Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Miura, Daisuke; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hiroi, Kosuke; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oku, Takayuki; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
Hamon, 34(2), p.50 - 53, 2024/05
Spin-contrast-variation (SCV) small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) enabled us to determine structure of nano-ice crystals that were generated in rapidly frozen sugar solution. In the frozen glucose solution, we found that the nano-ice crystals formed a planar structure with a radius larger than several tens of nanometers and a thickness of 2-3 nm, which was close to the critical nucleation size of ice crystals in supercooled water. This result suggests that the glucose molecules were preferentially bound to a specific face of nano-ice crystals, and then blocked the crystal growth perpendicular to that face.
Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Miura, Daisuke; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hiroi, Kosuke; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oku, Takayuki; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(34), p.7638 - 7643, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The structure of nano-ice crystals in rapidly frozen glucose solution was elucidated by using spin-contrast-variation small-angle neutron scattering, which distinguishes the nano-ice crystal signal from the frozen amorphous solution signal by the polarization-dependent neutron scattering. The analysis revealed that the nano-ice crystals form a planar structure with a diameter exceeding tens of nanometers and a thickness of 1 nm, which is close to the critical nucleation size. This result suggests that the glucose molecules are preferentially bound to a specific face of nano-ice crystals, and then block the crystal growth perpendicular to that face.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kubo, Shinji; Yokota, Hiroki*; Kawai, Daisuke*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/05
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processes (IS process) is one of candidates for the large-scale production of hydrogen using heat from solar power. Severe corrosive environment which is thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid exists in the IS process. A hybrid material with the corrosion-resistance and the ductility was made by a plasma spraying and laser treatment. The specimen had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid. This was attributed to the formation of SiO on the surface. A corrosion test of the container was performed in 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid until 500 hours to evaluate the corrosion characteristic of the container. No peeling was observed on the inner surface of the container after the corrosion test. The container had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid.
on the surface. A corrosion test of the container was performed in 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid until 500 hours to evaluate the corrosion characteristic of the container. No peeling was observed on the inner surface of the container after the corrosion test. The container had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kawai, Daisuke*; Yokota, Hiroki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Kubo, Shinji
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2020/08
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processes (IS process) is one of candidates for the large-scale production of hydrogen using heat from solar power. Severe corrosive environment which is thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid exists in the IS process. A hybrid material with the corrosion-resistance and the ductility was made by a plasma spraying and laser treatment. The specimen had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid. This was attributed to the formation of SiO on the surface. The container using the hybrid material was experimentally made. The pre-oxidized container using hybrid technique was prepared for the corrosion test in boiling sulfuric acid to evaluate the corrosion characteristics of the container. There was no detaching of the surface with the weld part and the R processing. We proposed the calculation method of corrosion rate from the ions dissolved in the sulfuric acid solution after the corrosion test.
on the surface. The container using the hybrid material was experimentally made. The pre-oxidized container using hybrid technique was prepared for the corrosion test in boiling sulfuric acid to evaluate the corrosion characteristics of the container. There was no detaching of the surface with the weld part and the R processing. We proposed the calculation method of corrosion rate from the ions dissolved in the sulfuric acid solution after the corrosion test.
Ioka, Ikuo; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Kawai, Daisuke*; Yokota, Hiroki*; Kubo, Shinji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00377_1 - 19-00377_11, 2020/06
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processes (IS process) is one of candidates for the large-scale production of hydrogen with high cost performance. Severe corrosive environment which is thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid exists in the IS process. A hybrid material with the corrosion-resistance and the ductility was made by a plasma spraying and laser treatment. The specimen had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid. This was attributed to the formation of SiO on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment. It was confirmed that the construction of the container with high corrosion resistance in sulfuric acid was possible in the hybrid technique.
on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment. It was confirmed that the construction of the container with high corrosion resistance in sulfuric acid was possible in the hybrid technique.
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C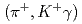 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 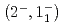 was measured to be
was measured to be 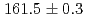 (stat)
(stat)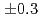 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 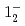 and
and 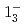 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 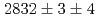 , keV and
, keV and 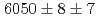 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.
 N-nitrate in transgenic rice plant over-expressing nitrate transporter
N-nitrate in transgenic rice plant over-expressing nitrate transporterSato, Daisuke*; Mori, Mari*; Katayama, Hisato*; Kitamura, Harushige*; Kawai, Toshihiko*; Fujimaki, Shu; Suzui, Nobuo; Kawachi, Naoki; Ishii, Satomi; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 128, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Miura, Daisuke*; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hiroi, Kosuke; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oku, Takayuki; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The structure of nano-ice crystals in rapidly frozen sugar solution was elucidated by using spin-contrast-variation small-angle neutron scattering, which distinguishes the nano-ice crystal signal from the frozen amorphous solution signal by the polarization-dependent neutron scattering. The analysis revealed that the nano-ice crystals form a planar structure with a diameter exceeding tens of nanometers and a thickness of 1 nm, which is close to the critical nucleation size. This result suggests that the sugar molecules are preferentially bound to a specific face of nano-ice crystals, and then block the crystal growth perpendicular to that face.
Makino, Hitoshi; Asano, Hidekazu*; Usami, Tsuyoshi*; Tsukada, Takeshi*; Ikeda, Takao*; Kawai, Kota*; Watanabe, Daisuke*
no journal, ,
This presentation shows current status of discussion on "An assessment for MOX plu-thermal cycle" which is a challenge as part of an attempt to assess total performance of advanced nuclear fuel cycle in the Research Committee on Disposal of Radioactive Waste and Partitioning-Transmutation Technology.
Makino, Hitoshi; Asano, Hidekazu*; Usami, Tsuyoshi*; Kanehira, Norio*; Ikeda, Takao*; Kawai, Kota*; Watanabe, Daisuke*
no journal, ,
This presentation shows current status of discussion on "A trial assessment for MOX plu-thermal cycle" which is a challenge as part of an attempt to assess total performance of advanced nuclear fuel cycle in the Research Committee on Disposal of Radioactive Waste and Partitioning-Transmutation Technology.