Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Komeno, Akira; Nakamichi, Shinya; Kashimura, Motoaki
Proceedings of 10th OECD/NEA Information Exchange Meeting on Actinide and Fission Product Partitioning and Transmutation (CD-ROM), p.201 - 209, 2010/00
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed homogeneous MOX fuel containing minor actinide (MA) elements such as Np and Am. To measure physical properties of the fuel is essential for its development, because their data are needed to evaluate irradiation behavior. In this report, the physical properties, melting temperature, thermal conductivity, lattice parameter, oxygen potential and phase separation behavior, were reviewed, and effect of MA content was discussed.
 system
systemNakamichi, Shinya; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uchida, Teppei; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kashimura, Motoaki; Kihara, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 389(1), p.191 - 196, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Japan Atomic Energy Agency researchers have developed mixed oxide (MOX) fuels containing minor actinides (MA). These fuels were irradiated for ten minutes in the FBR Joyo in some short-term irradiation tests. The Si-condensed phases were observed at the center of the pellets in the post irradiation examination. Si impurities came to be mixed into the raw materials in the ball milling process, because Si rubber was used as the lining of the milling pot. Content of Si in the pellets was within the specification of the fuel. It is important to investigate the Si state in MOX at high temperatures like the reactor operating temperature of the fuel to evaluate irradiation behavior. In the present work, MOX specimens with mixed SiO impurity were prepared. The ratio of MOX to SiO
impurity were prepared. The ratio of MOX to SiO was controlled at a mol fraction of 3 to 1. The specimens were first heated at 1973K in atmospheres of three different oxygen partial pressures to adjust the O/M ratio. Then these specimens were sealed in a tungsten capsule, and heated at 2273K or 2673K. Compounds consisting of Pu and Si were observed at grain boundaries of the MOX matrix in specimens after heat treatment. These compounds were not observed in grain interior and MOX matrix was not affected significantly by Si impurity. These compounds tended to form in specimens with low O/M ratio and in specimens heated at higher temperatures.
was controlled at a mol fraction of 3 to 1. The specimens were first heated at 1973K in atmospheres of three different oxygen partial pressures to adjust the O/M ratio. Then these specimens were sealed in a tungsten capsule, and heated at 2273K or 2673K. Compounds consisting of Pu and Si were observed at grain boundaries of the MOX matrix in specimens after heat treatment. These compounds were not observed in grain interior and MOX matrix was not affected significantly by Si impurity. These compounds tended to form in specimens with low O/M ratio and in specimens heated at higher temperatures.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Nakamichi, Shinya; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Konashi, Kenji*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 7(4), p.420 - 428, 2008/12
The melting temperatures of MOX for fast reactor fuel were investigated as functions of Pu content, Am content and oxygen-to-metal (O/M) ratio using thermal arrest technique. Rhenium inner was used for the measurement to prevent the reaction between the sample and capsule materials. The solidus temperatures decreased with increasing Pu and Am content and increased with decreasing O/M ratio. It is considered that the maximum temperature in U-Pu-O system varies in hypostoichiometric composition region. The melting temperatures were evaluated by ideal solid solution model in UO -PuO
-PuO -AmO
-AmO -PuO
-PuO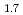 system, and the model was derived for calculating solidus and liquidus temperature. The derived model reproduced the experimental data with
system, and the model was derived for calculating solidus and liquidus temperature. The derived model reproduced the experimental data with  25 K.
25 K.
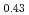 Am
Am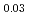 U
U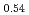 )O
)O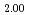
Nakamichi, Shinya; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 96(1), p.191 - 192, 2007/06
JAEA has developed plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) containing 20-32%Pu content as a fuel of the fast breeder reactor. During irradiation, large temperature gradient in radial direction of a fuel pellet causes redistribution of Pu and U, and the Pu content increases to about 43% at the pellet center. The maximum temperature of the fuel pellet during irradiation is limited within the design criterion to prevent fuel melting. So, it is important to evaluate melting points of MOX containing 43%Pu. In this work, it is confirmed that the MOX with 43%Pu content is not melted by heat treatment just below the melting point which was determined by thermal arrest technique using Re inner capsule. The MOX specimen with 43%Pu content was heated at 2978K for 40s using Re inner capsule. Optical micrograph and XRD results show the specimen was heated at the temperature less than solidus temperature. So it was confirmed that (Pu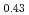 Am
Am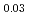 U
U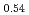 )O
)O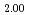 was solid phase at 2978K
was solid phase at 2978K 20K.
20K.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Komeno, Akira; Nakamichi, Shinya; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sugata, Hiromasa*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-049, 32 Pages, 2006/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a fast breeder reactor(FBR), and plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) having low density and 20-30%Pu content has used as a fuel of the FBR, Monju. In plutonium, Americium has been accumulated during long-term storage, and Am content will be increasing up to 2-3% in the MOX. It is essential to evaluate the influence of Am content on physical properties of MOX on the development of FBR in the future. In this study melting points and thermal conductivities which are important data on the fuel design were measured systematically in wide range of composition, and the effects of Am accumulated were evaluated. The solidus temperatures of MOX were measured as a function of Pu content, oxygen to metal ratio(O/M) and Am content using thermal arrest technique. The sample was sealed in a tungsten capsule in vacuum for measuring solidus temperature. In the measurements of MOX with Pu content of more than 30%, a rhenium inner capsule was used to prevent the reaction between MOX and tungsten. In the results, it was confirmed that the melting points of MOX decrease with as an increase of Pu content and increase slightly with a decrease of O/M ratio. The effect of Am content on the fuel design was negligible small in the range of Am content up to 3%. Thermal conductivities of MOX were evaluated from thermal diffusivity measured by laser flash method and heat capacity calculated by Nuemann- Kopp's law. The thermal conductivity of MOX decreased slightly in the temperature of less than 1173K with increasing Am content. The effect of Am accumulated in long-term storage fuel was evaluated from melting points and thermal conductivities measured in this study. It is concluded that the increase of Am in the fuel barely affect the fuel design in the range of less than 3%Am content.
Nakamichi, Shinya; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Shibata, Katsuya*; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -UO
-UO -AmO
-AmO system
systemKato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Nakamichi, Shinya; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Uno, Hiroki*; Shibata, Katsuya*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 binary system
binary systemNakamichi, Shinya; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kihara, Yoshiyuki; Kashimura, Motoaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Nakamichi, Shinya; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Uno, Hiroki*; Shibata, Katsuya*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakamichi, Shinya; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kashimura, Motoaki; Kihara, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Segawa, Tomoomi; Nakamichi, Shinya; Komeno, Akira; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Kashimura, Motoaki; Suzuki, Masahiro; Kihara, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
JAEA has been researching in the fundamental properties of MOX fuel including Minor Actinides(Am and Np). In this presentation, melting point, thermal conductivity, oxygen potential and lattice constant of (Am, Np, Pu, U)O are reported.
are reported.
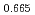 Pu
Pu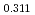 Am
Am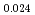 )O
)O
Nakamichi, Shinya; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kashimura, Motoaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Tsujimura, Norio; Yamazaki, Takumi; Kashimura, Shinya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakamichi, Shinya; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kashimura, Motoaki; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Takayasu, Tetsuya*; Kashimura, Shinya*; Tago, Itaru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English