Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Suzuki, Yuji*; Kabasawa, Satsuki; Kato, Tomoko
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-001, 21 Pages, 2024/03
Model catchments have developed for use in testing various assessment models that can consider specific surface environmental conditions such as topography, riverine systems, and land use in the biosphere assessment of HLW geological disposal. The model catchments consist of the topography and riverine system of the catchment area created using existing tools, as well as land use and population distribution, river discharge, sediment flux data set by algorithms from topographical data. Datasets of three types of model watersheds (Types 1 to 3, watershed area: 730 to 770 km ) with different topographical characteristics have released as raster data that can be handled by geographic information systems (GIS). Since the model catchments were created virtually reflecting as much as possible the main characteristics of Japan's surface environment, they can be used as a test bed for conducting hydraulic/mass transport analysis to set the GBI and compartment model.
) with different topographical characteristics have released as raster data that can be handled by geographic information systems (GIS). Since the model catchments were created virtually reflecting as much as possible the main characteristics of Japan's surface environment, they can be used as a test bed for conducting hydraulic/mass transport analysis to set the GBI and compartment model.
Doda, Norihiro; Kato, Shinya; Hamase, Erina; Kuwagaki, Kazuki; Kikuchi, Norihiro; Ohgama, Kazuya; Yoshimura, Kazuo; Yoshikawa, Ryuji; Yokoyama, Kenji; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; et al.
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.946 - 959, 2023/08
An innovative design system named ARKADIA is being developed to realize the design of advanced nuclear reactors as safe, economical, and sustainable carbon-free energy sources. This paper focuses on ARKADIA-Design for design studies as a part of ARKADIA and introduces representative verification methods for numerical analysis methods of the core design. ARKADIA-Design performs core performance analysis of sodium-cooled fast reactors using a multiphysics approach that combines neutronics, thermal-hydraulics, core mechanics, and fuel pin behavior analysis codes. To confirm the validity of these analysis codes, validation matrices are identified with reference to experimental data and reliable numerical analysis results. The analysis models in these codes and the representative practices for the validation matrices are described.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 38(2), p.347 - 358, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Analytical)To develop remote isotopic analysis for the nuclids with small isotope shifts, Doppler-free fluorescence spectroscopy of Ca was performed using laser ablation plume. Counter-propagating laser beams from two external cavity diode lasers were used to irradiate the plume in order to excite the ground-state Ca atoms to the  D
D state through a double resonance scheme of
state through a double resonance scheme of  S
S

 P
P

 D
D . Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the
. Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the  D
D to
to  P
P states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step
states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step  P
P

 D
D transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,
transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,  Ca,
Ca, 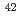 Ca, and
Ca, and 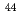 Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Doda, Norihiro; Kato, Shinya; Iida, Masaki*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/10
In the conventional core design in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs), negative reactivity feedback due to core deformation was neglected because of large uncertainty in analytical evaluation. To optimize core design, it is necessary to develop an analytical evaluation method and eliminate excessive conservativeness. An evaluation method for core deformation reactivity has been developed by coupling analysis of neutronics, thermal-hydraulics, and structural mechanics. For the verification study of the neutronics calculation method, the reactivity was calculated for the deformed core geometry in which the fuel assembly (FA) moved horizontally in the radial direction for each row from the core center. Compared to reference values derived from Monte Carlo calculations, the calculated reactivity due to FA displacement agreed well in the core region and was overestimated in the reflector region. The modification challenges in development of the core deformation model were identified.
 Co radiation source under an intense
Co radiation source under an intense  Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr
Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fields
spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.983 - 992, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
 structure observation of pyroelectric ceramics during power generation cycle
structure observation of pyroelectric ceramics during power generation cycleKawasaki, Takuro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Sakamoto, Tomokazu*; Murayama, Ichiro*; Kato, Takanori*; Baba, Masaaki*; Hashimoto, Hideki*; Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 131(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.38(Physics, Applied) -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of nuclear facilities being decommissioned has been increasing worldwide, in particular following the accident of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011. In these nuclear facilities, proper management of radioactive materials is required. Then, A  -ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr
-ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr scintillators with a dimension of
scintillators with a dimension of 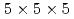
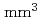 was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the
was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the  -ray exposure study under
-ray exposure study under  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields. Under the
Co radiation fields. Under the  Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2
Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0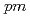 0.03%, and 9.0
0.03%, and 9.0 0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioningKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:89.29(Instruments & Instrumentation)An increasing number of nuclear facilities have been decommissioned worldwide following the 2011 accident of the TEPCO' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. During the decommissioning, radioactive materials have to be retrieved under proper management. In this study, a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm was manufactured to perform
5 mm was manufactured to perform  -ray spectroscopy under intense
-ray spectroscopy under intense  -ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform
-ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform  -ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a
-ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a  Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a
Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a  Co radiation field, which suggested to realize
Co radiation field, which suggested to realize  -ray assessment of
-ray assessment of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Makino, Hitoshi
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(2), p.72 - 82, 2020/12
An efficient analytical tool to calculate temporal change of topography and repository depth due to uplift and erosion was developed for use in performance assessment of high level radioactive waste geological disposal. The tool was developed as ArcGIS model, incorporating simplified landform development simulation, to enable trial calculation of various conditions such as initial topography, uplift rate and its distributions, and repository location. This tool enables to support decision on which processes, features, and their changes should be taken into account for performance assessment, by calculating topography change and repository depth change under various conditions.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Applied Physics A, 126(3), p.213_1 - 213_10, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in low pressure rare gas ambient was investigated with laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy for three refractory metals, i.e. titanium, zirconium and hafnium. A comparison of the plume expansion behaviors for the species of these elements revealed an atomic weight effect on the plume structure formation. A hemispherical thin layer and cavity structure reported previously for gadolinium were observed also for these elements. It was found that the plume size increases as well as the layer thickness decreases with increasing atomic weight. For ground state atoms of Ti, substantial amount of atoms were observed even at the center of the plume. Also, the persistence of the Ti atomic plume was as long as 300  s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
Kim, J.*; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Murayama, Ichiro*; Kato, Takanori*; Sakamoto, Tomokazu*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Sekino, Toru*; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Takeda, Masatoshi*; et al.
Sustainable Energy & Fuels (Internet), 4(3), p.1143 - 1149, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:64.8(Chemistry, Physical)Kim, J.*; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Nakajima, Akira*; Kato, Takanori*; Kim, Y.*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yoshii, Kenji; Nishihata, Yasuo; Baba, Masaaki*; Takeda, Masatoshi*; et al.
Advanced Sustainable Systems (Internet), 2(11), p.1800067_1 - 1800067_8, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.76(Green & Sustainable Science & Technology)Kim, J.*; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Nakajima, Akira*; Kato, Takanori*; Kim, Y.*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yoshii, Kenji; Nishihata, Yasuo; Baba, Masaaki*; Takeda, Masatoshi*; et al.
Ferroelectrics, 512(1), p.92 - 99, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:56.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Jung, K.; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Khumaeni, A.*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 134, p.42 - 51, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:91.46(Spectroscopy)Spectroscopic properties of atomic species of plutonium were investigated by combining laser ablation and resonance absorption techniques for the analysis of a plutonium oxide sample. For 17 transitions of Pu atoms and ions, the absorbance, isotope shift, and hyperfine splitting were determined via Voigt profile fitting of the recorded absorption spectra. Three transitions were selected as candidates for analytical use. Using these transitions, we investigated the analytical performance that was attainable and determined a correlation coefficient R2 between the absorbance and plutonium concentration of 0.9999, a limit of detection of 30-130 ppm, and a relative standard deviation of approximately 6% for an abundance of  Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Yamanaka, Satoru*; Kim, J.*; Nakajima, Akira*; Kato, Takanori*; Kim, Y.*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yoshii, Kenji; Nishihata, Yasuo; Baba, Masaaki*; Yamada, Noboru*; et al.
Advanced Sustainable Systems (Internet), 1(3-4), p.1600020_1 - 1600020_6, 2017/04
no abstracts in English
Wakasugi, Keiichiro; Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Koo, Shigeru*; Nagao, Fumiya; Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Ebashi, Takeshi; Umeki, Hiroyuki*; Niibori, Yuichi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 16(1), p.15 - 33, 2017/03
This study provides a method of safety assessment for the geological disposal of HLW to evaluate the effects of uplift and erosion which are widespread phenomena identified on regional and global scales, and are more or less difficult to avoid in Japan. This method enables to deal with different uplift rate and erosion rate, and to evaluate repository depth, the time required for a repository to reach the weathered zone and surface of the ground, and the number of waste packages eroded as a function of time by using a landform evolution model. Based on trial analysis, the result shows that the maximum dose in the Base Case (uplift rate: 0.3 mm/y) is less than the targeted criterion suggested by the international organization even if the repository reaches the ground surface. Furthermore, the diversifying effect on timing the waste packages to reach to weathered zone due to heterogeneity on altitude of bottom of weathered zone reduces one order magnitude of result of the existed dose assessment. The new method is applicable to evaluate safety of geological disposal based on realistic phenomena of uplift and erosion and to quantify a safety margin and robustness of the disposal system.
Kaburagi, Masaaki; Yamada, Hironao*; Miyakawa, Takeshi*; Morikawa, Ryota*; Takasu, Masako*; Kato, Takamitsu*; Uesaka, Mitsuru*
Polymer Journal, 48(2), p.189 - 195, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:18.83(Polymer Science)We performed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of telomeric single-stranded DNA and POT1 for 100 ns. The distance between 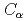 (POT1) and O5' (telomeric ssDNA) is calculated to verify the binding system for 100 ns MD. We then calculated the distance between the bases of telomeric DNA ends and the root mean square deviation and gyration radius in single and binding states. We compared the root mean square fluctuations between single and binding states and calculated the number of hydrogen bonds between POT1 and telomeric DNA. There are many hydrogen bonds between Gln94 and the first guanine of the closest TTAGGG sequence in telomeric single-stranded DNA. These Gln94 and the guanine have a large difference in root mean square fluctuation between single and binding states. We found that Gln94 and guanine are important components of the binding system, and they are related to its stability.
(POT1) and O5' (telomeric ssDNA) is calculated to verify the binding system for 100 ns MD. We then calculated the distance between the bases of telomeric DNA ends and the root mean square deviation and gyration radius in single and binding states. We compared the root mean square fluctuations between single and binding states and calculated the number of hydrogen bonds between POT1 and telomeric DNA. There are many hydrogen bonds between Gln94 and the first guanine of the closest TTAGGG sequence in telomeric single-stranded DNA. These Gln94 and the guanine have a large difference in root mean square fluctuation between single and binding states. We found that Gln94 and guanine are important components of the binding system, and they are related to its stability.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Khumaeni, A.*; Kato, Masaaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 110, p.101 - 117, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:82.1(Spectroscopy)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in ambient gas has been investigated by laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy. The second harmonic beam from an Nd:YAG laser (0.5-6J/cm ) was focused on a sintered oxide pellet or a metal chip of gadolinium. The produced plume was subsequently intersected with a sheet-shaped UV beam from a dye laser so that time-resolved fluorescence images were acquired with an intensified CCD camera at various delay times. The obtained cross-sectional images of the plume indicate that the ablated ground state atoms and ions of gadolinium accumulate in a hemispherical contact layer between the plume and the ambient gas, and a cavity containing a smaller density of ablated species is formed near the center of the plume. At earlier expansion stage, another luminous component also expands in the cavity so that it coalesces into the hemispherical layer. The splitting and coalescence for atomic plume occur later than those for ionic plume. Furthermore, the hemispherical layer of neutral atoms appears later than that of ions; however, the locations of the layers are nearly identical. This coincidence of the appearance locations of the layers strongly suggests that the neutral atoms in the hemispherical layer are produced as a consequence of three-body recombination of ions through collisions with gas atoms. The obtained knowledge regarding plume expansion dynamics and detailed plume structure is useful for optimizing the experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.
) was focused on a sintered oxide pellet or a metal chip of gadolinium. The produced plume was subsequently intersected with a sheet-shaped UV beam from a dye laser so that time-resolved fluorescence images were acquired with an intensified CCD camera at various delay times. The obtained cross-sectional images of the plume indicate that the ablated ground state atoms and ions of gadolinium accumulate in a hemispherical contact layer between the plume and the ambient gas, and a cavity containing a smaller density of ablated species is formed near the center of the plume. At earlier expansion stage, another luminous component also expands in the cavity so that it coalesces into the hemispherical layer. The splitting and coalescence for atomic plume occur later than those for ionic plume. Furthermore, the hemispherical layer of neutral atoms appears later than that of ions; however, the locations of the layers are nearly identical. This coincidence of the appearance locations of the layers strongly suggests that the neutral atoms in the hemispherical layer are produced as a consequence of three-body recombination of ions through collisions with gas atoms. The obtained knowledge regarding plume expansion dynamics and detailed plume structure is useful for optimizing the experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.