Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
AIP Advances (Internet), 13(1), p.015314_1 - 015314_6, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The efficiency of the sorption of Sr on weathered biotite, a type of clay minerals was investigated. Removal of Sr
on weathered biotite, a type of clay minerals was investigated. Removal of Sr and Cs
and Cs is important in the treatment of contaminated water from the 1F accident, which is one of the radionuclide waste treatment problems. We focused on developing an adsorption method for Sr ions using weathered biotite, which are abundant in Fukushima. Applying a molten salt treatment, the amount of sorbed Sr
is important in the treatment of contaminated water from the 1F accident, which is one of the radionuclide waste treatment problems. We focused on developing an adsorption method for Sr ions using weathered biotite, which are abundant in Fukushima. Applying a molten salt treatment, the amount of sorbed Sr simply increased as the added mass ratio of strontium chloride (SrCl
simply increased as the added mass ratio of strontium chloride (SrCl ) increased from 1:1, 1:5, and 1:10 for the one-fold, five-fold, and ten-fold additions of SrCl
) increased from 1:1, 1:5, and 1:10 for the one-fold, five-fold, and ten-fold additions of SrCl , respectively. Then, the crystal structure of weathered biotite as an adsorbent was evaluated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. Thus, it was observed that the WB retained its original crystal structure even after the sorption of Sr
, respectively. Then, the crystal structure of weathered biotite as an adsorbent was evaluated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. Thus, it was observed that the WB retained its original crystal structure even after the sorption of Sr . Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis was performed to investigate the local sorption structure of Sr
. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis was performed to investigate the local sorption structure of Sr in the WB. The results revealed that Sr
in the WB. The results revealed that Sr was preferentially sorbed into the SiO
was preferentially sorbed into the SiO and Al
and Al O
O layers when Sr
layers when Sr was in the low mass ratio, while, it was mainly sorbed into the SiO
was in the low mass ratio, while, it was mainly sorbed into the SiO layer when the ratio was high.
layer when the ratio was high.
 molecular dynamics simulations reveal the hydration structure of the radium(II) ion
molecular dynamics simulations reveal the hydration structure of the radium(II) ionYamaguchi, Akiko; Nagata, Kojiro*; Kobayashi, Keita; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Shimojo, Kojiro; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Kaneta, Yui; Matsuda, Shohei; et al.
iScience (Internet), 25(8), p.104763_1 - 104763_12, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:68.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Matsuda, Shohei; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Toru; Kaneta, Yui; Simonnet, M.; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Shimojo, Kojiro; Doi, Reisuke; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 8(20), p.eabn1991_1 - eabn1991_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:58.16(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kobayashi, Keita; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimojo, Kojiro; Tanida, Hajime; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Kaneta, Yui; Matsuda, Shohei; et al.
Hosha Kagaku, (45), p.28 - 30, 2022/03
no abstracts in English
Haraga, Tomoko; Hishinuma, Yukio*; Kaneta, Yui*; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Amamoto, Ippei; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Ayame, Yasuo; Hasegawa, Yoshio*; Utsumi, Kazuo*; Takeshita, Kenji*; Inaba, Yusuke*; Onoe, Jun*; Koshizaka, Akiko*; Kaneta, Yui*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kaneta, Yui*; Suzuki, Shinichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kaneta, Yui; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsunori; Goto, Takuya*; Kaneta, Yui; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
We have been investigating the restoration of the environment in Fukushima. One of the issues to be solved is the removal of cesium from the soil of Fukushima. As we studied the technology to remove cesium from the soil of Fukushima, we thought that the reclamation could be accelerated by adding new functions (e.g., thermoelectric properties) to the clay minerals after removal. Soil clay minerals are composed of Si, Al, Fe, etc., and are low environmental load materials. Soil clay minerals were reduced by molten salt electrochemistry and their properties were investigated. Thermal diffusivity measurements showed no temperature dependence in the untreated sample, while the temperature dependence was significantly different in the case of -1.4 V molten salt electrolysis treatment.
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimojo, Kojiro; Tanida, Hajime; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Kaneta, Yui; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimojo, Kojiro; Tanida, Hajime; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Kaneta, Yui; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
Ten years have passed since the earthquake and nuclear power plant accident at 1F that occurred in 2011, and the contaminated soil generated in Fukushima Prefecture is now being managed as removed soil at intermediate storage facilities. In the course of developing technology to remove cesium from the removed soil, we have focused on the functionality of crystalline minerals after removal of cesium, and have been investigating their potential as thermoelectric materials. In this study, we report on the evaluation of thermoelectric properties (electrical conductivity, thermal diffusivity, and Seebeck coefficient) and structural analysis of crystalline minerals.
Kaneta, Yui; Kobayashi, Toru; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Honda, Mitsunori; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
Ten years have passed since the Great East Japan Earthquake and the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, and the contaminated soil generated in Fukushima Prefecture has been decontaminated and managed as removal soil. We have been conducting research on the volume reduction and recycling of Fukushima weathered biotite, which is known to be a strong adsorbent of radioactive Cs contained in the removed soil. In this study, thermoelectric properties (Seebeck coefficient, electrical conductivity, and thermal diffusivity) of soil clay minerals and molten salt-electrolyzed soil clay minerals were evaluated in order to clarify their properties as thermoelectric materials.
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
Twelve years have passed since the 1F accident that occurred in 2011, and contaminated soil generated in Fukushima Prefecture is being managed as removed soil. We have focused on the functionality of several crystalline minerals obtained in the process of developing a technology to remove Cs from the removed soil, and are examining their potential as thermoelectric conversion materials. In this study, we report on the evaluation of thermoelectric properties (electrical conductivity, thermal diffusivity, and Seebeck coefficient) of the crystalline minerals.
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Iino, Chiaki*; Oda, Masato*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
In this study, thermoelectric properties (electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal diffusivity) were evaluated (OZMA-1-S1) for polycrystalline minerals obtained by systematically changing the conditions of WB and the molten treatment. The Seebeck coefficient and thermal diffusivity were evaluated on the same sample. Macroscopic and microscopic structures were identified by various X-ray analyses and first-principles calculations. As for the electrical conductivity results of WB, the biotite material is usually known as an electrical insulator at room temperature, but after grinding, classification, molten salt treatment, and sintering, it was found to have electrical conductivity on the order of 1.49  10
10 (
( V/K) in the temperature range 650-850
V/K) in the temperature range 650-850 C, indicating that it has semiconducting electrical conductivity properties. Seebeck coefficient measurements in the same temperature range showed a high value of -2.0
C, indicating that it has semiconducting electrical conductivity properties. Seebeck coefficient measurements in the same temperature range showed a high value of -2.0 10
10 (
( V/K). Calculating the dimensionless performance index
V/K). Calculating the dimensionless performance index 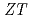 from the obtained results,
from the obtained results, 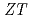 =0.29 was obtained. Regarding the thermoelectric property evaluation results for the molten salt treated polycrystalline minerals, higher electrical conductivity properties than WB were obtained for the same temperature range. These results suggest that WB can be used to show useful thermoelectric properties in the high temperature region above 650
=0.29 was obtained. Regarding the thermoelectric property evaluation results for the molten salt treated polycrystalline minerals, higher electrical conductivity properties than WB were obtained for the same temperature range. These results suggest that WB can be used to show useful thermoelectric properties in the high temperature region above 650 C.
C.
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*
no journal, ,
Our research focuses on the use of weathered biotite (WB) as an alternative material to thermoelectric materials, which have traditionally been made from rare and toxic elements. After WB was crushed and classified, crystals with conductivity comparable to that of Si semiconductors in the temperature range of 650-850 C were obtained by heat treatment using the molten salt method. In this study, we report on the results of the dimensionless evaluation index ZT calculated from the conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal diffusion measurements in the high temperature range, and the thermal conductivity calculated from the specific heat and specific gravity.
C were obtained by heat treatment using the molten salt method. In this study, we report on the results of the dimensionless evaluation index ZT calculated from the conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal diffusion measurements in the high temperature range, and the thermal conductivity calculated from the specific heat and specific gravity.