150-MeV electron beam and the Nd:YAG laser. In particular, we show the result of the X-ray generation experiment and of the laser pulse compression for increasing the X-ray flux.
Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A.*; Tampo, Motonobu; Pikuz, T.*; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Yogo, Akifumi; Sakaki, Hironao; Kameshima, Takashi*; et al.
Progress in Ultrafast Intense Laser Science VII, p.225 - 240, 2011/05
 http://www.springer.com/physics/atomic,+molecular,+optical+%26+plasma+physics/book/978-3-642-18326-3
http://www.springer.com/physics/atomic,+molecular,+optical+%26+plasma+physics/book/978-3-642-18326-3We present substantial enhancement of the accelerated ion energies up to 10-20 MeV per nucleon by utilizing the unique properties of the cluster-gas target irradiated with 40-fs laser pulses of only 150 mJ energy, corresponding to approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using thin foil targets. A particle-in-cell simulation infers that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in sub-critical density plasmas. The demonstrated method can be important in the development of efficient laser ion accelerators for hadron therapy and other applications.
Togashi, Tadashi*; Takahashi, Eiji*; Midorikawa, Katsumi*; Aoyama, Makoto; Yamakawa, Koichi; Sato, Takahiro*; Iwasaki, Atsushi*; Owada, Shigeki*; Okino, Tomoya*; Yamanouchi, Kaoru*; et al.
Optics Express (Internet), 19(1), p.317 - 324, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:96 Percentile:96.39(Optics)The 13th harmonic of a Ti:sapphire (Ti:S) laser in the plateau region was injected as a seeding source to a 250-MeV free-electron-laser (FEL) amplifier. When the amplification conditions were fulfilled, strong enhancement of the radiation intensity by a factor of 650 was observed. The random and uncontrollable spikes, which appeared in the spectra of the Self-Amplified Spontaneous Emission (SASE) based FEL radiation without the seeding source, were found to be suppressed drastically to form to a narrow-band, single peak profile at 61.2 nm. The properties of the seeded FEL radiation were well reproduced by numerical simulations. We discuss the future precept of the seeded FEL scheme to the shorter wavelength region.
Kawase, Keigo; Kando, Masaki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Daito, Izuru; Kondo, Shuji; Homma, Takayuki; Kameshima, Takashi*; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Chen, L. M.*; Fukuda, Yuji; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2010-002, p.95 - 98, 2010/06
At the previous symposium in Advanced Photon Research, we proposed and demonstrated the laser pulse compression via stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) for increasing the flux of the Compton backscattered X rays. After that, we improved the SBS pulse compression system by introducing the image relay in the laser transport line. As a result, we achieve the stably compressed laser pulse with a duration of 2.1 ns and with an energy of 0.84 J. By installing this system into the Compton backscattered X-ray source, the X-ray flux will be increased 3.2 times for the present system at the KPSI-JAEA.
Kawase, Keigo; Kando, Masaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Homma, Takayuki; Kameshima, Takashi*; Daito, Izuru; Hayashi, Yukio; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Fukuda, Yuji; Esirkepov, T. Z.; et al.
Applied Physics Express, 3, p.016101_1 - 016101_3, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.36(Physics, Applied)A new observation method of providing a precise collision of two full-power counter-propagating laser pulses is proposed and demonstrated. The method is a combination of top-view imaging, side-view shadowgram, extra-ultraviolet (XUV) spectrograph, and returning pulse monitoring. This allows us to align two counter-propagating laser pulses at their colliding point in a real situation (full power laser operation in plasma). The achieved spatial resolution of the monitor in the plasma is 1.35 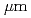 with the precision level of alignment better than 15
with the precision level of alignment better than 15 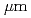 even when there is plasma present.
even when there is plasma present.
Kando, Masaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kawase, Keigo; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Fukuda, Yuji; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Okada, Hajime; Daito, Izuru; Kameshima, Takashi; Hayashi, Yukio; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(23), p.235003_1 - 235003_4, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:100 Percentile:93.73(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kotaki, Hideyuki; Daito, Izuru; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Kawase, Keigo; Kameshima, Takashi*; Fukuda, Yuji; Homma, Takayuki; Ma, J.*; Chen, L. M.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(19), p.194803_1 - 194803_4, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:88.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Fukuda, Yuji; Yogo, Akifumi; Tampo, Motonobu; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Kameshima, Takashi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Pikuz, T. A.*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 16(11), p.113106_1 - 113106_8, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:52.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Generation of high energy negative ions from laser plasmas by Coulomb implosion mechanism is investigated. When clusters or underdense plasmas are irradiated by an intense laser pulse, positive ions are accelerated inside the clusters or in the self-focusing channel by the Coulomb explosion. This could lead to the acceleration of negative ions towards target center. The maximum energy of negative ions is typically several times lower than that of positive ions. A theoretical description and corresponding Particle-in-Cell simulations of Coulomb implosion mechanism are presented. We show the evidence of the negative ion acceleration observed in our experiments using high intensity laser pulse and the cluster-gas targets.
Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A. Y.; Tampo, Motonobu; Pikuz, T. A.*; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Yogo, Akifumi; Sakaki, Hironao; Kameshima, Takashi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(16), p.165002_1 - 165002_4, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:164 Percentile:96.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A new approach for accelerating ions, based on the use of a cluster-gas target and a compact ultrashort pulse laser, is presented. It is shown that ions with energy 10-20 MeV per nucleon having a small divergence (full angle) of 3.4 are generated, corresponding to an approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using solid targets. It is inferred from a particle-in-cell code simulation that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in near-critical density plasmas.
are generated, corresponding to an approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using solid targets. It is inferred from a particle-in-cell code simulation that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in near-critical density plasmas.
Faenov, A. Y.; Pikuz, T. A.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Homma, Takayuki; Kawase, Keigo; Kameshima, Takashi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 95(10), p.101107_1 - 101107_3, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:75.81(Physics, Applied)Kando, Masaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Fukuda, Yuji; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Daito, Izuru; Kawase, Keigo; Ma, J. L.*; Chen, L. M.*; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
European Physical Journal D, 55(2), p.465 - 474, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:63.80(Optics)Nonlinear interaction of intense laser beams with plasma causes a number of different regimes of generation of high energy particle beams and of strong radiation with the emitted photon energy from the X-ray to THz frequency range. The review of the first proof-of-principle experiment and the latest progress on the flying mirror is presented. A low frequency EM radiation emission has also been observed in our experiments. The interpretation invokes the relativistic electromagnetic solitons. The solitons are formed in an underdense plasma in the process of the laser pulse frequency downshift. They store a portion of EM wave energy with the polarization inherited from the laser and emit it at the plasma-vacuum interface in a form of the low frequency EM bursts. We present the results of the polarization-resolved measurements.
Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kando, Masaki; Daito, Izuru; Homma, Takayuki; Kameshima, Takashi; Kawase, Keigo; Chen, L.-M.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1153, p.176 - 181, 2009/07