Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kanamori, Masashi
Saigai Taisaku Zensho, 2, p.30 - 35, 2011/07
no abstracts in English
Kanamori, Masashi; Suto, Toshiyuki; Tanaka, Kenichi*; Takada, Jun*
JAEA-Technology 2011-004, 12 Pages, 2011/03
In the previous report "A Study on Dose Control for JCO Criticality Accident Termination" (JAEA-Technology 2009-043), we discussed how to control the dose received during the termination work of the criticality accident. In this paper, we focused on the difference of the way in which dose rate attenuates between within 100 m from the source point and beyond 100 m and discussed the validity of using log-log plotting/semi-log plotting of dose rate - distance relation in order to extrapolate the dose rate at work place near the criticality accident point. In addition, we studied on the effect of the number of dose rate measurement data to be used for extrapolation. We recommend that about 10 mSv which is a half of 20 mSv annual dose limit should be used as worker's dose control target for the high neutron dose field work to ensure enough safety margin considering the following three points; (1) annual dose limit for workers, (2) dose received before, (3) measurement error.
Kanamori, Masashi; Suto, Toshiyuki; Tanaka, Kenichi*; Takada, Jun*
JAEA-Technology 2010-042, 11 Pages, 2011/01
JAEA-Technology 2009-043 "A Study on dose control for JCO criticality accident termination", the dose we discuss how to manage termination of the criticality accident at work or (we refer as previously report) As a result, based on the measurements from around 40 m to 100 m, we made a re-evaluation of the dose. Reevaluated doses match with the degree of accuracy 60% to 80% compared with the respective individual dose. In this paper, we validate by these doses by using log-log plots and semi-log plots for the distance from the source approximately 100 m and further attenuation. As a result, if the field is under high doses of neutrons, dose constraint assessment should consider some points, by using 10 mSv, half of the annual limit 20 mSv, as dose reference, the work performed could safely be managed. And summaries the valid range of log-log plots for intense neutron dose estimation.
Kanamori, Masashi; Shirakawa, Yusuke; Yamashita, Toshiyuki; Okuno, Hiroshi; Terunuma, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Sato, Sohei; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Fukumoto, Masahiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2010-037, 60 Pages, 2010/09
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) provides technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire station and license holder etc. They are designated public organizations conforming to the basic law on emergency preparedness and the basic plan for disaster countermeasures. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance & Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an off-site center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, provides for the dispatch of specialist as required, supplies emergency equipments and materials to the national government and municipal office. NEAT provide various lectures and training course concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. And NEAT researches on nuclear disaster prevention and also cooperate with international organizations. This annual report summarized the activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2009.
Kanamori, Masashi; Suto, Toshiyuki; Tanaka, Kenichi*; Takada, Jun*
JAEA-Technology 2010-025, 11 Pages, 2010/08
Verification of dose control method for Tokaimura JCO criticality accident was performed. Personal dose estimation for Tokaimura criticality accident termination was performed based on measurements of neutron and  ray doses taken before the work commenced, but the personal dose for the workers as a result of the termination work was found to be approximately 50 times higher than the previous estimation. For this report, we reevaluated doses based on the results of close range measurements from 40 meters to 100 meters, and the results were found to match personal doses with an accuracy of between 60-80%.
ray doses taken before the work commenced, but the personal dose for the workers as a result of the termination work was found to be approximately 50 times higher than the previous estimation. For this report, we reevaluated doses based on the results of close range measurements from 40 meters to 100 meters, and the results were found to match personal doses with an accuracy of between 60-80%.
Kanamori, Masashi
JAEA-Technology 2009-079, 44 Pages, 2010/07
In 2001, we summarized the circumstances surrounding termination of the JCO criticality accident based on testimony in the Mito District Court on December 17, 2001. JCO was the company for uranium fuels production in Japan. That document was assembled based on actual testimony in the belief that a description of the work involved in termination of the accident would be useful in some way for preventing nuclear disasters in the future. This year is the tenth year of the JCO criticality accident. To mark this occasion we have decided to translate the record of what occurred at the accident site into English so that more people can draw lessons from this accident.
Kanamori, Masashi
JAEA-Technology 2009-073, 40 Pages, 2010/03
The JCO criticality accident occurred at about 10:35 A.M. on September 30, 1999 in Tokai-mura, Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. This year (2009) is full 10 years from that truly unfortunate accident. I was then the manager of safety section of Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) Tokai Works, and engaged in the operation of the criticality accident termination in JCO sites as an expert of the disaster prevention of national government. This report is summarized the circumstances surrounding termination of the JCO criticality accident based on testimony in the Mito District Court in 2001. Since then, comments have been received and I rewritten in this tenth year with my thought not to have to forget the accident. We hope that this report will be useful in some way in preventing nuclear disaster in the future.
Kanamori, Masashi; Hashimoto, Kazuichiro; Terunuma, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Omura, Akiko; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Watanabe, Fumitaka; Yamamoto, Kazuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-023, 61 Pages, 2009/09
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) provides technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire station and license holder etc. They are Designated Public Organizations conforming to the Basic Law on Emergency Preparedness and the Basic Plan for Disaster Countermeasures. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an Off-Site Center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, provides for the dispatch of specialist as required, supplies emergency equipments and materials to the Joint Council of Nuclear Disaster Countermeasures, which meets at the Off-Site Center. NEAT provide various lectures and training course concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. And NEAT researches on nuclear disaster prevention and also cooperate with international organizations. This annual report summarized the activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2008.
Kanamori, Masashi; Tanaka, Kenichi*; Takada, Jun*
JAEA-Technology 2009-043, 32 Pages, 2009/08
At the time of the JCO criticality accident termination, dose estimation from the preliminary neutron and  measurement, it was about around 50 times lower. The estimation might effect from the surrounding buildings. In this report, re-estimation based on the measurements at short distances from the criticality, around 40 m to 100 m, which are 20 mSv/h to 3 mSv/h was done. The re-estimated doses are correspond with the measured doses within 60-80% error. Dose estimation under the high radiation field, around 100 mSv, in order to decide the dose limit for the preliminary measurement, annual dose limit, other exposure possibility and measurement error have to be considered. From this point of view, the dose limit for the preliminary measurement itself considered to be 10 mSv, which is half of annual 20 mSv limit.
measurement, it was about around 50 times lower. The estimation might effect from the surrounding buildings. In this report, re-estimation based on the measurements at short distances from the criticality, around 40 m to 100 m, which are 20 mSv/h to 3 mSv/h was done. The re-estimated doses are correspond with the measured doses within 60-80% error. Dose estimation under the high radiation field, around 100 mSv, in order to decide the dose limit for the preliminary measurement, annual dose limit, other exposure possibility and measurement error have to be considered. From this point of view, the dose limit for the preliminary measurement itself considered to be 10 mSv, which is half of annual 20 mSv limit.
Yanagibashi, Katsumi; Kanamori, Masashi; Okamoto, Naritoshi
JNC TN8420 2004-002, 109 Pages, 2005/02
On September 30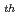 1999, the criticality accident occurred at JCO's uranium conversion building in Tokai. The accident occurred during reconversion from U
1999, the criticality accident occurred at JCO's uranium conversion building in Tokai. The accident occurred during reconversion from U O
O to uranium nitrate solution (UNH) with uranium enriched 18.8% and about 60 kgU. JCO contracted with JNC to supply UNH that is fuel material for the experimental fast breeder reactor "JOYO". JNC has contracted with JCO that had started nuclear fuel material processing business following a definite policy of Japanese government and developed "SUMITOMO ADU PROCESS". JNC made the first contract with JCO in 1985 and has made a contact every year. There had never been a problem in their products. JNC inspected products based on contract. JNC discharge our duty as customer inspecting products based on contract. As for safety control, JCO had taken licensing safety review and had been permitted to be "a processing facility". Therefore JNC understood that JCO produced following this license. "The Uranium Processing Plant Criticality Accident Investigation" showed that JCO had been taking a different method from the permit and violating the license. However JNC had never been explained about that and JCO's operation procedures had never described about that. Therefore the Criticality Accident couldn't be avoided. The reports is the revision of former JNC TN8420 2003-003.
to uranium nitrate solution (UNH) with uranium enriched 18.8% and about 60 kgU. JCO contracted with JNC to supply UNH that is fuel material for the experimental fast breeder reactor "JOYO". JNC has contracted with JCO that had started nuclear fuel material processing business following a definite policy of Japanese government and developed "SUMITOMO ADU PROCESS". JNC made the first contract with JCO in 1985 and has made a contact every year. There had never been a problem in their products. JNC inspected products based on contract. JNC discharge our duty as customer inspecting products based on contract. As for safety control, JCO had taken licensing safety review and had been permitted to be "a processing facility". Therefore JNC understood that JCO produced following this license. "The Uranium Processing Plant Criticality Accident Investigation" showed that JCO had been taking a different method from the permit and violating the license. However JNC had never been explained about that and JCO's operation procedures had never described about that. Therefore the Criticality Accident couldn't be avoided. The reports is the revision of former JNC TN8420 2003-003.
Kanamori, Masashi; Kawata, Tomio; Hitoshi, Watanabe,; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Sugiyama, Toshihide; Miyabe, Kenjiro; Kobayashi, Hirohide
JNC TN8450 2003-009, 506 Pages, 2004/03
This paper describes all the activities that were executed by JNC related to JCO criticality accident on September 30,1999. During the JCO accident, the activities of radiation monitoring, environmental monitoring, criticality termination operation, computer simulation of criticality accident, whole body exposure measurements by WBC about 24-Na, back up of local government like consultation of residents near by were performed by JNC. After the accident Japanese government and Nuclear Safety Commission establishes the investigation committee of JCO accident. JNC has also back up this activity. For example, investigation of the causes, accident scenario, estimation of the doses of the workers and personnel for deserter, counter measure operation. This paper summarizes all the important activity executed by JNC in the meantime.
Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8450 2003-007, 77 Pages, 2003/12
On September 30 at around 10:35 AM, criticality accident occurred at the JCO's conversion building in Tokai-mura. Since criticality accident had not been anticipated, neither devices for termination of criticality accident nor neutron detectors were available. Immediately after the information of the accident, our emergency staff (Japan Nuclear cycle development institute staff) went to JCO site, to measure the intensity of neutrons and gammas. There were four main tasks, first one was to measure the radiation intensity, second one was to terminate the criticality accident, third one is to alert the residents surrounding the JCO site, fourth one is to evacuate the employees in the site. These tasks were successfully performed until October 1. This paper describes about how these operations were performed by the relevant staff. And also pointed out related reviewed points for the futer.
Kanamori, Masashi; Yanagibashi, Katsumi;
JNC TN8420 2002-004, 76 Pages, 2002/12
On September 30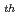 1999, the criticality accident occurred at JCO's uranium conversion building in Tokai. The accident occurred during reconversion from U
1999, the criticality accident occurred at JCO's uranium conversion building in Tokai. The accident occurred during reconversion from U O
O to uranium nitrate solution (UNH) with uranium enriched 18.8% and about 60 kgU. JCO contracted with JNC to supply UNH that is fuel material for the experimental fast breeder reactor "JOYO". JNC has contracted with JCO that had started nuclear fuel material processing business following a definite policy of Japanese government and developed "SUMITOMO ADU PROCESS". JNC made the first contract with JCO in 1985 and has made a contact every year. There had never been a problem in their products. JNC inspected products based on contract. JNC discharge our duty as customer inspecting products based on contract. As for safety control, JCO had taken licensing safety review and had been permitted to be "a processing facility". Therefore JNC understood that JCO produced following this license. "The Uranium Processing Plant Criticality Accident Investigation" showed that JCO had been taking a different method from the permit and violating the license. However JNC had never been explained about that and JCO's operation procedures had never described about that. Therefore the Criticality Accident couldn't be avoided. This report describes the relationship of JNC and JCO in the uranium reconversion contract for JOYO, atomic development policy of Japanese government, process to the order and the contents of contract.
to uranium nitrate solution (UNH) with uranium enriched 18.8% and about 60 kgU. JCO contracted with JNC to supply UNH that is fuel material for the experimental fast breeder reactor "JOYO". JNC has contracted with JCO that had started nuclear fuel material processing business following a definite policy of Japanese government and developed "SUMITOMO ADU PROCESS". JNC made the first contract with JCO in 1985 and has made a contact every year. There had never been a problem in their products. JNC inspected products based on contract. JNC discharge our duty as customer inspecting products based on contract. As for safety control, JCO had taken licensing safety review and had been permitted to be "a processing facility". Therefore JNC understood that JCO produced following this license. "The Uranium Processing Plant Criticality Accident Investigation" showed that JCO had been taking a different method from the permit and violating the license. However JNC had never been explained about that and JCO's operation procedures had never described about that. Therefore the Criticality Accident couldn't be avoided. This report describes the relationship of JNC and JCO in the uranium reconversion contract for JOYO, atomic development policy of Japanese government, process to the order and the contents of contract.
Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8440 2002-008, 120 Pages, 2002/06
The business of the Safety administration Division became a wide range such as the management of a labor safety health, the crisis management, the security and the management of an entrance, and the business of the following concerning the Tokai Works, the protection of nuclear materials, the business of the sanction, the nuclear material safeguards, the transport of nuclear materials and the business of a quality assurance. For the purpose of summarizing these businesses and utilizing the data concerning the businesses, the report about the businesses achievement has been periodically drawn up as quarter news since 2001, when the Safety Administration Division was established. This report describes about the business achievement of the fourth quarter news from January to March in 2002.
Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8440 2002-004, 121 Pages, 2002/04
The business of the Safety administration Division became a wide range such as the management of a labor safety health, the crisis management, the security and the management of an entrance, and the business of the following concerning the Tokai Works, the protection of nuclear materials, the business of the sanction, the nuclear material safeguards, the transport of nuclear materials and the business of a quality assurance. For the purpose of summarizing these businesses and utilizing the data concerning the businesses, the report about the businesses achievement has been periodically drawn up as quarter news since 2001, when the Safety Administration Division was established. This report describes about the business achievement of the third quarter news from October to December in 2001.
Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8440 2001-023, 110 Pages, 2001/12
The business of the Safety administration Division became a wide range such as the management of a labor safety health, the crisis management, the security and the management of an entrance, and the business of the following concerning the Tokai Works, the protection of nuclear materials, the business of the sanction, the nuclear material safeguards, the transport of nuclear materials and the business of a quality assurance. For the purpose of summarizing these businesses and utilizing the data concerning the businesses, the report about the businesses achievement has been periodically drawn up as quarter news since 2001, when the Safety Administration Division was established. This report describes about the business achievement of the second quarter news from July to September in 2001.
Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8440 2001-018, 50 Pages, 2001/12
On September 30 at around 10:35 AM, criticality accident occurred at the JCO's conversion building in Tokai-mura. Since criticality accident had not been anticipated, neither devices for termination of criticality accident nor neutron detectors were available. Immediately after the information of the accident, our emergency staff (Japan Nuclear cycle development institute staff) went to JCO site, to measure the intensity of neutrons and gammas. There were four main tasks, first one was to measure the radiation intensity, second one was to terminate the criticality accident, third one is to alert the residents surrounding the JCO site, fourth one is to evacuate the employees in the site. These tasks were successfully performed until October 1. This paper describes about how these operations were performed by the relevant staffs.
Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8440 2001-015, 100 Pages, 2001/09
As a consequence of this reorganization, the business of the Safety Administration Division became a wide range such as the management of a labor safety health, the crisis management, the security and the management of an entrance, the business of the sanction concerning the Tokai Works, the protection of nuclear materials, the nuclear material safeguards, the transport of nuclear materials and the business of a quality assurance. In the respect of the purpose of summarizing these businesses and utilizing the data concerning the businesses, the report about a business achievement was determined to make.
Noda, Kimio; Shinohara, Kunihiko; Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8410 2001-010, 35 Pages, 2000/10
We, the radiation control section of JNC have had two important experiences on the JCO critical accident and the JNC fire-explosion accident. Especially, at the critical accident in JCO, it was essential to take an action on the radiation protection activities for the evacuated neighboring inhabitants to the safety area. During the accident, we carried out the radiation protection activities, at the beginning of the accident, environmental monitoring of the surrounding area. Especially for the JCO accident, we took an action to terminate criticality, radiation shielding and monitoring, environmental monitoring, radiation survey of the residents, radiation monitoring of exhaust air.