Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kimura, Masanori; Munakata, Masahiro; Hato, Shinji*; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-002, 38 Pages, 2020/03
To consider the method of implementing urgent protective actions in a nuclear accident appropriately, the authors have been assessing the effects of reducing doses by taking urgent protective actions using a Level 3 Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) code, the OSCAAR, developed by the JAEA. Iodine thyroid blocking is an effective urgent protective action to reduce equivalent doses to the thyroid due to inhalation of radioactive iodine. However, the timing of the administration of stable iodine (SI) is important to maximize the effectiveness for thyroidal blocking. Therefore, the careful consideration should be given to the most effective way of iodine thyroid blocking when preparing off-site emergency plans. In the present study, the authors developed a new metabolic model for thyroid by combining the respiratory tract model (Publ.66) and gastrointestinal tract model (Publ.30) of the ICRP with a metabolic model for thyroid (Johnson's model) in order to calculate the behavior of radioiodine and stable iodine in the body more realistically. The model is useful to evaluate the effect of the administration of SI for reducing equivalent doses to the thyroid depending on the its timing. We also calculated the reduction factor for equivalent doses to the thyroid in order to the thyroid by using the model, and then developed the its database for the OSCAAR. Consequently, the OSCAAR can evaluate the effectiveness for thyroidal blocking realistically and promptly.
Kanno, Ryutaro*; Nunami, Masanori*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Matsuoka, Seikichi; Takamaru, Hisanori*
Nuclear Fusion, 58(1), p.016033_1 - 016033_7, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The electron heat transport in a torus plasma which involves a radially-bounded ergodic region, where flux surfaces are partially destroyed by perturbative magnetic fields, is studied. In this paper, we have demonstrated that the radial heat conduction by the particles' parallel motion is reduced by trapped particles.
Kimura, Masanori; Hato, Shinji*; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2017/11
The authors developed a new metabolic model for iodine by combining the respiratory tract model (Publ.66), the gastrointestinal tract model (Publ.30) of the ICRP and the metabolic model for iodine (Johnson's model) in order to evaluate the behavior of radioiodine and stable iodine in the body more realistically. The developed metabolic model indicated that a reduction factor (RF) depends on dosage of stable iodine, timing of the administration of stable iodine, different iodine isotopes ( I -
I -  I), and age groups. Therefore, the RF was calculated by changing these parameters and then a database of the RF was constructed for the application to the OSCAAR code.
I), and age groups. Therefore, the RF was calculated by changing these parameters and then a database of the RF was constructed for the application to the OSCAAR code.
Kanno, Ryutaro*; Nunami, Masanori*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Matsuoka, Seikichi; Takamaru, Hisanori*
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 56(6-8), p.592 - 597, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.54(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A drift-kinetic 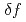 simulation code is developed for estimating collisional transport in quasi-steady state of toroidal plasma affected by resonant magnetic perturbations and radial electric field. In this paper, validity of the code is confirmed through several test calculations. It is found that radial electron flux is reduced by positive radial-electric field, although radial diffusion of electron is strongly affected by chaotic field-lines under an assumption of zero electric field.
simulation code is developed for estimating collisional transport in quasi-steady state of toroidal plasma affected by resonant magnetic perturbations and radial electric field. In this paper, validity of the code is confirmed through several test calculations. It is found that radial electron flux is reduced by positive radial-electric field, although radial diffusion of electron is strongly affected by chaotic field-lines under an assumption of zero electric field.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Takeyasu, Masanori; Nakano, Masanao; Sumiya, Shuichi; Nemoto, Hiromi*; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*
Proceedings of 3rd Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-3) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/05
The dose to the public at hypothetical accident of nuclear facility is estimated on the basis of the method described in the Japanese meteorological guideline. However, the radioactive decay during atmospheric dispersion of released radionuclide is not considered in the calculation formula in the guideline. Therefore, when the radionuclide of the half life such as a few min is released, the dose may be excessively over-estimated. In this study, the calculation code was developed which could consider the radioactive decay of the released radionuclide and the generation of the product. The dose calculated on the basis of the developed code was compared with that on the basis of the guideline.
Hirano, Masashi; Kanno, Masanori*; Koyama, Masakuni*
Hozengaku, 9(1), p.23 - 25, 2010/04
In March 2006, the Japan Nuclear Energy Safety Organization (JNES) formed the Committee on Coordination of Technical Information with three working groups (WGs), namely, the WG on Safety Research, that on Information Base and that on International Cooperation. In this report, the major activities of the WG on International Cooperation that are being done through the cooperation of the governmental organizations, industries, academia, and academic societies and associations are overviewed.
Kaminaga, Masanori; Niimi, Motoji; Hori, Naohiko; Takahashi, Kunihiro; Kanno, Masaru; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Ishihara, Masahiro; Kawamura, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2009-056, 20 Pages, 2010/02
The JMTR is a light water moderated and cooled, beryllium reflected tank- type reactor using LUE silicide plate-type fuels. Its thermal power is 50 MW, maximum thermal and fast neutron flux is 4  10
10 m
m s
s . First criticality was achieved in March 1968, and its operation was stopped from August, 2006 for the refurbishment. The refurbishment is scheduled from the beginning of FY2007 to the end of FY2010. The renewed and upgraded JMTR will be re-started from FY2011. An investigation on aged components (aged-investigation) was carried out for concrete structures of the JMTR reactor building, exhaust stack, etc., and for tanks in the primary cooling system, heat exchangers, pipes in the secondary cooling system, cooling tower, emergency generators and so on, in order to identify their integrity. The aged-investigation was carried out at the beginning of FY2007. As a result, some components were decided to replace from viewpoints of future maintenance and improvement of reliability, and some components or structures were decided to repair. A visual inspection of inner side of the pressure vessel was carried out using an underwater camera in FY2008, and no serious damage was observed. Up to now, refurbishment works are in progress according to the planned schedule. In this paper, current status of JMTR refurbishment project is presented.
. First criticality was achieved in March 1968, and its operation was stopped from August, 2006 for the refurbishment. The refurbishment is scheduled from the beginning of FY2007 to the end of FY2010. The renewed and upgraded JMTR will be re-started from FY2011. An investigation on aged components (aged-investigation) was carried out for concrete structures of the JMTR reactor building, exhaust stack, etc., and for tanks in the primary cooling system, heat exchangers, pipes in the secondary cooling system, cooling tower, emergency generators and so on, in order to identify their integrity. The aged-investigation was carried out at the beginning of FY2007. As a result, some components were decided to replace from viewpoints of future maintenance and improvement of reliability, and some components or structures were decided to repair. A visual inspection of inner side of the pressure vessel was carried out using an underwater camera in FY2008, and no serious damage was observed. Up to now, refurbishment works are in progress according to the planned schedule. In this paper, current status of JMTR refurbishment project is presented.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Akie, Hiroshi; Kugo, Teruhiko; Yonomoto, Taisuke; Kureta, Masatoshi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Araya, Fumimasa; Okajima, Shigeaki; et al.
JAERI-Research 2004-008, 383 Pages, 2004/06
The present report contains the achievement of "Research and Development on Reduced-Moderation Light Water Reactor with Passive Safety Features", which was performed by Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), Hitachi Ltd., Japan Atomic Power Company and Tokyo Institute of Technology in FY2000-2002 as the innovative and viable nuclear energy technology (IVNET) development project operated by the Institute of Applied Energy (IAE). In the present project, the reduced-moderation water reactor (RMWR) has been developed to ensure sustainable energy supply and to solve the recent problems of nuclear power and nuclear fuel cycle, such as economical competitiveness, effective use of plutonium and reduction of spent fuel storage. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as high burnup, long operation cycle, multiple recycling of plutonium (Pu) and effective utilization of uranium resources based on accumulated LWR technologies.