Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Onishi, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Kato, Masato*
JAEA-Research 2025-002, 18 Pages, 2025/05
It is advocated as a development target of fast reactors (FRs) to allow for the of use of mixed oxide (MOX) fuels containing minor actinide (MA) separated and recovered from spent fuels with the aim of reducing the volume and toxicity of high-level radioactive waste generated from nuclear reactors. In the development of MAMOX fuels, it is important behavior to understand the thermal properties such as thermal conductivity for fuel design and analysis of the irradiation. However, there are only a few reports on the thermal properties of MA-MOX fuels, and neither the effects of MA contents nor of oxygen non-stoichiometry in MOX fuels on their thermal conductivities have been fully understood. In this study, the thermal conductivities of MOX fuels with up to 15% Am content were measured at near-stoichiometric composition and the relationship between thermal conductivity and Am content was evaluated. Moreover, the thermal conductivities of Am-doped UO fuels were also measured and evaluated by comparison with Am-MOX to evaluate the effect of Am content. The fuel samples used in this study were three types of MOX with a Pu content of 30% and different Am contents (5%, 10%, and 15%), and UO
fuels were also measured and evaluated by comparison with Am-MOX to evaluate the effect of Am content. The fuel samples used in this study were three types of MOX with a Pu content of 30% and different Am contents (5%, 10%, and 15%), and UO containing 15% Am. The thermal conductivities of specimens were calculated from the thermal diffusivities measured by the laser flash method, the density of the specimens and, the heat capacity at constant pressure. The oxygen partial pressure during the measurement was controlled at that of the targeted near-stoichiometric composition. The thermal conductivities of all specimens exhibited a decline with increasing temperature and Am content, with a particularly pronounced reduction observed below 1,173 K. The results of the classical phonon scattering model analysis of the measured thermal conductivities showed that the effect of lattice strain due to the Am addition was significant on the thermal resistivity change, and the effect was comparable for both MOX and UO
containing 15% Am. The thermal conductivities of specimens were calculated from the thermal diffusivities measured by the laser flash method, the density of the specimens and, the heat capacity at constant pressure. The oxygen partial pressure during the measurement was controlled at that of the targeted near-stoichiometric composition. The thermal conductivities of all specimens exhibited a decline with increasing temperature and Am content, with a particularly pronounced reduction observed below 1,173 K. The results of the classical phonon scattering model analysis of the measured thermal conductivities showed that the effect of lattice strain due to the Am addition was significant on the thermal resistivity change, and the effect was comparable for both MOX and UO .
.
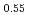 Pu
Pu Am
Am )O
)O
Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Usui, Akane; Seki, Takayuki*; Onishi, Takashi; Kato, Masato
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 42, p.101908_1 - 101908_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Oxygen potential of high Am content MOX, (U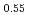 Pu
Pu Am
Am )O
)O , was measured at 1273 K, 1473 K, 1573 K, and 1623 K. by gas equilibrium method using thermogravimeter. Comparing the measured data with the literature data, it was found that the addition of 15% Am increases the oxygen potential of (U, Pu)O
, was measured at 1273 K, 1473 K, 1573 K, and 1623 K. by gas equilibrium method using thermogravimeter. Comparing the measured data with the literature data, it was found that the addition of 15% Am increases the oxygen potential of (U, Pu)O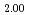 by 100-150 kJ/mol for the same Pu content and O/M ratio. The proportion of cations in the stoichiometric composition was determined as (U
by 100-150 kJ/mol for the same Pu content and O/M ratio. The proportion of cations in the stoichiometric composition was determined as (U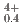 U
U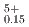 Pu
Pu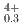 Am
Am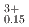 )O
)O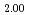 , assuming the presence of Am
, assuming the presence of Am and partial oxidation of U
and partial oxidation of U to U
to U . The relationship between oxygen partial pressure and deviation x from stoichiometry in (U
. The relationship between oxygen partial pressure and deviation x from stoichiometry in (U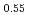 Pu
Pu Am
Am )O
)O was analyzed by defect chemistry model. The equation to represent the O/M ratio was derived as a function of temperature and oxygen partial pressure. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214921.
was analyzed by defect chemistry model. The equation to represent the O/M ratio was derived as a function of temperature and oxygen partial pressure. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214921.
 Am
Am O
O at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K
at 1473, 1573, and 1673 KWatanabe, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Vauchy, R.; Kato, Masato; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Seki, Takayuki*; Hino, Tetsushi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 599, p.155232_1 - 155232_5, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:79.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxygen potential data of U Am
Am O
O were measured at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K by thermogravimetry. In U
were measured at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K by thermogravimetry. In U An
An O
O , where An stands for Pu or Am, and for a given value of y and Oxygen/Metal ratio, the oxygen potential of U
, where An stands for Pu or Am, and for a given value of y and Oxygen/Metal ratio, the oxygen potential of U Am
Am O
O is higher than that of U
is higher than that of U Pu
Pu O
O . The valence of cations in the hypostoichiometric region is similar to that of Nd-doped UO
. The valence of cations in the hypostoichiometric region is similar to that of Nd-doped UO . At the stoichiometric composition, it is estimated to be Am
. At the stoichiometric composition, it is estimated to be Am , U
, U , and U
, and U (for charge compensation of Am
(for charge compensation of Am ). The experimental data were analyzed using a defect chemistry model, and a relationship connecting the oxygen-to-metal ratio, the temperature, and the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure was proposed.
). The experimental data were analyzed using a defect chemistry model, and a relationship connecting the oxygen-to-metal ratio, the temperature, and the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure was proposed.
Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.13(Materials Science, Ceramics)Higuchi, Yuki*; Yoshimune, Wataru*; Kato, Satoru*; Hibi, Shogo*; Setoyama, Daigo*; Isegawa, Kazuhisa*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Harada, Masashi*; et al.
Communications Engineering (Internet), 3, p.33_1 - 33_7, 2024/02
Kato, Masato; Nakamichi, Shinya; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Ishii, Katsunori
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(2), p.51 - 58, 2023/04
Uranium and Plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) pellets used as fast reactor fuels have been produced from several raw materials by mechanical blending method through processes of ball milling, additive blending, granulation, pressing, sintering and so on. It is essential to control the pellet density which is one of the important fuel specifications, but it is difficult to understand relationships among many parameters in the production. Database for MOX production was prepared from production results in Japan, and input data of eighteen types were chosen from production process and made a data set. Machine learning model to predict sintered density of MOX pellet was derived by gradient boosting regressor, and represented the measured sintered density with coefficient of determination of R =0.996
=0.996
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.2217_1 - 2217_8, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:74.59(Multidisciplinary Sciences) , ThO
, ThO , UO
, UO , PuO
, PuO , and (U, Pu)O
, and (U, Pu)O
Kato, Masato; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 1, p.1081473_1 - 1081473_10, 2023/01
Watanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 1, p.1082324_1 - 1082324_9, 2023/01
Since the oxygen potential and the oxygen coefficient of UO have a significant impact on fuel performance, many experimental data have been obtained. However, experimental data of the oxygen potential and the oxygen diffusion coefficient in the high temperature region above 1673 K are very limited. In the present study, we aimed to obtain these data and analyze them by defect chemistry. The oxygen potentials and the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient of UO
have a significant impact on fuel performance, many experimental data have been obtained. However, experimental data of the oxygen potential and the oxygen diffusion coefficient in the high temperature region above 1673 K are very limited. In the present study, we aimed to obtain these data and analyze them by defect chemistry. The oxygen potentials and the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient of UO were measured by the gas equilibrium method in the near stoichiometric region at temperatures ranging from 1673 to 1873 K. A data set of oxygen potentials was made together with literature data and analyzed by defect chemistry. The oxygen potential of UO
were measured by the gas equilibrium method in the near stoichiometric region at temperatures ranging from 1673 to 1873 K. A data set of oxygen potentials was made together with literature data and analyzed by defect chemistry. The oxygen potential of UO was determined as a function of O/U ratio and temperature, and an equation representing the relationship was derived. The oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient values obtained in this study were reasonably close to the literature values. The oxygen partial pressure dependence of the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficients was predicted from the evaluated results of the oxygen potential data, but no clear dependence was observed.
was determined as a function of O/U ratio and temperature, and an equation representing the relationship was derived. The oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient values obtained in this study were reasonably close to the literature values. The oxygen partial pressure dependence of the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficients was predicted from the evaluated results of the oxygen potential data, but no clear dependence was observed.
Kato, Masato; Machida, Masahiko; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kobayashi, Keita; Ozawa, Takayuki; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; et al.
Materials Science and Fuel Technologies of Uranium and Plutonium mixed Oxide, 171 Pages, 2022/10
Innovative and advanced nuclear reactors using plutonium fuel has been developed in each country. In order to develop a new nuclear fuel, irradiation tests are indispensable, and it is necessary to demonstrate the performance and safety of nuclear fuels. If we can develop a technology that accurately simulates irradiation behavior as a technology that complements the irradiation test, the cost, time, and labor involved in nuclear fuel research and development will be greatly reduced. And safety and reliability can be significantly improved through simulation of nuclear fuel irradiation behavior. In order to evaluate the performance of nuclear fuel, it is necessary to know the physical and chemical properties of the fuel at high temperatures. And it is indispensable to develop a behavior model that describes various phenomena that occur during irradiation. In previous research and development, empirical methods with fitting parameters have been used in many parts of model development. However, empirical techniques can give very different results in areas where there is no data. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to construct a scientific descriptive model that can extrapolate the basic characteristics of fuel to the composition and temperature, and to develop an irradiation behavior analysis code to which the model is applied.
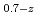 Pu
Pu Am
Am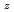 )O
)O (z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)
(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15)Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Tokoro, Daishiro*; Sugimoto, Masatoshi*; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Hino, Tetsushi*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 31, p.101156_1 - 101156_7, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:68.73(Nuclear Science & Technology)In current nuclear fuel cycle systems, to reduce the amount of high-level radioactive waste, minor actinides (MAs) bearing MOX fuel is one option for burning MAs using fast reactor. However, the effects of Am content in fuel on thermal conductivity are unclear because there are no experimental data on thermal conductivity of high Am bearing MOX fuel. In this study, The thermal conductivities of near stoichiometric (U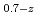 Pu
Pu Am
Am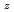 )O
)O solid solutions(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15) have been measured between room temperature (RT) and 1473 K. The thermal conductivities decreased with increasing Am content and satisfied the classical phonon transport model ((A+BT)
solid solutions(z = 0.05, 0.10, and 0.15) have been measured between room temperature (RT) and 1473 K. The thermal conductivities decreased with increasing Am content and satisfied the classical phonon transport model ((A+BT) ) up to about 1473 K. A values increased linearly with increasing Am content because the change in ionic radius affects the conduction of the phonon due to the solid solution in U
) up to about 1473 K. A values increased linearly with increasing Am content because the change in ionic radius affects the conduction of the phonon due to the solid solution in U and Am
and Am . B values were independent of Am content.
. B values were independent of Am content.
 based on experimental data and density functional theory calculation result
based on experimental data and density functional theory calculation resultWatanabe, Masashi; Nakamura, Hiroki; Suzuki, Kiichi; Machida, Masahiko; Kato, Masato
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 105(3), p.2248 - 2257, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.41(Materials Science, Ceramics)Properties of CeO were evaluated by DFT simulation to determine band gap, Frenkel defect formation energy and defect migration energy. Band gap and Frenkel defect formation energy were used to analyze defect equilibria. Oxygen partial pressure dependence of defect equilibria was evaluated based on oxygen potential experimental data and DFT calculation, and a Brouwer diagram was derived. The defect formation energies, including Frenkel defect, electron-hole pair and so on, were determined and used to evaluate the properties, including oxygen diffusion coefficients, electrical conduction, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Mechanisms of various properties were discussed for a deeper understanding based on defect chemistry, and the relationship among properties were systematically described.
were evaluated by DFT simulation to determine band gap, Frenkel defect formation energy and defect migration energy. Band gap and Frenkel defect formation energy were used to analyze defect equilibria. Oxygen partial pressure dependence of defect equilibria was evaluated based on oxygen potential experimental data and DFT calculation, and a Brouwer diagram was derived. The defect formation energies, including Frenkel defect, electron-hole pair and so on, were determined and used to evaluate the properties, including oxygen diffusion coefficients, electrical conduction, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Mechanisms of various properties were discussed for a deeper understanding based on defect chemistry, and the relationship among properties were systematically described.
 at high temperatures of 1673-1873 K
at high temperatures of 1673-1873 KWatanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 542, p.152472_1 - 152472_7, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The oxygen self-diffusion coefficients in near stoichiometric (U,Pu)O at high temperatures were successfully measured by thermogravimetry combined with the oxygen isotope exchange method. The activation energy for oxygen diffusion in the stoichiometric composition of (U,Pu)O
at high temperatures were successfully measured by thermogravimetry combined with the oxygen isotope exchange method. The activation energy for oxygen diffusion in the stoichiometric composition of (U,Pu)O was evaluated from experimental data, and the value was determined to be 248 kJ/mol. In addition, the defect migration energies of (U,Pu)O
was evaluated from experimental data, and the value was determined to be 248 kJ/mol. In addition, the defect migration energies of (U,Pu)O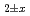 were derived, and the oxygen self-diffusion coefficients were evaluated using these. As a result, good agreement was found between the experimental data and the oxygen self-diffusion coefficients calculated using the defect migration energies.
were derived, and the oxygen self-diffusion coefficients were evaluated using these. As a result, good agreement was found between the experimental data and the oxygen self-diffusion coefficients calculated using the defect migration energies.
 O)
O) ]
] with nitrate ions by using density functional theory calculation
with nitrate ions by using density functional theory calculationKato, Akane*; Kaneko, Masashi; Nakashima, Satoru*
RSC Advances (Internet), 10(41), p.24434 - 24443, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:28.34(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Complexation reactions of ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes in HNO solution were investigated by density functional theory (DFT) calculations in order to predict the stability of Ru species in high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) solution. Equilibrium structure of [Ru(NO)(NO
solution were investigated by density functional theory (DFT) calculations in order to predict the stability of Ru species in high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) solution. Equilibrium structure of [Ru(NO)(NO )
) (H
(H O)
O) ] obtained by DFT calculations reproduced the experimental Ru-ligands bond lengths and IR frequencies reported previously. Comparison of the Gibbs energies among the geometrical isomers revealed that the complexation reactions of the ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes with NO
] obtained by DFT calculations reproduced the experimental Ru-ligands bond lengths and IR frequencies reported previously. Comparison of the Gibbs energies among the geometrical isomers revealed that the complexation reactions of the ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes with NO
 proceed via the NO
proceed via the NO
 coordination to the equatorial plane toward the Ru-NO axis. We also estimated Gibbs energy differences on the stepwise complexation reactions to succeed in reproducing the fraction of Ru-NO species in 6 M HNO
coordination to the equatorial plane toward the Ru-NO axis. We also estimated Gibbs energy differences on the stepwise complexation reactions to succeed in reproducing the fraction of Ru-NO species in 6 M HNO solution, such as in HLLW, by considering the association energy between the Ru-NO species and the substituting ligands. Electron density analyses of the complexes indicated that the strength of the Ru-ligands coordination bonds depends on the stability of the Ru species and the Ru complex without NO
solution, such as in HLLW, by considering the association energy between the Ru-NO species and the substituting ligands. Electron density analyses of the complexes indicated that the strength of the Ru-ligands coordination bonds depends on the stability of the Ru species and the Ru complex without NO
 at the axial position is more stable than that wit NO
at the axial position is more stable than that wit NO
 , which might attribute to the difference in the trans influence between H
, which might attribute to the difference in the trans influence between H O and NO
O and NO
 . Finally, we demonstrated the complexation kinetics in the reactions
. Finally, we demonstrated the complexation kinetics in the reactions 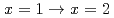 . The present study is expected to enable us to model the precise complexation reactions of platinum-group metals in HNO
. The present study is expected to enable us to model the precise complexation reactions of platinum-group metals in HNO solution.
solution.

Watanabe, Masashi; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato
2018 GIF Symposium Proceedings (Internet), p.315 - 320, 2020/05
Recently, a research group studying at Plutonium Fuel Development Facility (PFDF) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency has systematically measured vast amounts of physical properties in the non-stoichiometric (U, Pu)O . Lattice parameter, elastic modulus, thermal expansion, oxygen potential, oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient and thermal conductivity were successfully measured as function of Pu content, O/M ratio and temperature, and the effects of Pu content and O/M ratio on their physical properties were evaluated. In this work, those experimental data are reviewed, and latest experimental data set on the non-stoichiometric (U, Pu)O
. Lattice parameter, elastic modulus, thermal expansion, oxygen potential, oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient and thermal conductivity were successfully measured as function of Pu content, O/M ratio and temperature, and the effects of Pu content and O/M ratio on their physical properties were evaluated. In this work, those experimental data are reviewed, and latest experimental data set on the non-stoichiometric (U, Pu)O are presented. The data set would be available in development of a fuel performance code.
are presented. The data set would be available in development of a fuel performance code.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.99(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
 Ru M
Ru M ssbauer parameters of ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes
ssbauer parameters of ruthenium-nitrosyl complexesKaneko, Masashi; Kato, Akane*; Nakashima, Satoru*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(20), p.14024 - 14033, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:56.50(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We applied density functional theory calculations to ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes, which are known to exist in high-level radioactive waste, to give a theoretical correlation between  Ru M
Ru M ssbauer spectroscopic parameters (
ssbauer spectroscopic parameters ( and
and 
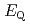 ) and ligand field strength (
) and ligand field strength (
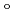 ) for the first time. The structures of the series of complexes, [Ru(NO)L
) for the first time. The structures of the series of complexes, [Ru(NO)L ] (L = Br
] (L = Br , Cl
, Cl , NH
, NH , CN
, CN ), were modeled based on the corresponding single-crystal X-ray coordinates. The comparisons of the geometries and total energies between the different spin states suggested that the singlet spin state of [Ru(II)(NO
), were modeled based on the corresponding single-crystal X-ray coordinates. The comparisons of the geometries and total energies between the different spin states suggested that the singlet spin state of [Ru(II)(NO )L
)L ] complexes were the most stable. The calculated results of both the
] complexes were the most stable. The calculated results of both the  and
and 
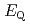 values reproduced the experimental results by reported previously and increased in the order of L = Br
values reproduced the experimental results by reported previously and increased in the order of L = Br , Cl
, Cl , NH
, NH , CN
, CN . Finally, we estimated the ligand field strength (
. Finally, we estimated the ligand field strength (
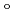 ) based on molecular orbitals, assuming C
) based on molecular orbitals, assuming C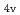 symmetry and showed the increase of
symmetry and showed the increase of 
 values in that order, being consistent with well-known spectrochemical series of ligands. The increase attributes to the strengthening of the abilities of
values in that order, being consistent with well-known spectrochemical series of ligands. The increase attributes to the strengthening of the abilities of  -donor and
-donor and  -acceptor of the L-ligands to the Ru atom, resulting in the increase of the
-acceptor of the L-ligands to the Ru atom, resulting in the increase of the  values.
values.
Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Watanabe, Masashi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 118, p.1624 - 1626, 2018/06
This study suggested the time development of oxygen-to-metal ratio (O/M) redistribution model with oxygen-related properties in MOX. Irradiation simulation including the suggested O/M redistribution and pore migration with vaporization-condensation model which bares density redistribution was demonstrated. The simulation results showed that O/M redistribution proceeded at lower temperature than density redistribution, which indicated that oxygen diffusion got influential at lower temperature than vaporization-condensation of MOX. Another find was that O/M redistribution was very slow at the surface because temperature kept low. However, near the surface (inside from the surface) where the temperature exceeded 1000 K, O/M redistribution was rather recognizable with oxygen flown from inner region to the near-surface. The results will be evaluated by comparison with post-irradiation examination data.

Kato, Masato; Nakamura, Hiroki; Watanabe, Masashi; Matsumoto, Taku; Machida, Masahiko
Defect and Diffusion Forum, 375, p.57 - 70, 2017/05
The basic properties of PuO were reviewed, and the equilibrium defects in PuO
were reviewed, and the equilibrium defects in PuO were evaluated from the experimental data of the oxygen potential and electrical conductivity as well as the Ab-initio calculation results. Consistency among various properties was confirmed, and the mechanistic models for thermal property representations were derived.
were evaluated from the experimental data of the oxygen potential and electrical conductivity as well as the Ab-initio calculation results. Consistency among various properties was confirmed, and the mechanistic models for thermal property representations were derived.

Watanabe, Masashi; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Kato, Masato
Defect and Diffusion Forum, 375, p.84 - 90, 2017/05
The oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient in (U, Pu)O was determined by thermo-gravimetry as functions of the Pu content, oxygen-to-metal ratio and temperature. The surface reaction was considered in the diffusion coefficient determination. The activation energy for the chemical diffusion coefficient was 60 kJ/mol and 65 kJ/mol, respectively, in (U
was determined by thermo-gravimetry as functions of the Pu content, oxygen-to-metal ratio and temperature. The surface reaction was considered in the diffusion coefficient determination. The activation energy for the chemical diffusion coefficient was 60 kJ/mol and 65 kJ/mol, respectively, in (U Pu
Pu )O
)O and (U
and (U Pu
Pu )O
)O .
.