Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Keisuke; Nakagawa, Takuya; Shimojo, Hiroto; Kijima, Jun; Miura, Daiya; Onose, Yoshihiko*; Namba, Koji*; Uchida, Hiroaki*; Sakamoto, Kazuhiko*; Ono, Chika*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-019, 211 Pages, 2025/02
The uranium enrichment facilities at the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) were constructed sequentially to develop uranium enrichment technology with centrifugal separation method. The developed technologies were transferred to Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited until 2001. And the original purpose has been achieved. Wastewater Treatment Facility, one of the uranium enrichment facilities, was constructed in 1976 to treat radioactive liquid waste generated at the facilities, and it finished the role in 2008. In accordance with the Medium/Long-Term Management Plan of JAEA Facilities, interior equipment installed in this facility had been dismantled and removed since November 2021 to August 2023. This report summarizes the findings obtained through the work related to the contamination inspection methods cancellation the controlled area of Wastewater Treatment Facility from September 2023 to March 2024.
Sakaba, Nariaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Hara, Teruo; Kato, Ryoma; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 7(3), p.242 - 256, 2008/09
Nuclear hydrogen production is necessary in an anticipated hydrogen society that demands massive quantity of hydrogen without economic disadvantage. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has launched the conceptual design study of a hydrogen production system with a near-term plan to connect it to Japan's first high-temperature gas-cooled reactor HTTR. The candidate hydrogen production system is based on the thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulphur (IS) process. The heat of 10 MW that approximately 900 C, which can be provided by the secondary helium from the intermediate heat exchanger of the HTTR, is the energy input to the hydrogen production system. The paper describes the recent progresses made in the conceptual design of advanced process heat exchangers of the HTTR-IS hydrogen production system. A new concept of sulphuric acid decomposer is proposed that integrates three separate functions of sulphuric acid decomposer, sulphur trioxide decomposer and process heat exchanger in the previous design. A new mixer-settler type of Bunsen reactor is also designed that integrates three separate functions of Bunsen reactor, phase separator, and pump in the previous design. The new concepts are expected to result in improved economics through construction and operation cost reductions because the number of process equipment and complicated connections between the equipment has been substantially reduced.
C, which can be provided by the secondary helium from the intermediate heat exchanger of the HTTR, is the energy input to the hydrogen production system. The paper describes the recent progresses made in the conceptual design of advanced process heat exchangers of the HTTR-IS hydrogen production system. A new concept of sulphuric acid decomposer is proposed that integrates three separate functions of sulphuric acid decomposer, sulphur trioxide decomposer and process heat exchanger in the previous design. A new mixer-settler type of Bunsen reactor is also designed that integrates three separate functions of Bunsen reactor, phase separator, and pump in the previous design. The new concepts are expected to result in improved economics through construction and operation cost reductions because the number of process equipment and complicated connections between the equipment has been substantially reduced.
Sakaba, Nariaki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Hara, Teruo; Kato, Ryoma; Ohashi, Kazutaka; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Research 2007-058, 31 Pages, 2007/08
Since hydrogen produced by nuclear should be competitiveness economically compared by other method in a hydrogen society, it is important to built hydrogen production system to be coupled with the reactor as a conventional chemical plant. Japan Atomic Energy Agency started the safety study to establish a new safety philosophy with safety requirements and with considering non-nuclear grade hydrogen production system for the nuclear coupling system. Also, structural concepts with integrating functions for the Bunsen reactor and sulphuric acid decomposer were proposed to reduce construction cost of the IS process hydrogen production system. In addition, HI decomposer which enabled the process condition to be eased and could adopt conventional materials and technologies was studied. Moreover, basic approval of the HTTR-IS system in which the hydrogen production rate of 1,000 Nm /h by using the supplied heat of 10 MW from the intermediate heat exchanger of the HTTR was confirmed. This paper describes the conceptual design of the HTTR-IS hydrogen production system.
/h by using the supplied heat of 10 MW from the intermediate heat exchanger of the HTTR was confirmed. This paper describes the conceptual design of the HTTR-IS hydrogen production system.
Sugai, Hiroyuki; Maeta, Hiroshi*; Matsumoto, Norimasa*; Kato, Teruo; Haruna, Katsuji*; Sataka, Masao; Ono, Fumihisa*
Physica Status Solidi (C), 4(8), p.2963 - 2966, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The synthetic semiconductor diamond is potentially one of the best materials for electronic devices in severe environments like high temperature and radiation. We have studied the electrical transport properties of boron-doped synthetic semiconductor diamond and characterized natural and synthetic single crystal diamonds by measurements of the X-ray integrated scattering intensity, lattice parameter and diffuse scattering. The synthetic diamond were irradiated with 100 MeV carbon-ion at Tandem accelerator in JAEA-Tokai. After the irradiation, measurements of lattice parameters X-ray diffuse scattering were made at room temperature. The lattice parameters increased with ion fluence. The scattering intensity of the irradiated synthetic diamond diffuses asymmetrically to form a streak along the [-1 0 0] direction parallel to the reciprocal lattice vector. The result suggests that interstitial atoms and vacancies aggregate to form dislocation loop on the (100) plane.
Homma, Hiroyuki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Kasahara, Seiji; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Hara, Teruo; Kato, Ryoma; Sakaba, Nariaki
JAEA-Technology 2007-006, 60 Pages, 2007/02
At the present time, we are alarmed by depletion of fossil energy and adverse effect of rapid increase in fossil fuel burning on environment such as climate changes and acid rain, because our lives depend still heavily upon fossil energy. It is thus widely recognized that hydrogen is one of important future energy carriers in which it is used without emission of carbon dioxide greenhouse gas and atmospheric pollutants and that hydrogen demand will increase greatly as fuel cells are developed and applied widely in the near future. To meet massive demand of hydrogen, hydrogen production from water utilizing nuclear, especially by thermochemical water-splitting Iodine-Sulphur (IS) process utilizing heat from High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs), offers one of the most attractive zero-emission energy strategies and the only one practical on a substantial scale. However, to establish a technology based for the HTGR hydrogen production by the IS process, we should close several technology gaps through R&D with the High-Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), which is the only Japanese HTGR built and operated at the Oarai Research & Development Centre of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). We have launched design studies of the IS process hydrogen production system coupled with the HTTR (HTTR-IS system) to demonstrate HTGR hydrogen production. In designing the HTTR-IS system, it is necessary to consider preventive and breakdown maintenance against accidents occurred in the IS process as a chemical plant. This report describes case study on chemical plant accidents relating to the IS process plant and shows a proposal of accident protection measures based on above case study, which is necessary for flow-sheet design of the HTTR-IS System.
Sugai, Hiroyuki; Matsunami, Noriaki*; Fukuoka, Osamu*; Sataka, Masao; Kato, Teruo; Okayasu, Satoru; Shimura, Tetsuo*; Tazawa, Masato*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 250(1-2), p.291 - 294, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:69.07(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the effects on electrical properties of Al-doped ZnO (AZO) semiconductor films induced by high-energy heavy ion. The AZO films with c-axis on SiO glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400
glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400  C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3
C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3  m. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5
m. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5 10
10 to 8
to 8 10
10 S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4
S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4 10
10 /cm
/cm , as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3
, as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3 10
10 /cm
/cm (7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4
(7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4 10
10 /cm
/cm is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
Maeta, Hiroshi*; Matsumoto, Norimasa; Kato, Teruo; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Otsuka, Hideo*; Sataka, Masao
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 232(1-4), p.312 - 316, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.20(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Maeta, Hiroshi; Yamakawa, Koiji*; ; Haruna, K.*; Kato, Teruo; Ono, Fumihisa*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 97, p.491 - 494, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Kato, Teruo; Maeta, Hiroshi
Teion Kogaku, 30(3), p.143 - 149, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Kato, Teruo
Teion Kogaku, 30(11), p.510 - 518, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu O
O
; Okayasu, Satoru; Kato, Teruo
Physics and Materials Science of High Temperature Superconductors,II, p.595 - 608, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
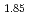 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO single crystal superconductor by X-ray diffraction
single crystal superconductor by X-ray diffractionMaeta, Hiroshi; Kato, Teruo; Ono, Fumihisa*; Haruna, K.*; ;
Physica C, 185-189, p.1383 - 1384, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.33(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 O, and doped with Ag ions
O, and doped with Ag ionsKato, Teruo; ; Maeta, Hiroshi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.169, p.337 - 340, 1990/00
None
 Ba
Ba CCu
CCu O
O superconductors
superconductorsWatanabe, Mitsuo; Kato, Teruo; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Maeta, Hiroshi; Shiraishi, Kensuke; ; Iwase, Akihiro; Iwata, Tadao
Advances in Superconductivity, p.469 - 474, 1989/00
no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu O
O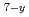 irradiated by
irradiated by  -rays and 14MeV neutrons
-rays and 14MeV neutronsKato, Teruo; Watanabe, Mitsuo; ; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Iwata, Tadao; Ikeda, Yujiro; Maekawa, Hiroshi; Nakamura, Tomoo
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 27(11), p.L2097 - L2099, 1988/11
no abstracts in English
 Na
Na CuO
CuO and LaBaCaCu
and LaBaCaCu O
O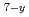
Kato, Teruo; Watanabe, Mitsuo; Maeta, Hiroshi; Naramoto, Hiroshi; ; Iwata, Tadao
Teion Kogaku, 23(5), p.302 - 306, 1988/05
no abstracts in English
 superconductor in a 2.7 GHz RF cavity
superconductor in a 2.7 GHz RF cavityOkubo, Makio; Minehara, Eisuke; ; Kawarasaki, Yuki; Katano, Susumu; Takamura, Saburo; Kato, Teruo; Watanabe, Mitsuo; Naramoto, Hiroshi;
Proceedings of 12th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.42 - 43, 1987/00
no abstracts in English
Kato, Teruo; Watanabe, Mitsuo; Iwase, Akihiro; Iwata, Tadao
Proceedings of 12th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.117 - 119, 1987/00
no abstracts in English
Kato, Junya; Miyauchi, Atsushi; Aoshima, Atsushi; Shiotsuki, Masao; Yamashita, Teruo; Nakajima, Masayoshi; Morikawa, Yo; Miura, Akihiko; Fukui, Toshiki*; Yamasaki, Akito*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kato, Junya; Miura, Akihiko; Yamashita, Teruo; Shiotsuki, Masao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English