Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Am
Am O
O at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K
at 1473, 1573, and 1673 KWatanabe, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Vauchy, R.; Kato, Masato; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Seki, Takayuki*; Hino, Tetsushi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 599, p.155232_1 - 155232_5, 2024/10
Oxygen potential data of U Am
Am O
O were measured at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K by thermogravimetry. In U
were measured at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K by thermogravimetry. In U An
An O
O , where An stands for Pu or Am, and for a given value of y and Oxygen/Metal ratio, the oxygen potential of U
, where An stands for Pu or Am, and for a given value of y and Oxygen/Metal ratio, the oxygen potential of U Am
Am O
O is higher than that of U
is higher than that of U Pu
Pu O
O . The valence of cations in the hypostoichiometric region is similar to that of Nd-doped UO
. The valence of cations in the hypostoichiometric region is similar to that of Nd-doped UO . At the stoichiometric composition, it is estimated to be Am
. At the stoichiometric composition, it is estimated to be Am , U
, U , and U
, and U (for charge compensation of Am
(for charge compensation of Am ). The experimental data were analyzed using a defect chemistry model, and a relationship connecting the oxygen-to-metal ratio, the temperature, and the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure was proposed.
). The experimental data were analyzed using a defect chemistry model, and a relationship connecting the oxygen-to-metal ratio, the temperature, and the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure was proposed.
 Pu
Pu )O
)O (x = 0, 0.18, 0.45, and 1) and analysis of heat capacity
(x = 0, 0.18, 0.45, and 1) and analysis of heat capacityHirooka, Shun; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Matsumoto, Taku; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Kato, Masato; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 598, p.155188_1 - 155188_9, 2024/09
no abstracts in English
 compounds
compoundsFrazer, D.*; Saleh, T. A.*; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; McClellan, K.*; White, J. T.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 423, p.113136_1 - 113136_7, 2024/07
Nanoindentation based techniques can be employed on minute volumes of material to measure mechanical properties, including Young's modulus, hardness, and creep stress exponents. In this study, (U,Ce)O solid solutions samples are used to develop elevated temperature nanoindentation and nanoindentation creep testing methods for use on mixed oxide fuels. Nanoindentation testing was performed on 3 separate (Ux-1,Cex)O
solid solutions samples are used to develop elevated temperature nanoindentation and nanoindentation creep testing methods for use on mixed oxide fuels. Nanoindentation testing was performed on 3 separate (Ux-1,Cex)O compounds ranging from x equals 0.1 to 0.3 at up to 800
compounds ranging from x equals 0.1 to 0.3 at up to 800  C: their Young's modulus, hardness, and creep stress exponents were evaluated. The Young's modulus decreases in the expected linear manner while the hardness decreases in the expected exponential manner. The nanoindentation creep experiments at 800
C: their Young's modulus, hardness, and creep stress exponents were evaluated. The Young's modulus decreases in the expected linear manner while the hardness decreases in the expected exponential manner. The nanoindentation creep experiments at 800  C give stress exponent values, n=4.7-6.9, that suggests dislocation motion as the deformation mechanism.
C give stress exponent values, n=4.7-6.9, that suggests dislocation motion as the deformation mechanism.
Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Ceramics)Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Hibino, Kinya*; Kawata, Kazumasa*; Onishi, Munehiro*; Takita, Masato*; Munakata, Kazuoki*; Kato, Chihiro*; Shimoda, Susumu*; Shi, Q.*; Wang, S.*; et al.
Progress of Earth and Planetary Science (Internet), 11, p.26_1 - 26_14, 2024/05
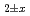 mixed oxides
mixed oxidesVauchy, R.; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154786_1 - 154786_13, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154799_1 - 154799_20, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal conductivities of near-stoichiometric (U,Pu,Am)O doped with Nd
doped with Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O , which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT)
, which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT) . The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C
. The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C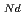 and C
and C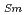 , respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70
, respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70  10
10 + 0.93C
+ 0.93C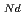 + 1.20C
+ 1.20C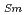 , B(m/W)=2.39
, B(m/W)=2.39  10
10 .
.
Takasaki, Koji; Yasumune, Takashi; Yamaguchi, Yukako; Hashimoto, Makoto; Maeda, Koji; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1437 - 1446, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The aerodynamic radioactive median diameter (AMAD) is necessary information to assess the internal exposure. On June 6, 2017, at a plutonium handling facility in Oarai site of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), during the inspection work of a storage container that contains nuclear fuel materials, accidental contamination occurred and five workers inhaled radioactive materials including plutonium. Some smear papers and an air sampling filter were measured with the imaging plate, and we conservatively estimated minimum AMADs for two cases, plutonium nitrate and plutonium dioxide. As a result of AMAD estimation, even excluding a giant particle of a smear sample, the minimum AMADs of plutonium nitrate from smear papers were 4.3 - 11.3  m and those of plutonium dioxide were 5.6 - 14.1
m and those of plutonium dioxide were 5.6 - 14.1  m. Also, the minimum AMAD of plutonium nitrate from an air sampling filter was 3.0
m. Also, the minimum AMAD of plutonium nitrate from an air sampling filter was 3.0  m and that of plutonium dioxide was 3.9
m and that of plutonium dioxide was 3.9  m.
m.
Hirooka, Shun; Horii, Yuta; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Vauchy, R.; Hayashizaki, Kohei; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1313 - 1323, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:92.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Additive MOX pellets are fabricated by a conventional dry powder metallurgy method. Nd O
O and Sm
and Sm O
O are chosen as the additive materials to simulate the corresponding soluble fission products dispersed in MOX. Shrinkage curves of the MOX pellets are obtained by dilatometry, which reveal that the sintering temperature is shifted toward a value higher than that of the respective regular MOX. The additives, however, promote grain growth and densification, which can be explained by the effect of oxidized uranium cations covering to a pentavalent state. Ceramography reveals large agglomerates after sintering, and Electron Probe Micro-Analysis confirms that inhomogeneous elemental distribution, whereas XRD reveals a single face-centered cubic phase. Finally, by grinding and re-sintering the specimens, the cation distribution homogeneity is significantly improved, which can simulate spent nuclear fuels with soluble fission products.
are chosen as the additive materials to simulate the corresponding soluble fission products dispersed in MOX. Shrinkage curves of the MOX pellets are obtained by dilatometry, which reveal that the sintering temperature is shifted toward a value higher than that of the respective regular MOX. The additives, however, promote grain growth and densification, which can be explained by the effect of oxidized uranium cations covering to a pentavalent state. Ceramography reveals large agglomerates after sintering, and Electron Probe Micro-Analysis confirms that inhomogeneous elemental distribution, whereas XRD reveals a single face-centered cubic phase. Finally, by grinding and re-sintering the specimens, the cation distribution homogeneity is significantly improved, which can simulate spent nuclear fuels with soluble fission products.
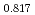 Pu
Pu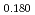 Am
Am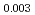 O
O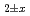 uranium-plutonium-americium mixed oxides at 1573, 1773, and 1873 K
uranium-plutonium-americium mixed oxides at 1573, 1773, and 1873 KVauchy, R.; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 580, p.154416_1 - 154416_11, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:96.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kato, Masato; Nakamichi, Shinya; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Ishii, Katsunori
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(2), p.51 - 58, 2023/04
Uranium and Plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) pellets used as fast reactor fuels have been produced from several raw materials by mechanical blending method through processes of ball milling, additive blending, granulation, pressing, sintering and so on. It is essential to control the pellet density which is one of the important fuel specifications, but it is difficult to understand relationships among many parameters in the production. Database for MOX production was prepared from production results in Japan, and input data of eighteen types were chosen from production process and made a data set. Machine learning model to predict sintered density of MOX pellet was derived by gradient boosting regressor, and represented the measured sintered density with coefficient of determination of R =0.996
=0.996
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.2217_1 - 2217_8, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:89.86(Multidisciplinary Sciences)
Watanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 1, p.1082324_1 - 1082324_9, 2023/01
Since the oxygen potential and the oxygen coefficient of UO have a significant impact on fuel performance, many experimental data have been obtained. However, experimental data of the oxygen potential and the oxygen diffusion coefficient in the high temperature region above 1673 K are very limited. In the present study, we aimed to obtain these data and analyze them by defect chemistry. The oxygen potentials and the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient of UO
have a significant impact on fuel performance, many experimental data have been obtained. However, experimental data of the oxygen potential and the oxygen diffusion coefficient in the high temperature region above 1673 K are very limited. In the present study, we aimed to obtain these data and analyze them by defect chemistry. The oxygen potentials and the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient of UO were measured by the gas equilibrium method in the near stoichiometric region at temperatures ranging from 1673 to 1873 K. A data set of oxygen potentials was made together with literature data and analyzed by defect chemistry. The oxygen potential of UO
were measured by the gas equilibrium method in the near stoichiometric region at temperatures ranging from 1673 to 1873 K. A data set of oxygen potentials was made together with literature data and analyzed by defect chemistry. The oxygen potential of UO was determined as a function of O/U ratio and temperature, and an equation representing the relationship was derived. The oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient values obtained in this study were reasonably close to the literature values. The oxygen partial pressure dependence of the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficients was predicted from the evaluated results of the oxygen potential data, but no clear dependence was observed.
was determined as a function of O/U ratio and temperature, and an equation representing the relationship was derived. The oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient values obtained in this study were reasonably close to the literature values. The oxygen partial pressure dependence of the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficients was predicted from the evaluated results of the oxygen potential data, but no clear dependence was observed.
 , ThO
, ThO , UO
, UO , PuO
, PuO , and (U, Pu)O
, and (U, Pu)O
Kato, Masato; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 1, p.1081473_1 - 1081473_10, 2023/01
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Matsumoto, Taku; Kato, Masato
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 1, p.1060218_1 - 1060218_18, 2022/12
Kato, Masato; Machida, Masahiko; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kobayashi, Keita; Ozawa, Takayuki; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; et al.
Materials Science and Fuel Technologies of Uranium and Plutonium mixed Oxide, 171 Pages, 2022/10
Innovative and advanced nuclear reactors using plutonium fuel has been developed in each country. In order to develop a new nuclear fuel, irradiation tests are indispensable, and it is necessary to demonstrate the performance and safety of nuclear fuels. If we can develop a technology that accurately simulates irradiation behavior as a technology that complements the irradiation test, the cost, time, and labor involved in nuclear fuel research and development will be greatly reduced. And safety and reliability can be significantly improved through simulation of nuclear fuel irradiation behavior. In order to evaluate the performance of nuclear fuel, it is necessary to know the physical and chemical properties of the fuel at high temperatures. And it is indispensable to develop a behavior model that describes various phenomena that occur during irradiation. In previous research and development, empirical methods with fitting parameters have been used in many parts of model development. However, empirical techniques can give very different results in areas where there is no data. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to construct a scientific descriptive model that can extrapolate the basic characteristics of fuel to the composition and temperature, and to develop an irradiation behavior analysis code to which the model is applied.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:81.82(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Kato, Atsushi; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Ando, Masato; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Murakami, Hisatomo*; Oyama, Kazuhiro*; Kaneko, Fumiaki*; Higurashi, Koichi*; Chanteclair, F.*; Chenaud, M.-S.*; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 8, p.11_1 - 11_10, 2022/06
This paper provides an overview of plant system studies to establish a common technical view for Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor concept between France and Japan based on ASTRID600 and the new concept with downsized output called ASTRID150. One of important issues on a reactor structure design is to enhance seismic resistance to be tolerable against strong earthquake such that postulated in Japan. A concept of High Frequency Design is shared, and the design options related to HFD have been examined and design recommendations are established. In addition, this paper include results of studies for a steam generator, a decay heat removal system, a fuel handling system and a containment vessel.
 GeP
GeP S
S by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurements
by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurementsHori, Satoshi*; Kanno, Ryoji*; Kwon, O.*; Kato, Yuki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Matsuura, Masato*; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Kawakita, Yukinobu
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(22), p.9518 - 9527, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:61.59(Chemistry, Physical)