Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Catumba, G.*; Hiraguchi, Atsuki; Hou, W.-S.*; Jansen, K.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; David Lin, C.-J.*; Ramos, A.*; Sarkar, M.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(4), p.043172_1 - 043172_12, 2024/11
Gauge theories with matter fields in various representations play an important role in different branches of physics. Recently, it was proposed that several aspects of the interesting pseudogap phase of cuprate superconductors near optimal doping may be explained by an emergent SU(2) gauge symmetry. Around the transition with positive hole-doping, one can construct a (2+1)-dimensional SU(2) gauge theory coupled to four adjoint scalar fields which gives rise to a rich phase diagram with a myriad of phases having different broken symmetries. We study the phase diagram of this model on the Euclidean lattice using the Hybrid Monte Carlo algorithm. We find the existence of multiple broken phases as predicted by previous mean field studies. Depending on the quartic couplings, the SU(2) gauge symmetry is broken down either to U(1) or 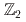 in the perturbative description of the model. We further study the confinement-deconfinement transition in this theory, and find that both the broken phases are deconfining in the range of volumes that we studied. However, there exists a marked difference in the behavior of the Polyakov loop between the two phases.
in the perturbative description of the model. We further study the confinement-deconfinement transition in this theory, and find that both the broken phases are deconfining in the range of volumes that we studied. However, there exists a marked difference in the behavior of the Polyakov loop between the two phases.
Catumba, G.*; Hiraguchi, Atsuki; W.-S. Hou, G.*; Jansen, K.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; David Lin, C.-J.*; Ramos, A.*; Sarkar, M.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 453, p.362_1 - 362_7, 2024/11
We study a 3-dimensional SU(2) gauge theory with 4 Higgs fields which transform under the adjoint representation of the gauge group, that has been recently proposed by Sachdev et al. to explain the physics of cuprate superconductors near optimal doping. The symmetric confining phase of the theory corresponds to the usual Fermi-liquid phase while the broken (Higgs) phase is associated with the interesting pseudogap phase of cuprates. We employ the Hybrid Monte-Carlo algorithm to study the phase diagram of the theory. We find the existence of a variety of broken phases in qualitative accordance with earlier mean-field predictions and discuss their role in cuprates. In addition, we investigate the behavior of Polyakov loop to probe the confinement/deconfinement phase transition, and find that the Higgs phase hosts a stable deconfining phase consistent with previous studies.
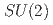 gauge fields
gauge fieldsCatumba, G.*; Hiraguchi, Atsuki; W.-S. Hou, G.*; Jansen, K.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; David Lin, C.-J.*; Ramos, A.*; Sarkar, M.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 453, p.87_1 - 87_9, 2024/11
We study the most general Two Higgs Doublet Model with 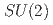 gauge fields on the lattice. The phase space is probed through the computation of gauge-invariant global observables serving as proxies for order parameters. In each phase, the spectrum of the theory is analysed for different combinations of bare couplings and different symmetry breaking patterns. The scale setting and determination of the running gauge coupling are performed through the Wilson flow computation of the action density.
gauge fields on the lattice. The phase space is probed through the computation of gauge-invariant global observables serving as proxies for order parameters. In each phase, the spectrum of the theory is analysed for different combinations of bare couplings and different symmetry breaking patterns. The scale setting and determination of the running gauge coupling are performed through the Wilson flow computation of the action density.
Yogo, Akifumi*; Lan, Z.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; Mori, Takato*; Golovin, D.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Iwata, Natsumi*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:96.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Grsic, Z.*; Halsall, C.*; Heinrich, G.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Ku a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
IAEA-TECDOC-2001, 226 Pages, 2022/06
The IAEA organized a programme from 2012 to 2015 entitled Modelling and Data for Radiological Impact Assessments (MODARIA), which aimed to improve capabilities in the field of environmental radiation dose assessment by acquiring improved data, model testing and comparison of model inputs, assumptions and outputs, reaching a consensus on modelling philosophies, aligning approaches and parameter values, developing improved methods and exchanging information. This publication describes the activities of Working Group 2, Exposures in Contaminated Urban Environments and Effect of Remedial Measures.
Thiessen, K. M.*; Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Federspiel, L.; Gra i
i , B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
, B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(2), p.020502_1 - 020502_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:60.29(Environmental Sciences) -type PbS
-type PbSRathore, E.*; Juneja, R.*; Sarkar, D.*; Roychowdhury, S.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Singh, A. K.*; Biswas, K.*
Materials Today Energy (Internet), 24, p.100953_1 - 100953_9, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.61(Chemistry, Physical) Hg* and
Hg* and 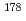 Pt* nuclei at intermediate excitation energies
Pt* nuclei at intermediate excitation energiesKozulin, E. M.*; Knyazheva, G. N.*; Itkis, I. M.*; Itkis, M. G.*; Mukhamejanov, Y. S.*; Bogachev, A. A.*; Novikov, K. V.*; Kirakosyan, V. V.*; Kumar, D.*; Banerjee, T.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 105(1), p.014607_1 - 014607_12, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:95.56(Physics, Nuclear)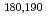 Hg and
Hg and 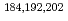 Pb formed in the reactions with
Pb formed in the reactions with  Ar and
Ar and 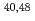 Ca ions
Ca ionsBogachev, A. A.*; Kozulin, E. M.*; Knyazheva, G. N.*; Itkis, I. M.*; Itkis, M. G.*; Novikov, K. V.*; Kumar, D.*; Banerjee, T.*; Diatlov, I. N.*; Cheralu, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(2), p.024623_1 - 024623_11, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:94.70(Physics, Nuclear)For the purpose of the study of asymmetric and symmetric fission modes of 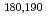 Hg and
Hg and 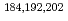 Pb nuclei, mass-energy distributions of fission fragments of
Pb nuclei, mass-energy distributions of fission fragments of 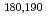 Hg and
Hg and 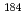 Pb formed in the
Pb formed in the  Ar +
Ar + 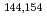 Sm and
Sm and  Ca +
Ca +  Sm reactions, respectively, at energies near the Coulomb barrier have been measured using the double-arm time-of-flight spectrometer CORSET and compared with previously measured
Sm reactions, respectively, at energies near the Coulomb barrier have been measured using the double-arm time-of-flight spectrometer CORSET and compared with previously measured 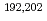 Pb isotopes produced in the
Pb isotopes produced in the  Ca +
Ca + 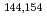 Sm reactions. Conclusion is the studied properties of asymmetric fission of
Sm reactions. Conclusion is the studied properties of asymmetric fission of 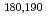 Hg and
Hg and 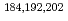 Pb nuclei point out the existence of well deformed proton shell at Z
Pb nuclei point out the existence of well deformed proton shell at Z 36 and less deformed proton shell at Z
36 and less deformed proton shell at Z 46.
46.
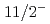 isomeric state in
isomeric state in  La
LaLaskar, Md. S. R.*; Palit, R.*; Mishra, S. N.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Garg, U.*; Biswas, S.*; Babra, F. S.*; Gala, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(3), p.034315_1 - 034315_8, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:49.74(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Zhang, Y.*; Guo, H.*; Kim, S. B.*; Wu, Y.*; Ostojich, D.*; Park, S. H.*; Wang, X.*; Weng, Z.*; Li, R.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; et al.
Lab on a Chip, 19(9), p.1545 - 1555, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:189 Percentile:99.70(Biochemical Research Methods)This paper introduces two important advances in recently reported classes of soft, skin-interfaced microfluidic systems for sweat capture and analysis: (1) a simple, broadly applicable means for collection of sweat that bypasses requirements for physical/mental exertion or pharmacological stimulation and (2) a set of enzymatic chemistries and colorimetric readout approaches for determining the concentrations of creatinine and urea in sweat, across physiologically relevant ranges. The results allow for routine, non-pharmacological capture of sweat across patient populations, such as infants and the elderly, that cannot be expected to sweat through exercise, and they create potential opportunities in the use of sweat for kidney disease screening/monitoring.
 -factor measurement of the 2738 keV isomer in
-factor measurement of the 2738 keV isomer in  La
LaLaskar, Md. S. R.*; Saha, S.*; Palit, R.*; Mishra, S. N.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Naik, Z.*; Babra, F. S.*; Biswas, S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(1), p.014308_1 - 014308_6, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:61.17(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Bandodkar, A. J.*; Gutruf, P.*; Choi, J.*; Lee, K.-H.*; Sekine, Yurina; Reeder, J. T.*; Jeang, W. J.*; Aranyosi, A. J.*; Lee, S. P.*; Model, J. B.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 5(1), p.eaav3294_1 - eaav3294_15, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:566 Percentile:99.88(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Interest in advanced wearable technologies increasingly extends beyond systems for biophysical measurements to those that enable continuous, non-invasive monitoring of biochemical markers in biofluids. Here, we introduce battery-free, wireless microelectronic platforms that perform sensing via schemes inspired by the operation of biofuel cells. Combining these systems in a magnetically releasable manner with chrono-sampling microfluidic networks that incorporate assays based on colorimetric sensing yields thin, flexible, lightweight, skin-interfaced technologies with broad functionality in sweat analysis. A demonstration device allows simultaneous monitoring of sweat rate/loss, along with quantitative measurements of pH and of lactate, glucose and chloride concentrations using biofuel cell and colorimetric approaches.
Kim, S. B.*; Lee, K.-H.*; Raj, M. S.*; Reeder, J. T.*; Koo, J.*; Hourlier-Fargette, A.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; Won, S. M.*; Sekine, Yurina; Choi, J.*; et al.
Small, 14(45), p.1802876_1 - 1802876_9, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:95 Percentile:94.03(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Excretion of sweat from eccrine glands is a dynamic physiological process that varies with body position, activity level, and health status. Information content embodied in sweat rate and chemistry can be used to assess health status and athletic performance. This paper presents a thin, miniaturized, skin-interfaced microfluidic technology that includes a reusable, battery-free electronics module for measuring sweat conductivity and rate in real-time using wireless power from and data communication with capabilities in near field communications (NFC). Systematic studies of these combined microfluidic/electronic systems, accurate correlations of measurements performed with them to those of laboratory standard instrumentation, and field tests on human subjects establish the key operational features and their utility in sweat analytics.
 quantitative analysis of sweat chemistry
quantitative analysis of sweat chemistrySekine, Yurina; Kim, S. B.*; Zhang, Y.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; Xu, S.*; Choi, J.*; Irie, Masahiro*; Ray, T. R.*; Kohli, P.*; Kozai, Naofumi; et al.
Lab on a Chip, 18(15), p.2178 - 2186, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:185 Percentile:99.61(Biochemical Research Methods)The rich composition of solutes and metabolites in sweat and its relative ease of collection upon excretion from skin pores make this class of biofluid an attractive candidate for point of care analysis. Here, we present a complementary approach that exploits fluorometric sensing modalities integrated into a soft, skin-interfaced microfluidic system which, when paired with a simple smartphone-based imaging module, allows for in-situ measurement of important biomarkers in sweat. A network array of microchannels and a collection of microreservoirs pre-filled with fluorescent probes that selectively react with target analytes in sweat (e.g. probes), enable quantitative, rapid analysis. Field studies on human subjects demonstrate the ability to measure the concentrations of chloride, sodium and zinc in sweat, with accuracy that matches that of conventional laboratory techniques.
Kim, S. B.*; Zhang, Y.*; Won, S. M.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; Sekine, Yurina; Xue, Y.*; Koo, J.*; Harshman, S. W.*; Martin, J. A.*; Park, J. M.*; et al.
Small, 14(12), p.1703334_1 - 1703334_11, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:128 Percentile:96.23(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)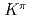 = 8
= 8 two-quasineutron isomer in
two-quasineutron isomer in  Pu
PuHota, S.*; Tandel, S.*; Chowdhury, P.*; Ahmad, I.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Chiara, C. J.*; Greene, J. P.*; Hoffman, C. R.*; Jackson, E. G.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(2), p.021303_1 - 021303_5, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.99(Physics, Nuclear)The decay of a 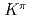 = 8
= 8 isomer in
isomer in  Pu and the collective band structure populating the isomer are studied using deep inelastic excitations with
Pu and the collective band structure populating the isomer are studied using deep inelastic excitations with  Ti and
Ti and  Pb beams, respectively. Precise measurements of
Pb beams, respectively. Precise measurements of 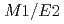 branching ratios in the band confirm a clean 9/2
branching ratios in the band confirm a clean 9/2 [734]
[734]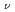
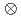 7/2
7/2 [624]
[624]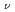 for the isomer, validating the systematics of K
for the isomer, validating the systematics of K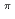 = 8
= 8 two-quasineutron isomers observed in even-
two-quasineutron isomers observed in even- ,
,  = 150 isotones. These isomers around the deformed shell gap at
= 150 isotones. These isomers around the deformed shell gap at  = 152 provide critical benchmarks for theoretical predictions of single-particle energies in this gateway region to superheavy nuclei.
= 152 provide critical benchmarks for theoretical predictions of single-particle energies in this gateway region to superheavy nuclei.
Ghobadi, A. F.*; Letteri, R.*; Parelkar, S. S.*; Zhao, Y.; Chan-Seng, D.*; Emrick, T.*; Jayaraman, A.*
Biomacromolecules, 17(2), p.546 - 557, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:58.72(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Sarri, G.*; Kar, S.*; Romagnani, L.*; Bulanov, S. V.; Cecchetti, C. A.*; Galimberti, M.*; Gizzi, L. A.*; Heathcote, R.*; Jung, R.*; Kourakis, I.*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 18(8), p.080704_1 - 080704_4, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:65.11(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas) isomer in
isomer in  Rf
RfRobinson, A. P.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Ahmad, I.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Chowdhury, P.*; Davids, C. N.*; Greene, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064311_1 - 064311_7, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:85.36(Physics, Nuclear)We have identified an isomer with a half-life of 17  s in
s in  Rf through a calorimetric conversion electron measurement tagged with implanted
Rf through a calorimetric conversion electron measurement tagged with implanted  Rf nuclei using the fragment mass analyzer at Argonne National Laboratory. The low population yield for this isomer suggests that this isomer should not be a 2-quasiparticle high-
Rf nuclei using the fragment mass analyzer at Argonne National Laboratory. The low population yield for this isomer suggests that this isomer should not be a 2-quasiparticle high- isomer which is typically observed in the N = 152 isotones, but should be a 4-quasiparticle one. Possible reasons of the non-observation of a 2-quasiparticle isomer are this isomer decays by fission with a half-life similar to that of the ground state of
isomer which is typically observed in the N = 152 isotones, but should be a 4-quasiparticle one. Possible reasons of the non-observation of a 2-quasiparticle isomer are this isomer decays by fission with a half-life similar to that of the ground state of  Rf. Another possibility, that there is no 2-quasiparticle isomer at all, would imply an abrupt termination of axially symmetric deformed shape at Z=104.
Rf. Another possibility, that there is no 2-quasiparticle isomer at all, would imply an abrupt termination of axially symmetric deformed shape at Z=104.