Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suekuni, Koichiro*; Lee, C. H.*; Tanaka, Hiromi*; Nishibori, Eiji*; Nakamura, Atsushi*; Kasai, Hidetaka*; Mori, Hitoshi*; Usui, Hidetomo*; Ochi, Masayuki*; Hasegawa, Takumi*; et al.
Advanced Materials, 30(13), p.1706230_1 - 1706230_6, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:89.52(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Thermoelectric materials for highly efficient devices must satisfy conflicting requirements of high electrical conductivity and low thermal conductivity. In this paper, we studied the crystal structure and phonon dynamics of tetrahedrites (Cu,Zn) (Sb,As)
(Sb,As) S
S . The results revealed that the Cu atoms in a planar coordination are rattling, which effectively scatter phonons. These findings provide a new strategy for the development of highly efficient thermoelectric materials with planar coordination.
. The results revealed that the Cu atoms in a planar coordination are rattling, which effectively scatter phonons. These findings provide a new strategy for the development of highly efficient thermoelectric materials with planar coordination.
Mitamura, Hiroyuki*; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Kaneko, Koji; Sakakibara, Toshiro*
Kotai Butsuri, 50(12), p.821 - 832, 2015/12
no abstracts in English
Mitamura, Hiroyuki*; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Kaneko, Koji; Onozaki, Norimichi*; Amo, Yuta*; Kittaka, Shunichiro*; Kobayashi, Riki*; Shimura, Yasuyuki*; Yamamoto, Isao*; Suzuki, Kazuya*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 113(14), p.147202_1 - 147202_5, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:77.54(Physics, Multidisciplinary)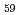 N
NFerdows, M.; Suzuya, Kentaro; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kohara, Shinji*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Yamamoto, Kazunori; Shamoto, Shinichi; Hirata, Takamichi*; Omote, Kenji*; Kasama, Yasuhiko*; et al.
Abstracts of 7th International Symposium on Advanced Materials in Asia-Pacific (NT 2010)/JAIST International Symposium on Nano Technology 2010 (7th ISAMAP), p.25 - 28, 2010/09
We performed Reverse Monte Carlo analysis (RMCA) to study amorphous structure of a heterofullerene, C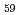 N by using pulsed neutron powder diffraction data. The scattering function S(Q) shows that the structure is amorphous, while the atomic pair distribution function (PDF) shows that the local structure is similar to that of C
N by using pulsed neutron powder diffraction data. The scattering function S(Q) shows that the structure is amorphous, while the atomic pair distribution function (PDF) shows that the local structure is similar to that of C . Obtained structures strongly depend on the initial models. Problems for this RMCA method are discussed.
. Obtained structures strongly depend on the initial models. Problems for this RMCA method are discussed.
Ferdows, M.; Suzuya, Kentaro; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kohara, Shinji*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Yamamoto, Kazunori; Shamoto, Shinichi; Hirata, Takamichi*; Omote, Kenji*; Kasama, Yasuhiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
We performed Reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) simulations to study the amorphous structure of a heterofullerene, C59N. Neutron diffraction data of the powder sample with about 0.7 g were collected for 16 h at room temperature, using the neutron powder diffractometer NPDF [1] at the Manuel Lujan Neutron Scattering Center of Los Alamos National Laboratory. By using fourier transformation of the scattering function S(Q), the atomic pair distribution function (PDF) of the C59N was obtained.