Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
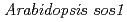 mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt tolerance
mutant in a salt-tolerant accession revealed an importance of salt acclimation ability in plant salt toleranceAriga, Hirotake*; Katori, Taku*; Yoshihara, Ryohei*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Nozawa, Shigeki; Narumi, Issei; Iuchi, Satoshi*; Kobayashi, Masatomo*; Tezuka, Kenji*; Sakata, Yoichi*; et al.
Plant Signaling & Behavior (Internet), 8(7), p.e24779_1 - e24779_5, 2013/07
Based on analysis of the salinity tolerance among 354  accessions, some accessions showed greater salt shock tolerance compared with a reference accession, Col-0 on a typical assay with drastic change in NaCl concentration from 0 mM to 225 mM. On the other hand, several accessions including Zu-0 exhibited marked acquired salt tolerance, which is induced after exposure to moderate salt stress (salt acclimation ability). It is likely that Arabidopsis plants have at least two types of tolerance abilities, salt shock tolerance and salt acclimation. To dissect the salt tolerance mechanisms of the salt tolerant accessions, we isolated a salt-sensitive mutant from ion beam-mutagenized Zu-0 seedlings. The mutant showed severe growth inhibition under salt shock stress due to a single base deletion in SOS1 gene as well-known salt shock tolerance gene, even more salt sensitive than Col-0. Nevertheless, the mutant was able to survive on the salt acclimation with 100 mM NaCl for 7 days followed with 750 mM sorbitol for 20 days (salt acclimation assay) as well as the Zu-0 wild type, whereas Col-0 showed apparent chlorosis under the condition. We propose that a gene for salt acclimation ability is different from a gene for salt shock tolerance and plays an important role in acquisition for marked salt- or osmotic tolerance.
accessions, some accessions showed greater salt shock tolerance compared with a reference accession, Col-0 on a typical assay with drastic change in NaCl concentration from 0 mM to 225 mM. On the other hand, several accessions including Zu-0 exhibited marked acquired salt tolerance, which is induced after exposure to moderate salt stress (salt acclimation ability). It is likely that Arabidopsis plants have at least two types of tolerance abilities, salt shock tolerance and salt acclimation. To dissect the salt tolerance mechanisms of the salt tolerant accessions, we isolated a salt-sensitive mutant from ion beam-mutagenized Zu-0 seedlings. The mutant showed severe growth inhibition under salt shock stress due to a single base deletion in SOS1 gene as well-known salt shock tolerance gene, even more salt sensitive than Col-0. Nevertheless, the mutant was able to survive on the salt acclimation with 100 mM NaCl for 7 days followed with 750 mM sorbitol for 20 days (salt acclimation assay) as well as the Zu-0 wild type, whereas Col-0 showed apparent chlorosis under the condition. We propose that a gene for salt acclimation ability is different from a gene for salt shock tolerance and plays an important role in acquisition for marked salt- or osmotic tolerance.
 113 of the 113th element
113 of the 113th elementMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Yoneda, Akira*; Tanaka, Kengo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(10), p.103201_1 - 103201_4, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:179 Percentile:97.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An isotope of the 113th element,  113, was produced in a nuclear reaction with a
113, was produced in a nuclear reaction with a  Zn beam on a
Zn beam on a  Bi target. We observed six consecutive
Bi target. We observed six consecutive  decays following the implantation of a heavy particle in nearly the same position in the semiconductor detector, in extremely low background condition. The fifth and sixth decays are fully consistent with the sequential decays of
decays following the implantation of a heavy particle in nearly the same position in the semiconductor detector, in extremely low background condition. The fifth and sixth decays are fully consistent with the sequential decays of  Db and
Db and  Lr both in decay energies and decay times. This indicates that the present decay chain consisted of
Lr both in decay energies and decay times. This indicates that the present decay chain consisted of  113,
113, 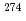 Rg (Z = 111),
Rg (Z = 111), 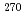 Mt (Z = 109),
Mt (Z = 109),  Bh (Z = 107),
Bh (Z = 107),  Db (Z = 105), and
Db (Z = 105), and  Lr (Z = 103) with firm connections. This result, together with previously reported results from 2004 and 2007, conclusively leads the unambiguous production and identification of the isotope
Lr (Z = 103) with firm connections. This result, together with previously reported results from 2004 and 2007, conclusively leads the unambiguous production and identification of the isotope  113, of the 113th element.
113, of the 113th element.
 Bh and
Bh and  Db produced in the
Db produced in the  Cm +
Cm +  Na reaction
Na reactionMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(6), p.064201_1 - 064201_6, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:77.45(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Decay properties of an isotope  Bh and its daughter nucleus
Bh and its daughter nucleus  Db produced by the
Db produced by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 ) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.
) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
 113
113Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Akiyama, Takahiro*; Goto, Shinichi*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Katori, Kenji*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Hisaaki*; et al.
RIKEN Accelerator Progress Report, Vol.42, P. 15, 2009/00
In 2003-2007, we had performed an experiment to synthesize an element 113 by a  Bi
Bi
 Zn reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN Nishina-Center. In a total of 241 days of net irradiation time experiment, two decay chains were observed and assigned from an isotope
Zn reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN Nishina-Center. In a total of 241 days of net irradiation time experiment, two decay chains were observed and assigned from an isotope  113. The cross section of the
113. The cross section of the  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction was determined to be 31
113 reaction was determined to be 31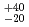 fb at that time. In order to increase the statistics of the decay property, we continued to produce more decay chains. The experiment was carried out from January 7 to March 31, 2008. The experimental conditions were identical to those used in the previous experiment.
fb at that time. In order to increase the statistics of the decay property, we continued to produce more decay chains. The experiment was carried out from January 7 to March 31, 2008. The experimental conditions were identical to those used in the previous experiment.  Zn ion beam of 353 MeV was extracted from RILAC. The net irradiation time was 83 days and the total dose of
Zn ion beam of 353 MeV was extracted from RILAC. The net irradiation time was 83 days and the total dose of  Zn was 2.28
Zn was 2.28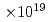 . In the present expriment any candidate of
. In the present expriment any candidate of  113 was not observed. Then combining the results of the present and previous experiments, the production cross section of
113 was not observed. Then combining the results of the present and previous experiments, the production cross section of  113 was determined to be 22
113 was determined to be 22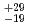 fb.
fb.
 112 by
112 by  Pb +
Pb +  Zn reaction
Zn reactionMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Akiyama, Takahiro*; Goto, Shinichi*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Katori, Kenji*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kudo, Hisaaki*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 76(4), p.043201_1 - 043201_5, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:154 Percentile:95.86(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The production and decay of  112 has been investigated using a gas-filled recoil ion separator in irradiations of
112 has been investigated using a gas-filled recoil ion separator in irradiations of  Pb targets with
Pb targets with  Zn beam at 349.5 MeV. We have observed two
Zn beam at 349.5 MeV. We have observed two  -decay chains that can be assigned to subsequent decays from
-decay chains that can be assigned to subsequent decays from 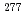 112 produced in the 208 Pb(
112 produced in the 208 Pb( Zn,n) reaction. After emitting four consecutive
Zn,n) reaction. After emitting four consecutive  -particles, the both chains ended by spontaneous fission decays of
-particles, the both chains ended by spontaneous fission decays of  Rf and decay energies and decay times of the both chains obtained in the present work agree well with those reported by a group at Gesellschaft f
Rf and decay energies and decay times of the both chains obtained in the present work agree well with those reported by a group at Gesellschaft f r Schwerionenforschung (GSI), Germany. The present result gives the first clear confirmation of the discovery of
r Schwerionenforschung (GSI), Germany. The present result gives the first clear confirmation of the discovery of 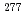 112 and its
112 and its  -decay products
-decay products 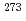 Ds reported previously.
Ds reported previously.
 113
113Morita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Akiyama, Takahiro*; Goto, Shinichi*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Katori, Kenji*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 76(4), p.045001_1 - 045001_2, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:208 Percentile:97.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The production and decay of  113 has been investigated using a gas-filled recoil ion separator in irradiations of
113 has been investigated using a gas-filled recoil ion separator in irradiations of  Bi targets with
Bi targets with  Zn beam at 353 MeV. We have observed one
Zn beam at 353 MeV. We have observed one  -decay chain that can be assigned to subsequent decays from
-decay chain that can be assigned to subsequent decays from  113 produced in the
113 produced in the  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n) reaction. After emitting four consecutive
Zn,n) reaction. After emitting four consecutive  -particles, the both chains ended by spontaneous fission decays of
-particles, the both chains ended by spontaneous fission decays of  Db and decay energies and decay times of the both chains obtained in the present work agree well with those reported by our group in 2004. The present result gives the first clear confirmation of the discovery of
Db and decay energies and decay times of the both chains obtained in the present work agree well with those reported by our group in 2004. The present result gives the first clear confirmation of the discovery of  113 and its
113 and its  -decay products
-decay products 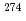 Rg reported previously.
Rg reported previously.
Morita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Akiyama, Takahiro*; Goto, Shinichi*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Kanungo, R.*; Katori, Kenji*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 891, p.3 - 9, 2007/03
A series of experiments studying the productions and their decays of the heaviest elements have been performed by using a gas-filled recoil separator GARIS at RIKEN. Results on the isotope of the 112th element, 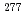 112, and on that of the 113th element,
112, and on that of the 113th element,  113, are reviewed. Two decay chains which are assigned to be ones originating from the isotope
113, are reviewed. Two decay chains which are assigned to be ones originating from the isotope 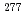 112 were observed in the
112 were observed in the  Pb(
Pb( Zn, n) reaction. The results provide a confirmation of the production and decay of the isotope
Zn, n) reaction. The results provide a confirmation of the production and decay of the isotope 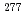 112 reported by a research group at GSI, Germany, produced via the same reaction by using a velocity filter. Two decay chains, both consisted of four consecutive alpha decays followed by a spontaneous fission, were observed also in the reaction
112 reported by a research group at GSI, Germany, produced via the same reaction by using a velocity filter. Two decay chains, both consisted of four consecutive alpha decays followed by a spontaneous fission, were observed also in the reaction  Bi(
Bi( Zn, n). Those are assigned to be the convincing candidate events of the isotope of the 113th element,
Zn, n). Those are assigned to be the convincing candidate events of the isotope of the 113th element,  113, and its daughter nuclei.
113, and its daughter nuclei. 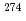 Rg,
Rg, 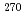 Mt,
Mt,  Bh, and
Bh, and  Db.
Db.
 Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113
113Morita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Akiyama, Takahiro*; Goto, Shinichi*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Kanungo, R.*; Katori, Kenji*; Koura, Hiroyuki; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 73(10), p.2593 - 2596, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:514 Percentile:99.21(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The isotope of the 113th element,  113, and its daughter nuclei,
113, and its daughter nuclei, 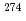 111 and
111 and 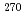 Mt, were obserbed, for the first time, in the
Mt, were obserbed, for the first time, in the  Bi +
Bi +  Zn reaction at a beam energy of 349.1 MeV with a total dose of 1.6
Zn reaction at a beam energy of 349.1 MeV with a total dose of 1.6 10
10 . The production cross section of
. The production cross section of  113 is deduced to be
113 is deduced to be 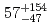 fb (
fb (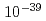 cm
cm ).
).
Inoue, Kazuhiko; Katori, Kenji*
JAERI 1041, 16 Pages, 1962/12
no abstracts in English
 Bh and its daughter nuclei
Bh and its daughter nucleiMorimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hanamuro, Takahiro; Yasue, Kenichi; Shibata, Kenji; Umeda, Koji; Takatori, Ryoichi*
no journal, ,
Petrographical and geochemical approaches were adopted by samples of the Inagawa Granite and Naegi-Agematsu Granite, distributed along upper river basin of Toki River. And gravel from upper layer of these rock bodies were investigated for identification of granitic rock bodies. Petrographic feature of these rock bodies are distinguished by hornblende or muscovite contents. Major element analyses of biotites by EPMA showed the samples from the Naegi-Agematsu Granite were rich in Fe relative to those from the Inagawa Granite. By using this method, the gravel from upper layer of these rock bodies is suggested to be from the Naegi-Agematsu Granite area. Therefore, chemical composition of biotite suggests good indicator for hinterland analysis in this case.
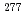 Cn produced in the reaction of
Cn produced in the reaction of  Pb+
Pb+ Zn
ZnSumita, Takayuki*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Katori, Kenji*; Sakai, Ryutaro*; Hasebe, Hiroo*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Yoneda, Akira*; Yoshida, Atsushi*; et al.
no journal, ,
The decay property of 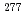 Cn (atomic number,
Cn (atomic number, 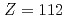 ) produced in the
) produced in the  Pb(
Pb( Zn,
Zn,  ) reaction was studied. The experiment was performed using the gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at the RIKEN liner accelerator facility (RILAC). The
) reaction was studied. The experiment was performed using the gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at the RIKEN liner accelerator facility (RILAC). The  Pb target with about 630
Pb target with about 630  g/cm
g/cm thickness was bombarded with 347.5, 351.5, and 355.5 MeV
thickness was bombarded with 347.5, 351.5, and 355.5 MeV  Zn beam. At the beam energy of 351.5 MeV, we observed one
Zn beam. At the beam energy of 351.5 MeV, we observed one  -decay chain from
-decay chain from 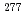 Cn. The
Cn. The  -particle energy of
-particle energy of 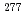 Cn was
Cn was 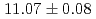 MeV and its lifetime was measured to be 0.370 ms. Including our previous result of the
MeV and its lifetime was measured to be 0.370 ms. Including our previous result of the 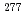 Cn production in 2004, the cross section of the
Cn production in 2004, the cross section of the  Pb(
Pb( Zn,
Zn,  ) reaction is deduced to be
) reaction is deduced to be 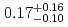 pb.
pb.
 113 produced by the
113 produced by the  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction
113 reactionMorimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We performed the experiment to synthesize an isotope of the element 113 produced by a  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN. Two decay chains were observed, and assigned to those originating from an isotope
113 reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN. Two decay chains were observed, and assigned to those originating from an isotope  113. Both chains were connected into the previously known decays of
113. Both chains were connected into the previously known decays of  Bh and
Bh and  Db via previously unknown decays of
Db via previously unknown decays of  113,
113, 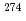 Rg, and
Rg, and 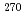 Mt. Although the
Mt. Although the  Bh was known nuclide, a number of atoms reported so far was limited. In order to study more precise decay property of the
Bh was known nuclide, a number of atoms reported so far was limited. In order to study more precise decay property of the  Bh, we performed the direct production of
Bh, we performed the direct production of  Bh by the
Bh by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5n)
Na,5n) Bh reaction. In this experiment, the
Bh reaction. In this experiment, the  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
Hanamuro, Takahiro; Takatori, Ryoichi; Yasue, Kenichi; Shibata, Kenji; Umeda, Koji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Bh and its daughter nuclei
Bh and its daughter nucleiMorimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A nuclide,  Bh, is the great-grand-daughter of
Bh, is the great-grand-daughter of  113 that is produced in the
113 that is produced in the  Bi +
Bi +  Zn reaction. The identification was based on a genetic link to the known daughter nucleus
Zn reaction. The identification was based on a genetic link to the known daughter nucleus  Db by alpha-decays. The main purpose of this work is to provide further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope
Db by alpha-decays. The main purpose of this work is to provide further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope  113. As a present result, a state in
113. As a present result, a state in  Bh, which decays by an alpha emission with the energies ranging from 9.05 to 9.23 MeV, feeds a state in
Bh, which decays by an alpha emission with the energies ranging from 9.05 to 9.23 MeV, feeds a state in  Db, which decays by alpha emission and by SF with a previously known half-life. The result provided a further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope of the 113th element,
Db, which decays by alpha emission and by SF with a previously known half-life. The result provided a further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope of the 113th element,  113, studied by a research group at RIKEN.
113, studied by a research group at RIKEN.