Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyaji, Noriko; Katsumura, Soichiro; Kawakami, Yukio
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-31-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2010/12
A large-scale hot cell laboratory named FMF is located by the experimental fast reactor Joyo in Oarai Research and Development Center (JNC-2 site), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). FMF conducts post irradiation examinations (PIE) of irradiated fuels in Joyo such as assemblies and pins. To the JNC-2 site, in the Integrated Safeguards (IS) approach, which treats FMF and Joyo as one sector, was applied in December, 2010. For this, a new verification system for the material transfer between Joyo and FMF has been developed. The system includes the followings: (1) surveillance system remotely monitoring movements of a declared transport cask, (2) random verifications for the nuclear material contained in the cask by measuring the neutron dose rate. The implementation of the IS incorporating the developed verification system to the JNC-2 site would strengthen effectiveness and efficiency of safeguards.
Katsumura, Soichiro; Seya, Michio; Wakaida, Ikuo
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-30-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2009/11
In next generation fuel fabrication facilities, low decontaminated MOX (Mixed Oxide Fuel) with MA (minor actinide) including  Cm is going to be treated. In case of the low decontaminated MOX with MA, if
Cm is going to be treated. In case of the low decontaminated MOX with MA, if  Cm is included more than 0.01% of
Cm is included more than 0.01% of  Pu, the amount of neutron generation from spontaneous fissions of
Pu, the amount of neutron generation from spontaneous fissions of  Cm exceed that of
Cm exceed that of  Pu. This is because that
Pu. This is because that  Cm produces near 10
Cm produces near 10 times higher than
times higher than  Pu. And also determination of Pu isotopic composition by
Pu. And also determination of Pu isotopic composition by  -ray spectroscopy seems to be less-accurate or impossible, because of high back ground
-ray spectroscopy seems to be less-accurate or impossible, because of high back ground  -rays generated by bremsstrahlung of beta-decay electrons from FPs in the low decontaminated MOX. In this presentation, the future issues of the verification of the low decontaminated MOX with MA are shown, and as one of possible verification approach, application of LIBS (Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) + AIRAS (Ablation Initiated Resonance Absorption Spectroscopy) is explained.
-rays generated by bremsstrahlung of beta-decay electrons from FPs in the low decontaminated MOX. In this presentation, the future issues of the verification of the low decontaminated MOX with MA are shown, and as one of possible verification approach, application of LIBS (Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) + AIRAS (Ablation Initiated Resonance Absorption Spectroscopy) is explained.
Katsumura, Soichiro; Kitabata, Takuya; Irie, Tsutomu; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Hashimoto, Yu; Kato, Keiji*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 99(1), P. 780, 2008/11
Senzaki, Masao; Kuno, Yusuke; Inoue, Naoko; Katsumura, Soichiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 50(6), p.368 - 373, 2008/06
, 50(6), p.368 - 373, 2008/06
The major international collaborative projects for Next Generation Nuclear Energy Systems have been started around 2000. Proliferation resistance is one of the development targets as well as economics, safety, and environment. It is especially important for proliferation resistance to build the international consensus. Therefore, it is essential to establish common understanding based on the mutual understanding across the areas of nuclear technology and nonproliferation, domestically and internationally. This paper introduces the discussions and their backgrounds regarding the study of proliferation resistance evaluation methodologies in the past three decades, and identifies the future challenges for nuclear proliferation resistance studies.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Niki, Hideaki*; Katsumura, Soichiro; Seya, Michio
no journal, ,
Basic study on remote analysis by combination of LIBS and AIRAS were performed. For the impurity measurement, detection linearity to % order, the detection limit of order 100 ppm and the error of about  3% based on statistical fluctuation were obtained by the use of Lanthanide or Uranium oxide sample. For the isotope analysis, by using the laser system specialized for the resonance spectroscopy, spectrum resolution of 800 MHz was performed and
3% based on statistical fluctuation were obtained by the use of Lanthanide or Uranium oxide sample. For the isotope analysis, by using the laser system specialized for the resonance spectroscopy, spectrum resolution of 800 MHz was performed and  U in natural uranium was clearly detected. These results suggest that the combination of LIBS and AIRAS will be one of the alternative techniques applicable for the safeguards analysis of next generation fuels without neutron detection by
U in natural uranium was clearly detected. These results suggest that the combination of LIBS and AIRAS will be one of the alternative techniques applicable for the safeguards analysis of next generation fuels without neutron detection by  He gas. In the next stage, we are going to apply this remote analysis to the measurement of Pu in MOX fuel. In this program, we develop the compact system inside the grove-box and will plan to accomplish the elemental and isotopic analysis of Pu and U within several ten minutes.
He gas. In the next stage, we are going to apply this remote analysis to the measurement of Pu in MOX fuel. In this program, we develop the compact system inside the grove-box and will plan to accomplish the elemental and isotopic analysis of Pu and U within several ten minutes.
Katsumura, Soichiro; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Hashimoto, Yu; Inoue, Naoko; Kitabata, Takuya; Irie, Tsutomu; Rochau, G.*; Cleary, V.*; Mcfadden, K.*; Mendez, C.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -rays
-raysHayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Katsumura, Soichiro; Seya, Michio; Harada, Hideo; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Ogaki, Hideaki
no journal, ,
We propose a non-destructive assay method for measuring an isotope and a chemical compound hidden by heavy shields such as iron plates of a thickness of several centimeters. We use a nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) measurement technique with an energy tunable laser Compton scattering (LCS)  -ray source. Isotope mapping of a block of
-ray source. Isotope mapping of a block of  Pb concealed in an iron box of 1.5 cm thickness has been demonstrated. We also demonstrate detection of a chemical compound of melamine, C
Pb concealed in an iron box of 1.5 cm thickness has been demonstrated. We also demonstrate detection of a chemical compound of melamine, C H
H N
N , shielded by 15-mm-thick iron and 4-mm-thick lead plates. We measure NRF
, shielded by 15-mm-thick iron and 4-mm-thick lead plates. We measure NRF  -rays of
-rays of  C and
C and  N of the melamine by using the LCS
N of the melamine by using the LCS  -rays of the energies of up to 5.0 MeV. The observed ratio (
-rays of the energies of up to 5.0 MeV. The observed ratio ( C/
C/ N)
N)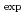 = 0.39
= 0.39  0.12 is consistent with (C/N)
0.12 is consistent with (C/N)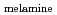 = 0.5.
= 0.5.
Seya, Michio; Kuno, Yusuke; Katsumura, Soichiro; Koyama, Tomozo
no journal, ,
A tentative study on basic factors for evaluating proliferation resistance of next generation reprocessing from a safeguards detection capability point of view based on INPRO-based JAEA methodology was made.
Kuno, Yusuke; Koyama, Tomozo; Seya, Michio; Katsumura, Soichiro; Koma, Yoshikazu; Yamamoto, Tokuhiro
no journal, ,
A study on proliferation resistance assessment of next generation reprocessing by INPRO-based JAEA methodology was made, including Comparison Study on Proliferation Resistance of Principal Reprocessing Technology from Institutional Barrier and Technical Barrier.