Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niide, Teppei*; Shimojo, Kojiro; Wakabayashi, Rie*; Goto, Masahiro*; Kamiya, Noriho*
Langmuir, 29(50), p.15596 - 15605, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:44.11(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Shimojo, Kojiro; Niide, Teppei*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Naganawa, Hirochika; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
Analyst, 137(10), p.2300 - 2303, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:27.8(Chemistry, Analytical)We report a one-pot biological approach to fabricate gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-ZZ domain conjugates using peptide-functionalized proteins that can simultaneously direct both biomineralization and surface modification of AuNPs. In addition, immuno-AuNPs are readily prepared through the specific binding of antibodies to the ZZ domain on the AuNPs.
Kubota, Fukiko*; Shimobori, Yosuke*; Baba, Yuzo*; Koyanagi, Yusuke*; Shimojo, Kojiro; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 44(5), p.307 - 312, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:82.68(Engineering, Chemical)The application of ionic liquids as alternatives to conventional organic solvents in extraction processes has been actively investigated. A crucial step towards the practical use of ionic liquids is the development of extractants that work effectively within these new media. In the present study, the extraction separation of rare earth metals into ionic liquids, 1-butyl, 1-octyl, and l-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([C min][Tf
min][Tf N],
N],  = 4, 8, 12), was performed using a novel extractant,
= 4, 8, 12), was performed using a novel extractant,  ,
, -dioctyldiglycol amic acid (DODGAA). Quantitative extraction of metal ions such as Y
-dioctyldiglycol amic acid (DODGAA). Quantitative extraction of metal ions such as Y and Eu
and Eu was selectively achieved in the presence of the base metal ion Zn
was selectively achieved in the presence of the base metal ion Zn , which was not extracted at all under the present experimental conditions. The extraction efficiency was enhanced for the shorter-alkyl-chain imidazolium ionic liquid [C
, which was not extracted at all under the present experimental conditions. The extraction efficiency was enhanced for the shorter-alkyl-chain imidazolium ionic liquid [C mim] [Tf
mim] [Tf N] compared to that for a conventional organic solvent system. Extraction mechanism studies elucidated that the metal extraction proceeds via proton exchange reactions between DODGAA and the metal ions in the ionic liquid (the same mechanism as in the conventional organic solvent). The stripping reaction, or recovery, of the metal ions from the extracting phase was readily accomplished with an acid solution such as nitric acid.
N] compared to that for a conventional organic solvent system. Extraction mechanism studies elucidated that the metal extraction proceeds via proton exchange reactions between DODGAA and the metal ions in the ionic liquid (the same mechanism as in the conventional organic solvent). The stripping reaction, or recovery, of the metal ions from the extracting phase was readily accomplished with an acid solution such as nitric acid.
 whole cell biocatalysts harboring P450cam mutants
whole cell biocatalysts harboring P450cam mutantsMouri, Tsuyoshi; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
Biochemical Engineering Journal, 53(2), p.229 - 233, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.82(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)In this paper, we have developed a new  whole-cell biocatalytic system that affords the efficient microbial indigo production by cytochrome P450cam mutants (Y96F or F87W-Y96F) in the cells. The novel system is comprised of two types of P450cam mutants (Y96F or F87W-Y96F), putidaredoxin, putidaredoxin reductase, and bacterial glycerol dehydrogenase. The present
whole-cell biocatalytic system that affords the efficient microbial indigo production by cytochrome P450cam mutants (Y96F or F87W-Y96F) in the cells. The novel system is comprised of two types of P450cam mutants (Y96F or F87W-Y96F), putidaredoxin, putidaredoxin reductase, and bacterial glycerol dehydrogenase. The present  whole-cell biocatalysts might be applicable to practical microbial indigo production.
whole-cell biocatalysts might be applicable to practical microbial indigo production.
Kubota, Fukiko*; Shimobori, Yosuke*; Koyanagi, Yusuke*; Shimojo, Kojiro; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
Analytical Sciences, 26(3), p.289 - 290, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:82.68(Chemistry, Analytical)We have developed a highly stable supported liquid membrane based on ionic liquids (ILs) for the separation of rare-earth metals, employing 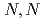 -dioctyldiglycol amic acid as a mobile carrier. The quantitative transport of Y and Eu through the membrane was successfully attained, and separation from metal impurities, Zn, was efficiently accomplished. A membrane stable enough for long-term operation was constructible from imidazolium-based ILs having a longer alkyl chain, such as octyl or dodecyl groups in an imidazolium cation.
-dioctyldiglycol amic acid as a mobile carrier. The quantitative transport of Y and Eu through the membrane was successfully attained, and separation from metal impurities, Zn, was efficiently accomplished. A membrane stable enough for long-term operation was constructible from imidazolium-based ILs having a longer alkyl chain, such as octyl or dodecyl groups in an imidazolium cation.
Kubota, Fukiko*; Shimobori, Yosuke*; Koyanagi, Yusuke*; Nakashima, Kazunori*; Shimojo, Kojiro; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 16, p.142 - 146, 2009/00
Kubota, Fukiko*; Koyanagi, Yusuke*; Nakashima, Kazunori*; Shimojo, Kojiro; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 15, p.81 - 87, 2008/00
Extraction of lanthanide ions was carried out with the organophosphorous extractant PC-88A dissolved in an imidazolium-based ionic liquid. PC-88A was soluble in ionic liquids having long-chain alkyl substituents such as octyl and dodecyl groups, [C mim] and [C
mim] and [C mim][TFSI], although short-chain imidazolium ionic liquids could not solubilize the extractant. The extraction equilibrium observed in the ionic liquid system was similar to that in the n-dodecane system, and the extraction behavior could be explained by the same proton exchange mechanism as for the conventional organic solvent system, although the extraction efficiency was not improved. An ionic liquid having shorter alkyl chain [C
mim][TFSI], although short-chain imidazolium ionic liquids could not solubilize the extractant. The extraction equilibrium observed in the ionic liquid system was similar to that in the n-dodecane system, and the extraction behavior could be explained by the same proton exchange mechanism as for the conventional organic solvent system, although the extraction efficiency was not improved. An ionic liquid having shorter alkyl chain [C mim] showed a higher extraction ability than [C
mim] showed a higher extraction ability than [C mim][TFSI]. Stripping of the metal ions from the ionic liquids was also examined. Quantitative stripping of the metal ions was achieved by nitric acid in the [C
mim][TFSI]. Stripping of the metal ions from the ionic liquids was also examined. Quantitative stripping of the metal ions was achieved by nitric acid in the [C mim][TFSI] system.
mim][TFSI] system.
Kubota, Fukiko*; Koyanagi, Yusuke*; Nakashima, Kazunori*; Shimojo, Kojiro; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 14, p.115 - 120, 2007/00
We carried out the extraction of a protein cytochrome c (Cyt-c) with an ionic liquid with an attached crown ether moiety in the imidazolium cation. The functional ionic liquid, [18C6mim][PF ], was dissolved in two different ionic liquids as diluents, one having a hydroxyethyl group, [C
], was dissolved in two different ionic liquids as diluents, one having a hydroxyethyl group, [C OHmim][Tf
OHmim][Tf N], and the other an ethyl group, [C
N], and the other an ethyl group, [C mim][Tf
mim][Tf N], respectively. The transfer of Cyt-c from the aqueous phase to the ionic liquid phase took place with [18C6mim][PF
N], respectively. The transfer of Cyt-c from the aqueous phase to the ionic liquid phase took place with [18C6mim][PF ] in the [C
] in the [C OHmim][Tf
OHmim][Tf N] system. Although the extraction ability was lower than that of dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6), the functionalized ionic liquid system gave a better stripping performance than the ordinary crown ether system. The extraction efficiency was not influenced by operating temperature when the concentration of [18C6mim] was high whereas it was greatly affected by temperature at low [18C6mim] concentration.
N] system. Although the extraction ability was lower than that of dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6), the functionalized ionic liquid system gave a better stripping performance than the ordinary crown ether system. The extraction efficiency was not influenced by operating temperature when the concentration of [18C6mim] was high whereas it was greatly affected by temperature at low [18C6mim] concentration.
 in ionic liquids via crown ether complexation
in ionic liquids via crown ether complexationShimojo, Kojiro; Kamiya, Noriho*; Tani, Fumito*; Naganawa, Hirochika; Naruta, Yoshinori*; Goto, Masahiro*
Analytical Chemistry, 78(22), p.7735 - 7742, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:92 Percentile:92.8(Chemistry, Analytical)We have found that dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 (DCH18C6) enables transfer of Lys-rich proteins into ionic liquids (ILs) via supramolecular complexation. The hydrophobicity and functional groups of ILs have a great influence on protein partitioning, and a hydroxyl group-containing IL with DCH18C6 is capable of the quantitative partitioning of Cyt- . UV-Vis, CD, and resonance Raman spectroscopic characterizations indicate that the sixth ligand Met 80 in the heme group of the Cyt-
. UV-Vis, CD, and resonance Raman spectroscopic characterizations indicate that the sixth ligand Met 80 in the heme group of the Cyt- -DCH18C6 complex in IL is replaced by other amino acid residues of the peptide chain, and that a non-natural six-coordinate, low-spin ferric heme structure is induced in IL. Solubilization of Cyt-
-DCH18C6 complex in IL is replaced by other amino acid residues of the peptide chain, and that a non-natural six-coordinate, low-spin ferric heme structure is induced in IL. Solubilization of Cyt- in IL causes the environmental change of the heme vicinity of Cyt-
in IL causes the environmental change of the heme vicinity of Cyt- , which triggers the functional conversion of Cyt-
, which triggers the functional conversion of Cyt- from an electron-transfer protein to peroxidase. The Cyt-
from an electron-transfer protein to peroxidase. The Cyt- -DCH18C6 complex in IL provides remarkably high peroxidase activity compared with native Cyt-
-DCH18C6 complex in IL provides remarkably high peroxidase activity compared with native Cyt- , because of enhancement of the affinity for H
, because of enhancement of the affinity for H O
O .
.
 in ionic liquids
in ionic liquidsShimojo, Kojiro; Nakashima, Kazunori*; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
Biomacromolecules, 7(1), p.2 - 5, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:97 Percentile:94.22(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English
Kubota, Fukiko*; Koyanagi, Yusuke*; Nakashima, Kazunori*; Shimojo, Kojiro; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kubota, Fukiko*; Koyanagi, Yusuke*; Nakashima, Kazunori*; Shimojo, Kojiro; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mouri, Tsuyoshi; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mouri, Tsuyoshi; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mouri, Tsuyoshi; Kamiya, Noriho*; Naganawa, Hirochika; Goto, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mouri, Tsuyoshi; Kamiya, Noriho*; Naganawa, Hirochika; Goto, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimojo, Kojiro; Niide, Teppei*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*; Naganawa, Hirochika
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimojo, Kojiro; Niide, Teppei*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*; Naganawa, Hirochika
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimojo, Kojiro; Niide, Teppei*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Naganawa, Hirochika; Kamiya, Noriho*; Goto, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English