Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Bi
Bi
Park, P.*; Ortiz, B. R.*; Spargue, M.*; Sakuya, A. P.*; Chen, S. A.*; Frontzek, M. D.*; Tian, W.*; Sibille, R.*; Mazzone, D. G.*; Tabata, Chihiro; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.4384_1 - 4384_9, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences) under pressure
under pressureKnafo, W.*; Thebault, T.*; Raymond, S.*; Manuel, P.*; Khalyavin, D. D.*; Orlandi, F.*; Ressouche, E.*; Beauvois, K.*; Lapertot, G.*; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
Physical Review X, 15(2), p.021075_1 - 021075_16, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0Hirata, Yoshinobu*; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Kaneko, Koji; Hagihara, Masato; Yamaguchi, Hideyuki*; Imaizumi, Teppei*; Nishizu, Takahisa*
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 306, p.141668_1 - 141668_7, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)We used quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) to investigate the effect of the ratio of water to rice on the molecular dynamics of cooked rice starch during retrogradation. X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetric measurements revealed that the degree of recrystallization and change in enthalpy were smaller with an increase in the amount of water added for cooking rice, whereas little difference in the crystallinity of the gelatinized rice starch was detected. The QENS measurements determined that the elastic incoherent structure factor (EISF) values of gelatinized samples were smaller with an increase in the amount of water added for cooking rice, indicating that the molecular dynamics of gelatinized rice starch with higher added water content were spatially more extended.
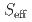 =
=  antiferromagnetic tetramer compound Yb
antiferromagnetic tetramer compound Yb SiO
SiO
Hase, Masashi*; Kaneko, Koji; Tabata, Chihiro; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Tsujii, Naohito*; D nni, A.*
nni, A.*
Physical Review B, 111(9), p.094403_1 - 094403_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) CuZn
CuZn P
P
May, A. F.*; Tabata, Chihiro; Okamoto, Satoshi*; Ortiz, B. R.*; Christianson, A. D.*; Yan, J.*; Kaneko, Koji; McGuire, M. A.*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(2), p.024406_1 - 024406_13, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kotegawa, Hisashi*; Nakamura, Akira*; Huyen, V. T. N.*; Arai, Yuki*; To, Hideki*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Hayashi, Junichi*; Takeda, Keiki*; Tabata, Chihiro; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214417_1 - 214417_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) -Mn
-MnAraki, Shingo*; Iwamoto, Kaisei*; Akiba, Kazuto*; Kobayashi, Tatsuo*; Munakata, Koji*; Kaneko, Koji; Osakabe, Toyotaka
Physical Review B, 110(9), p.094420_1 - 094420_7, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The  -Mn phase exhibits a large anomalous Hall effect (AHE) in its pressure-induced weak ferromagnetic (WFM) state, despite its relatively small spontaneous magnetization of 0.02
-Mn phase exhibits a large anomalous Hall effect (AHE) in its pressure-induced weak ferromagnetic (WFM) state, despite its relatively small spontaneous magnetization of 0.02 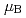 /Mn. To understand the underlying mechanism behind this AHE, we performed single crystal neutron diffraction measurements at 2.0 GPa to determine the magnetic structure of the WFM phase. Our investigation reveals a ferrimagnetic structure characterized by nearly collinear magnetic moments aligned along the [001] direction at sites I, II, III-1, and IV-1. In contrast, the small moments at sites III-2 and IV-2 lie within the (001) plane. The calculated net magnetization of this magnetic structure, (-0.020
/Mn. To understand the underlying mechanism behind this AHE, we performed single crystal neutron diffraction measurements at 2.0 GPa to determine the magnetic structure of the WFM phase. Our investigation reveals a ferrimagnetic structure characterized by nearly collinear magnetic moments aligned along the [001] direction at sites I, II, III-1, and IV-1. In contrast, the small moments at sites III-2 and IV-2 lie within the (001) plane. The calculated net magnetization of this magnetic structure, (-0.020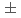 0.005)
0.005)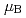 /Mn atom, is in excellent agreement with the experimentally determined spontaneous magnetization. The observation of a magnetic reflection at
/Mn atom, is in excellent agreement with the experimentally determined spontaneous magnetization. The observation of a magnetic reflection at  = (0, 0, 0) satisfies a key condition for the emergence of the AHE.
= (0, 0, 0) satisfies a key condition for the emergence of the AHE.
 RhSi
RhSiShamoto, Shinichi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Iida, Kazuki*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kaneko, Koji; Chen, Y.-S.*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Hsu, P.-T.*; Lee, M. K.*; Hall, A. E.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(3), p.033303_1 - 033303_7, 2024/09
The magnetic excitation extends at least from 0.3 to 140 meV. The integrated inelastic scattering intensity leads to a localized magnetic moment of about 5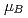 per Mn site fluctuating at 200 K in the wide energy range, although the long-range ordered magnetic moment is only 2.61
per Mn site fluctuating at 200 K in the wide energy range, although the long-range ordered magnetic moment is only 2.61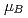 at 4 K. The result suggests that a large part of the magnetic moment does not order in Mn
at 4 K. The result suggests that a large part of the magnetic moment does not order in Mn RhSi.
RhSi.
 triangular skyrmion lattice state in the cubic chiral helimagnet EuPtSi
triangular skyrmion lattice state in the cubic chiral helimagnet EuPtSiMatsumura, Takeshi*; Tabata, Chihiro; Kaneko, Koji; Nakao, Hironori*; Kakihana, Masashi*; Hedo, Masato*; Nakama, Takao*; Onuki, Yoshichika*
Physical Review B, 109(17), p.174437_1 - 174437_8, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:78.60(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Pt
Pt Ga
Ga studied by resonant X-ray and neutron scattering
studied by resonant X-ray and neutron scatteringTabata, Chihiro; Kon, Fusako*; Ota, Kyugo*; Hibino, Ruo*; Matsumoto, Yuji*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*; Nakao, Hironori*; Haga, Yoshinori; Kaneko, Koji
Physical Review B, 109(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_7, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kaneko, Koji; Tabata, Chihiro; Hagihara, Masato; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Oba, Yojiro; Kumada, Takayuki; Kubota, Masato; Kojima, Yuki*; Nabatame, Nozomi; Sasaki, Miki; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011015_1 - 011015_6, 2024/03
 Pt
Pt Al
Al
Ota, Kyugo*; Matsumoto, Yuji*; Watabe, Yuki*; Kaneko, Koji; Tabata, Chihiro; Haga, Yoshinori
New Physics; Sae Mulli, 73(12), p.1170 - 1173, 2023/12
We have performed the neutron scattering study of antiferromagnet U Pt
Pt Al
Al with the honeycomb lattice to determine the magnetic structure. U
with the honeycomb lattice to determine the magnetic structure. U Pt
Pt Al
Al exhibits two phase transitions at
exhibits two phase transitions at 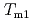 = 9 K and
= 9 K and 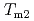 = 26 K. In phase I at
= 26 K. In phase I at 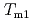



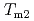 , the magnetic reflections described by a propagation vector
, the magnetic reflections described by a propagation vector 
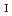 = (1/3, 0, 0) were observed. In phase II at
= (1/3, 0, 0) were observed. In phase II at 

 , magnetic reflections of
, magnetic reflections of 
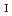 = (1/3, 0, 0) and
= (1/3, 0, 0) and 
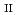 = (1/2, 0, 0) were observed and the magnetic reflection intensity of
= (1/2, 0, 0) were observed and the magnetic reflection intensity of 
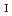 = (1/3, 0, 0) is weak but finite. The hysteresis in the temperature dependent intensities is observed across the phase transition at
= (1/3, 0, 0) is weak but finite. The hysteresis in the temperature dependent intensities is observed across the phase transition at 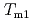 , suggesting that the transition at
, suggesting that the transition at 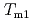 is of first order.
is of first order.

Sala, G.*; Stone, M. B.*; Hal sz, G. B.*; Lumsden, M. D.*; Fay, A, F,*; Pajerowski, D. M.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kaneko, Koji; Mazzone, D. G.*; Simutis, G.*; et al.
sz, G. B.*; Lumsden, M. D.*; Fay, A, F,*; Pajerowski, D. M.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kaneko, Koji; Mazzone, D. G.*; Simutis, G.*; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 6, p.234_1 - 234_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:66.52(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hirata, Yoshinobu*; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Kaneko, Koji; Hagihara, Masato; Yamaguchi, Hideyuki*; Omoto, Chie*; Katsuno, Nakako*; Imaizumi, Teppei*; Nishizu, Takahisa*
Food Hydrocolloids, 141, p.108728_1 - 108728_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:79.03(Chemistry, Applied)Crystallinity is reflected in the mechanical properties of foods and materials. Crystallinity should be related to the structural dynamics of starch. In this study, we used quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) to investigate changes in the molecular dynamics of cooked rice starch during retrogradation. The width of the measured QENS narrowed with retrogradation. The elastic incoherent structure factor (EISF) increased, which indicated that the molecular dynamics are spatially suppressed upon retrogradation. Analysis of EISF with a bimodal continuous diffusion model, where low and high mobilities are assumed to correspond to crystalline and amorphous phases, respectively, showed that the fraction of the low-mobility component increases with retrogradation.

Kaneko, Koji; Tabata, Chihiro; Hagihara, Masato; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Kubota, Masato; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Onuki, Yoshichika*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(8), p.085001_1 - 085001_2, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Oba, Yojiro; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Nagai, Takayuki; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.10071_1 - 10071_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Morishita, Yuki; Takasaki, Koji; Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Tagawa, Akihiro; Shibata, Takuya; Hoshi, Katsuya; Kaneko, Junichi*; Higuchi, Mikio*; Oura, Masatoshi*
Radiation Measurements, 160, p.106896_1 - 106896_10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:91.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study proposes a newly developed phoswich alpha/beta detector that can discriminate alpha and beta particles emitted from the alpha and beta contaminations in the FDNPS site. The phoswich alpha/beta detector is made up of two layers of scintillators that detect alpha and beta particles. The pulse shape discrimination (PSD) method was used to detect alpha particles in high beta particle and high gamma-ray (comparable to gamma-ray dose rate near the FDNPS reactor building) environments. Due to a 23.3% full width at half maximum (FWHM) energy resolution for alpha particles, the detector can be used to distinguish between nuclear fuel materials such as plutonium and its radon progeny (Po-214). Moreover, the detector could distinguish alpha particles from  Cs gamma rays with a dose rate background up to 9.0 mSv/h. It is the first to demonstrate that the developed phoswich detector can be used to discriminate and measure alpha and beta particles of the actual contaminated FDNPS samples.
Cs gamma rays with a dose rate background up to 9.0 mSv/h. It is the first to demonstrate that the developed phoswich detector can be used to discriminate and measure alpha and beta particles of the actual contaminated FDNPS samples.
 Pd
Pd )
) In close to a zero-temperature structural instability
In close to a zero-temperature structural instabilityGruner, T.*; Lucas, S.*; Geibel, C.*; Kaneko, Koji; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Schmalzl, K.*; Stockert, O.*
Physical Review B, 106(11), p.115142_1 - 115142_6, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) ;
;  SR studies and charge-spin percolation model
SR studies and charge-spin percolation modelSheng, Q.*; Kaneko, Tatsuya*; Yamakawa, Kohtaro*; Guguchia, Z.*; Gong, Z.*; Zhao, G.*; Dai, G.*; Jin, C.*; Guo, S.*; Fu, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033172_1 - 033172_14, 2022/09
Do, S.-H.*; Paddison, J. A. M.*; Sala, G.*; Williams, T. J.*; Kaneko, Koji; Kuwahara, Keitaro*; May, A. F.*; Yan, J.*; McGuire, M. A.*; Stone, M. B.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(6), p.L060408_1 - L060408_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:80.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)