Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oshima, Takayuki; Naito, Osamu; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Iba, Katsuyuki; Sato, Minoru; Sakata, Shinya; Tsugita, Tomonori; Matsuda, Toshiaki; Iwasaki, Keita*; Karube, Yukihiro*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 71(1-4), p.239 - 244, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the JT-60 tokamak at JAERI, environment for remote participation is planned to be developed by concentrating experts of nuclear fusion research of another research organizations and universities distributed all over the country. We are constructing a hierarchical remote research system, which consists of remote experiment, remote analysis, and remote diagnostic. In a remote collaboration, it is important to maintain the security of the system, as well as to share the information, atmosphere and presence between the participants. For the latter purpose, we developed a video conferencing system, and a video streaming system that can deliver the images of the JT-60 control room. Furthermore, a development of the remote analysis system called "VizAnalysis" has been started. And to assist the remote analysis, we developed a web based software system called "VizSquare". In the JT-60 tokamak at JAERI, security and authentication methods on a computer network and a new communication tool are developed, and probably they will be applied to the remote participation of ITER.
Tokuda, Shinji; Okubo, Hiroshi*; Fujisaki, Masahide*; Karube, Yukihiro*
no journal, ,
An MHD (MagnetoHydroDynamic) stability code MARG2D has recently been developed which identifies the stability against ideal MHD perturbations in a tokamak. The code reduces the stability problem to an eigenvalue problem and solves the problem less than ten seconds when a massively parallel computer (SGI Altix 3700Bx2) is used. Real time stability analysis therefore becomes probable since the characteristic time is 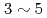 seconds for changing the pressure profile in ITER. To this end we are now developing by using FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) a special purpose computer that solves the eigenvalue problem. We report on the progress of this project, especially on matrix operations by FPGA with the study of performance.
seconds for changing the pressure profile in ITER. To this end we are now developing by using FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) a special purpose computer that solves the eigenvalue problem. We report on the progress of this project, especially on matrix operations by FPGA with the study of performance.