Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ono, Fumihisa*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kanamitsu, Hiroaki*; Matsushima, Yasushi*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Kambara, Tadashi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 257(1-2), p.402 - 405, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:40.96(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Ono, Fumihisa*; Kanamitsu, Hiroaki*; Matsushima, Yasushi*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kambara, Tadashi*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.166 - 170, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.39(Instruments & Instrumentation)Specimens of both ordered and disordered Fe-28.3at.%Pt alloys were irradiated with 200-MeV Xe ions to the fluence of 10 ions/cm
ions/cm . Measurements of AC-susceptibility-temperature curves were made for each specimen before and after the irradiation by using a specially designed apparatus for rapid measurements. In contrast to the expectation from the previous results for Fe-Ni alloys, in disordered Fe-Pt invar alloy the Curie temperature, T
. Measurements of AC-susceptibility-temperature curves were made for each specimen before and after the irradiation by using a specially designed apparatus for rapid measurements. In contrast to the expectation from the previous results for Fe-Ni alloys, in disordered Fe-Pt invar alloy the Curie temperature, T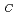 decreased about 15 K by the irradiation. This fact cannot be explained by considering the lattice expansion effect alone. In Fe-Pt invar alloys the effect of lattice expansion may be cancelled out by some other effects which may be originated from the large difference in atomic mass between the two elements. For ordered Fe-Pt alloy, T
decreased about 15 K by the irradiation. This fact cannot be explained by considering the lattice expansion effect alone. In Fe-Pt invar alloys the effect of lattice expansion may be cancelled out by some other effects which may be originated from the large difference in atomic mass between the two elements. For ordered Fe-Pt alloy, T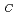 decreased as large as 60 K with the same fluence. The value of T
decreased as large as 60 K with the same fluence. The value of T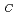 for both ordered and disordered Fe-Pt invar alloys coincide with each other after the irradiation. This fact can be explained by considering that the ordered state becomes disordered by the irradiation.
for both ordered and disordered Fe-Pt invar alloys coincide with each other after the irradiation. This fact can be explained by considering that the ordered state becomes disordered by the irradiation.
Matsushima, Yasushi*; Sun, N. Q.*; Kanamitsu, Hiroaki*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kambara, Tadashi*; Ono, Fumihisa*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 298(1), p.14 - 18, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:38.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Pressure dependence of the irradiation-induced ferromagnetism recently found in Fe-Ni invar alloys was investigated under hydrostatic pressures up to 7.5 GPa. A rectangular sheet of Fe-30.2at% Ni invar alloy was irradiated with 80-MeV Xe ions. The range was much smaller than the thickness of the sample. The Curie temperature of the irradiated part increased by 63 K, and the absolute value of the pressure coefficient, d
 /d
/d was smaller than that of non-irradiated part. The relation
was smaller than that of non-irradiated part. The relation 
 (
(
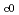 -
- 
 )
)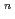 holds with n = 2 for both non-irradiated and irradiated part. The itinerant character was not so much modified by irradiation.
holds with n = 2 for both non-irradiated and irradiated part. The itinerant character was not so much modified by irradiation.