Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
井上 倫太郎*; 小田 隆; 中川 洋; 富永 大輝*; 池上 貴久*; 小沼 剛*; 岩瀬 裕希*; 川北 至信; 佐藤 衛*; 杉山 正明*
Biophysical Journal, 124(3), p.540 - 548, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Biophysics)Intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) show structural changes stimulated by changes in external conditions. This study aims to reveal the temperature dependence of the structure and the dynamics of the intrinsically disordered region of the helicase-associated endonuclease for fork-structured DNA, one of the typical IDPs, using an integrative approach. Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and circular dichroism (CD) studies revealed that the radius of gyration and ellipticity at 222 nm remained constant up to 313-323 K, followed by a decline above this temperature range. NMR studies revealed the absence of a promotion of the  -helix. As a result, SAXS, CD, and NMR data strongly suggest that these temperature-dependent structural changes were primarily due to a reduction in the content of the polyproline II (PPII) helix. Moreover, quasielastic neutron scattering studies revealed a slight change in the activation energy in a similar temperature range. Considering the concept of glass transition, it is posited that dynamical cooperativity between the PPII helix and water may play a significant role in these structural changes. The findings suggest that internal dynamics are crucial for regulating the structure of IDPs, highlighting the importance of considering dynamical cooperativity in future studies of protein behavior under varying temperature conditions.
-helix. As a result, SAXS, CD, and NMR data strongly suggest that these temperature-dependent structural changes were primarily due to a reduction in the content of the polyproline II (PPII) helix. Moreover, quasielastic neutron scattering studies revealed a slight change in the activation energy in a similar temperature range. Considering the concept of glass transition, it is posited that dynamical cooperativity between the PPII helix and water may play a significant role in these structural changes. The findings suggest that internal dynamics are crucial for regulating the structure of IDPs, highlighting the importance of considering dynamical cooperativity in future studies of protein behavior under varying temperature conditions.
Li, B.*; 川北 至信
革新的冷却技術; メカニズムから素子・材料・システム開発まで, p.19 - 28, 2024/01
専門書として出版を予定している「革新的冷却技術; メカニズムから素子・材料・システム開発まで」の第一章 各種冷却のメカニズム、の第1節として、柔粘性結晶の圧力熱量効果の解説を寄稿した。(1)柔粘性結晶とは?、(2)さまざまな熱量効果と圧力熱量効果、(3)NPGの巨大熱量効果、(4)中性子散乱による圧力熱量効果の検証、(4.1)中性子散乱、(4.2) QENS、(4.3)NPGのQENS測定結果、(5)柔粘性結晶の巨大熱量効果、(5.1)ネオペンタンとその由来物質、(5.2)アダマンタンとその由来物質、(5.3)クロソボランとその由来物質、(5.4)無機柔粘性結晶、(6)圧力熱量効果を固体冷媒として利用した冷却技術
Zhang, Z.*; Gong, W.; 川北 至信; 他9名*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(12), p.125402_1 - 125402_9, 2023/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:20.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)NH SCN exhibits successive phase transitions from monoclinic to orthorhombic, and then to tetragonal. The former phase transition is accompanied by an inverse colossal barocaloric effect and a huge negative thermal expansion. This transition is complicated by the possibly coexisting orientational disorder of NH
SCN exhibits successive phase transitions from monoclinic to orthorhombic, and then to tetragonal. The former phase transition is accompanied by an inverse colossal barocaloric effect and a huge negative thermal expansion. This transition is complicated by the possibly coexisting orientational disorder of NH
 and SCN
and SCN , and the mechanism is still unclear. Here, NH
, and the mechanism is still unclear. Here, NH SCN is investigated using high-resolution neutron powder diffraction, pair distribution function analysis, and Raman scattering. Both the average and local structural analysis indicate that only NH
SCN is investigated using high-resolution neutron powder diffraction, pair distribution function analysis, and Raman scattering. Both the average and local structural analysis indicate that only NH
 is orientationally disordered in the orthorhombic phase and SCN
is orientationally disordered in the orthorhombic phase and SCN becomes subsequently disordered in the tetragonal phase. Both temperature-induced and pressure-induced hardening behaviors of SCN
becomes subsequently disordered in the tetragonal phase. Both temperature-induced and pressure-induced hardening behaviors of SCN related vibrations are observed, which leads to the breakage of hydrogen bonds-linked NH
related vibrations are observed, which leads to the breakage of hydrogen bonds-linked NH
 with SCN
with SCN and further facilitates phase transition. Our findings provide a solid standing point of atomic structures and dynamics, on which the scenario of the phase transition and the associated physical properties is established.
and further facilitates phase transition. Our findings provide a solid standing point of atomic structures and dynamics, on which the scenario of the phase transition and the associated physical properties is established.
Lloveras, P.*; Zhang, Z.*; Zeng, M.*; Barrio, M.*; 川北 至信; Yu, D.*; Lin, S.*; Li, K.*; Moya, X.*; Tamarit, J.-L.*; et al.
Barocaloric Effects in the Solid State; Materials and methods, p.7_1 - 7_30, 2023/10
被引用回数:232 パーセンタイル:99.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)「固体状態における圧力熱量効果」と題する電子ブックの第一章として、様々な柔粘性結晶が紹介されている。柔粘性結晶における圧力熱量反応を決定する方法、その熱力学的な起源、中性子準弾性散乱からの分光学的洞察、柔粘性結晶の応用などが解説されている。
坂口 佳史*; 高田 慎一; 川北 至信; 藤村 由希; 近藤 啓悦
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(41), p.415403_1 - 415403_11, 2023/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)It is well-known that eutectic gold-silicon (Au-Si) alloys exhibit anomalous melting point depression, which is more than 1000  C from the melting point of elemental Si (1414
C from the melting point of elemental Si (1414  C). The melting point depression in eutectic alloys is generally explained in terms of a decrease of the free energy by mixing. However, it is difficult to understand the anomalous melting point depression only from the stability of the homogeneous mixing. Some researchers suggest that there are concentration fluctuations in the liquids, where the atoms are inhomogeneously mixed. In this paper, we measure the small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) of Au
C). The melting point depression in eutectic alloys is generally explained in terms of a decrease of the free energy by mixing. However, it is difficult to understand the anomalous melting point depression only from the stability of the homogeneous mixing. Some researchers suggest that there are concentration fluctuations in the liquids, where the atoms are inhomogeneously mixed. In this paper, we measure the small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) of Au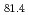 Si
Si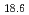 (eutectic composition) and Au
(eutectic composition) and Au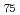 Si
Si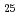 (off-eutectic composition) at temperatures from room temperature to 900
(off-eutectic composition) at temperatures from room temperature to 900  C in both solid and liquid states to observe such concentration fluctuations directly.
C in both solid and liquid states to observe such concentration fluctuations directly.
廣田 夕貴*; 富永 大輝*; 川端 隆*; 川北 至信; 松尾 康光*
Bioengineering (Internet), 10(5), p.622_1 - 622_17, 2023/05
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:38.63(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)Recently, it was reported that chitin and chitosan exhibited high-proton conductivity and function as an electrolyte in fuel cells. In particular, it is noteworthy that proton conductivity in the hydrated chitin becomes 30 times higher than that in the hydrated chitosan. Since higher proton conductivity is necessary for the fuel cell electrolyte, it is significantly important to clarify the key factor for the realization of higher proton conduction from a microscopic viewpoint for the future development of fuel cells. Therefore, we have measured proton dynamics in the hydrated chitin using quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) from the microscopic viewpoint and compared the proton conduction mechanism between hydrated chitin and chitosan. QENS results exhibited that a part of hydrogen atoms and hydration water in chitin are mobile even at 238 K, and the mobile hydrogen atoms and their diffusion increase with increasing temperature. It was found that the diffusion constant of mobile protons is two times larger and that the residence time is two times in chitin faster than that in chitosan. In addition, it is revealed from the experimental results that the transition process of dissociable hydrogen atoms between chitin and chitosan is different. To realize proton conduction in the hydrated chitosan, the hydrogen atoms of the hydronium ions (H O
O ) should be transferred to another hydration water. By contrast, in hydrated chitin, the hydrogen atoms can transfer directly to the proton acceptors of neighboring chitin. It is deduced that higher proton conductivity in the hydrated chitin compared with that in the hydrated chitosan is yielded by the difference of diffusion constant and the residence time by hydrogen-atom dynamics and the location and number of proton acceptors.
) should be transferred to another hydration water. By contrast, in hydrated chitin, the hydrogen atoms can transfer directly to the proton acceptors of neighboring chitin. It is deduced that higher proton conductivity in the hydrated chitin compared with that in the hydrated chitosan is yielded by the difference of diffusion constant and the residence time by hydrogen-atom dynamics and the location and number of proton acceptors.
 dynamics in the H
dynamics in the H conductors LaH
conductors LaH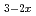 O
O
玉造 博夢; 福井 慧賀*; 飯村 壮史*; 本田 孝志*; 多田 朋史*; 村上 洋一*; 山浦 淳一*; 倉本 義夫*; 佐賀山 基*; 山田 武*; et al.
Physical Review B, 107(18), p.184114_1 - 184114_8, 2023/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:12.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using an incoherent quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) technique, we investigate H dynamics in a series of oxyhydrides LaH
dynamics in a series of oxyhydrides LaH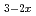 O
O that exhibit characteristic high H
that exhibit characteristic high H conductivity. In the end member LaH
conductivity. In the end member LaH (
( = 0), two kinds of H
= 0), two kinds of H dynamics are identified: the jump diffusion and the localized motion. The jump length in the jump diffusion mode increases with increasing
dynamics are identified: the jump diffusion and the localized motion. The jump length in the jump diffusion mode increases with increasing  . The localized motion is identified as a jump between the two inequivalent sites. These dynamics are corroborated by our molecular dynamical simulations. Our QENS data suggest that similar H
. The localized motion is identified as a jump between the two inequivalent sites. These dynamics are corroborated by our molecular dynamical simulations. Our QENS data suggest that similar H dynamics occurs also in oxyhydrides LaH
dynamics occurs also in oxyhydrides LaH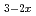 O
O (
(
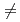 0), whose H
0), whose H concentration dependence is consistent with the previous measurement of ionic conductivity. We also discuss the possibility that LaH
concentration dependence is consistent with the previous measurement of ionic conductivity. We also discuss the possibility that LaH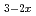 O
O is an example of H
is an example of H ion conductors governed by the concerted migration mechanism. The identified H
ion conductors governed by the concerted migration mechanism. The identified H dynamics is a key to understanding the anomalous hydrogen concentration dependence of the diffusion coefficient in lanthanum hydrides, which has been a longstanding mystery in this compound.
dynamics is a key to understanding the anomalous hydrogen concentration dependence of the diffusion coefficient in lanthanum hydrides, which has been a longstanding mystery in this compound.

中村 惇平*; 川北 至信; 岡部 博孝*; Li, B.*; 下村 浩一郎*; 末益 崇*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 175, p.111199_1 - 111199_8, 2023/04
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:22.06(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Muon spin rotation ( SR) experiments were performed to directly investigate the temperature dependence of the short-range order or correlations of chromium spins in the paramagnetic phase of AgCrSe
SR) experiments were performed to directly investigate the temperature dependence of the short-range order or correlations of chromium spins in the paramagnetic phase of AgCrSe . The detailed investigation of the
. The detailed investigation of the  SR spectra over a wide temperature range from low to high temperatures revealed that the short-range spin correlations developed below about 184 K. It also confirmed no short-range correlations at high temperatures, which had been controversial in previous quasi-elastic neutron scattering studies. In addition, the muon spin relaxation was qualitatively changed and showed large missing asymmetry below about 89 K, where the correlation clearly implied short-range spin order. There could be a preparative phenomenon of the phase transition or an anisotropic short-range spin correlation.
SR spectra over a wide temperature range from low to high temperatures revealed that the short-range spin correlations developed below about 184 K. It also confirmed no short-range correlations at high temperatures, which had been controversial in previous quasi-elastic neutron scattering studies. In addition, the muon spin relaxation was qualitatively changed and showed large missing asymmetry below about 89 K, where the correlation clearly implied short-range spin order. There could be a preparative phenomenon of the phase transition or an anisotropic short-range spin correlation.
廣田 夕貴*; 富永 大輝*; 川端 隆*; 川北 至信; 松尾 康光*
Bioengineering (Internet), 9(10), p.599_1 - 599_17, 2022/10
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:22.64(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)Chitosan, which is an environmentally friendly and highly bio-producible material, is a potential proton-conducting electrolyte for use in fuel cells. Thus, to microscopically elucidate proton transport in hydrated chitosan, we employed the quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) technique. QENS analysis showed that the hydration water, which was mobile even at 238 K, moved significantly more slowly than the bulk water, in addition to exhibiting jump diffusion. Furthermore, upon increasing the temperature from 238 to 283 K, the diffusion constant of water changed increased from 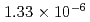 to
to 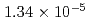 cm
cm /s. It was also found that a portion of the hydrogen atoms in chitosan undergo a jump-diffusion motion similar to that of the hydrogen present in water. Moreover, QENS analysis revealed that the activation energy for the jump-diffusion of hydrogen in chitosan and in the hydration water was 0.30 eV, which is close to the value of 0.38 eV obtained from the temperature-dependent proton conductivity results. Overall, it was deduced that a portion of the hydrogen atoms in chitosan dissociate and protonate the interacting hydration water, resulting in the chitosan exhibiting proton conductivity.
/s. It was also found that a portion of the hydrogen atoms in chitosan undergo a jump-diffusion motion similar to that of the hydrogen present in water. Moreover, QENS analysis revealed that the activation energy for the jump-diffusion of hydrogen in chitosan and in the hydration water was 0.30 eV, which is close to the value of 0.38 eV obtained from the temperature-dependent proton conductivity results. Overall, it was deduced that a portion of the hydrogen atoms in chitosan dissociate and protonate the interacting hydration water, resulting in the chitosan exhibiting proton conductivity.
大政 義典*; 高木 茂幸*; 戸嶋 健人*; 横山 凱乙*; 遠藤 亘*; 折茂 慎一*; 齋藤 寛之*; 山田 武*; 川北 至信; 池田 一貴*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033215_1 - 033215_9, 2022/09
Quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and neutron powder diffraction of the complex transition metalhydrides Li MoH
MoH and Li
and Li NbH
NbH were measured in a temperature range of 10-300 K to study their structures and dynamics, especially the dynamics of the hydrogen atoms. These hydrides contain unusual ninefold H coordinated complex ions (MoH
were measured in a temperature range of 10-300 K to study their structures and dynamics, especially the dynamics of the hydrogen atoms. These hydrides contain unusual ninefold H coordinated complex ions (MoH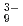 or NbH
or NbH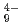 ) and hydride ions (H
) and hydride ions (H ). A QENS signal appeared
). A QENS signal appeared  150 K due to the relaxation of H atoms. The intermediate scattering functions derived from the QENS spectra are well fitted by a stretched exponential function called the Kohlrausch-Williams-Watts functions with a small stretching exponent
150 K due to the relaxation of H atoms. The intermediate scattering functions derived from the QENS spectra are well fitted by a stretched exponential function called the Kohlrausch-Williams-Watts functions with a small stretching exponent 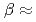 0.3-0.4, suggesting a wide relaxation time distribution. The
0.3-0.4, suggesting a wide relaxation time distribution. The  dependence of the elastic incoherent structure factor is reproduced by the rotational diffusion of MH
dependence of the elastic incoherent structure factor is reproduced by the rotational diffusion of MH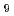 (M = Mo or Nb) anions. The results are well supported by a van Hove analysis for the motion of H atoms obtained using first-principles molecular dynamics calculations. We conclude that the wide relaxation time distribution of the MH
(M = Mo or Nb) anions. The results are well supported by a van Hove analysis for the motion of H atoms obtained using first-principles molecular dynamics calculations. We conclude that the wide relaxation time distribution of the MH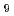 rotation is due to the positional disorder of the surrounding Li ions and a unique rotation with MH
rotation is due to the positional disorder of the surrounding Li ions and a unique rotation with MH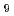 anion deformation (pseudorotation).
anion deformation (pseudorotation).
 GeP
GeP S
S by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurements
by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurements堀 智*; 菅野 了次*; Kwon, O.*; 加藤 祐樹*; 山田 武*; 松浦 直人*; 米村 雅雄*; 神山 崇*; 柴田 薫; 川北 至信
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(22), p.9518 - 9527, 2022/06
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:61.15(Chemistry, Physical)Understanding Li-ion conduction in superionic conductors accelerates the development of new solid electrolytes to enhance the charge-discharge performances of all-solid-state batteries. We performed a quasi-elastic neutron scattering study on a model superionic conductor (Li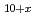 Ge
Ge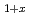 P
P S
S , LGPS), to reveal its ion dynamics on an angstrom-scale spatial range and a pico-to-nanosecond temporal range. The observation of spectra at 298 K confirmed the high lithium diffusivity. The obtained diffusion coefficient was in the order of 10
, LGPS), to reveal its ion dynamics on an angstrom-scale spatial range and a pico-to-nanosecond temporal range. The observation of spectra at 298 K confirmed the high lithium diffusivity. The obtained diffusion coefficient was in the order of 10 cm
cm s
s at temperatures
at temperatures 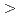 338 K and was higher than the reported diffusion coefficient over a longer time scale, as determined by the pulse-field gradient nuclear magnetic resonance method. This difference indicates that there are impediments to ionic motion over a longer time scale. The dynamic behavior of the Li ions was compared with that observed for the Li
338 K and was higher than the reported diffusion coefficient over a longer time scale, as determined by the pulse-field gradient nuclear magnetic resonance method. This difference indicates that there are impediments to ionic motion over a longer time scale. The dynamic behavior of the Li ions was compared with that observed for the Li P
P S
S O
O phase, which possesses the same crystal structure type, but a lower ionic conductivity. The LGPS phase possessed a high lithium mobility over a distance of
phase, which possesses the same crystal structure type, but a lower ionic conductivity. The LGPS phase possessed a high lithium mobility over a distance of 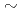 10
10  , as well as a larger fraction of mobile Li ions, thereby indicating that these features enhance lithium conduction over a longer spatial scale, which is important in all-solidstate batteries.
, as well as a larger fraction of mobile Li ions, thereby indicating that these features enhance lithium conduction over a longer spatial scale, which is important in all-solidstate batteries.
古池 美彦*; Ouyang, D.*; 富永 大輝*; 松尾 龍人*; 向山 厚*; 川北 至信; 藤原 悟*; 秋山 修志*
Communications Physics (Internet), 5(1), p.75_1 - 75_12, 2022/04
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:63.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Circadian clock proteins often reveal temperature-compensatory responses that counteract temperature influences to keep their enzymatic activities constant over a physiological range of temperature. This temperature-compensating ability at the reaction level is likely crucial for circadian clock systems, to which the clock proteins are incorporated, to achieve the system-level temperature compensation of the oscillation frequency. Nevertheless, temperature compensation is yet a puzzling phenomenon, since side chains that make up the clock proteins fluctuate more frequently due to greater thermal energy at higher temperature. Here, we investigated temperature influences on the dynamics of KaiC, a temperature-compensated enzyme (ATPase) that hydrolyzes ATP into ADP in the cyanobacterial circadian clock system, using quasielastic neutron scattering. The frequency of picosecond to subnanosecond incoherent local motions in KaiC was accelerated by a factor of only 1.2 by increasing the temperature by 10 C. This temperature insensitivity of the local motions was not necessarily unique to KaiC, but confirmed also for a series of temperature-sensitive mutants of KaiC and proteins other than clock-related proteins. Rather, the dynamics associated with the temperature-compensatory nature of the reaction- and system-level was found in global diffusional motions, which was suggested to regulate the temperature dependence of ATPase activity and dephosphorylation process presumably through changes in the hexamer conformation of KaiC. The spatiotemporal scale at which cross-scale causality of the temperature sensitivity is established is finite, and extends down to picosecond to subnanosecond dynamics only in a very limited part of KaiC, not in its entire part.
C. This temperature insensitivity of the local motions was not necessarily unique to KaiC, but confirmed also for a series of temperature-sensitive mutants of KaiC and proteins other than clock-related proteins. Rather, the dynamics associated with the temperature-compensatory nature of the reaction- and system-level was found in global diffusional motions, which was suggested to regulate the temperature dependence of ATPase activity and dephosphorylation process presumably through changes in the hexamer conformation of KaiC. The spatiotemporal scale at which cross-scale causality of the temperature sensitivity is established is finite, and extends down to picosecond to subnanosecond dynamics only in a very limited part of KaiC, not in its entire part.
富永 大輝*; 佐原 雅恵*; 川北 至信; 中川 洋; 山田 武*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 54(6), p.1631 - 1640, 2021/12
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:57.51(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)For quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) studies, sample cells made of pure or alloyed aluminum are frequently employed. Although the Al surface is protected by a passivating film, this film is not robust. Therefore, when the sample is an aqueous solution, chemical interactions between the Al surface and sample, promoted by corrosive entities such as chloride ions and certain conditions of pH, can compromise the integrity of the cell and interfere with the experiment. In this study, the corrosion susceptibilities of Al and its alloys were investigated by subjecting them to various treatments; the results were compared with those of other candidate materials with low chemical reactivity. This work showed that alloys with higher Al content and boehmite-coated surfaces are resistant to corrosion. In particular, for Al, the resistance is due to a reduction in the contact area achieved by reducing the surface roughness. QENS measurements of empty sample cells made of these materials revealed two results: (1) the profile of the cell fabricated with a copper-free Al alloy showed a minor dependence on the scattering vector magnitude  and (2) reducing the real surface area of Al effectively suppresses its scattering intensity, while boehmite coating strengthens the scattering. Cells fabricated with Mo, Nb and single-crystal sapphire can be used as alternatives to Al because of their low scattering intensity and reduced dependence on
and (2) reducing the real surface area of Al effectively suppresses its scattering intensity, while boehmite coating strengthens the scattering. Cells fabricated with Mo, Nb and single-crystal sapphire can be used as alternatives to Al because of their low scattering intensity and reduced dependence on  .
.
中村 惇平*; 川北 至信; 下村 浩一郎*; 末益 崇*
Journal of Applied Physics, 130(19), p.195701_1 - 195701_7, 2021/11
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:23.69(Physics, Applied)Hydrogen defects sometimes form shallow impurity levels in semiconductors, and it is an important topic for semiconductor research to investigate their details. One of the experimental methods to determine the state of hydrogen is the muon spin rotation ( SR) experiment. By observing formation of a pseudo-hydrogen atom, called muonium, it is possible to investigate the hydrogen defect levels. In a previous theoretical study, the pinning levels were calculated for various materials as a reference for hydrogen defect levels, and these levels were universally distributed near the hydrogen electrode potential. Based on the prediction,
SR) experiment. By observing formation of a pseudo-hydrogen atom, called muonium, it is possible to investigate the hydrogen defect levels. In a previous theoretical study, the pinning levels were calculated for various materials as a reference for hydrogen defect levels, and these levels were universally distributed near the hydrogen electrode potential. Based on the prediction,  SR experiments were performed for germanium sulfide (GeS) and germanium telluride (GeTe), where the hydrogen electrode potential is located in the bandgap for GeS, but not for GeTe. As a result, the
SR experiments were performed for germanium sulfide (GeS) and germanium telluride (GeTe), where the hydrogen electrode potential is located in the bandgap for GeS, but not for GeTe. As a result, the  SR spectra showed that the muonium forms in GeS, while it does not in GeTe. In GeS, 58
SR spectra showed that the muonium forms in GeS, while it does not in GeTe. In GeS, 58 of the muons formed muoniums. The activation energy was obtained as
of the muons formed muoniums. The activation energy was obtained as 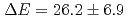 meV. The hyperfine coupling frequency was
meV. The hyperfine coupling frequency was 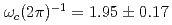 GHz, and the Bohr radius of muonium was 1.3 times larger than that in vacuum. These properties indicated that the identified muonium does not form a typical impurity level that affects the electrical properties.
GHz, and the Bohr radius of muonium was 1.3 times larger than that in vacuum. These properties indicated that the identified muonium does not form a typical impurity level that affects the electrical properties.
伊藤 華苗; 山田 武*; 篠原 朗大*; 高田 慎一; 川北 至信
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 125(39), p.21645 - 21652, 2021/10
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:41.67(Chemistry, Physical)The catalyst layer (CL) in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) plays a critical role in the performance of a PEFC. In this study, we investigate the water dynamics in the CL using quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and small-angle neutron scattering. The temperature dependence of the mean square displacement  u
u
 shows that the freezing of water does not occur at a melting temperature in the Nafion thin film of the CL, suggesting that the water is confined in a smaller region than
shows that the freezing of water does not occur at a melting temperature in the Nafion thin film of the CL, suggesting that the water is confined in a smaller region than  15
15  . The QENS measurements established three kinds of water in the CL: immobile water tightly connected to a sulfonic group, water in a fast mode assigned to free diffusion restricted in a sphere, and water in a slow mode described by a jump diffusion model. Assuming that these three modes were independent, the number of water molecules in each mode was estimated. On discussing the structure and dynamics elucidated in the study, we finally conclude that the coupled model of the fast and slow modes is plausible for describing the diffusion of water confined in the thin Nafion film of the CL.
. The QENS measurements established three kinds of water in the CL: immobile water tightly connected to a sulfonic group, water in a fast mode assigned to free diffusion restricted in a sphere, and water in a slow mode described by a jump diffusion model. Assuming that these three modes were independent, the number of water molecules in each mode was estimated. On discussing the structure and dynamics elucidated in the study, we finally conclude that the coupled model of the fast and slow modes is plausible for describing the diffusion of water confined in the thin Nafion film of the CL.
 Li
Li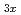 TiO
TiO (x = 0.13) studied by quasielastic neutron scattering
(x = 0.13) studied by quasielastic neutron scattering松浦 直人*; 藤原 靖幸*; 森分 博紀*; 尾原 幸治*; 川北 至信
Physical Review B, 104(9), p.094305_1 - 094305_7, 2021/09
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:46.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) measurements combined with first principles based molecular dynamics calculations were conducted to study the dynamics of Li ions in a solid-state electrolyte La
ions in a solid-state electrolyte La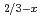 Li
Li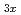 TiO
TiO (LLTO) with
(LLTO) with 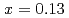 . By using a large
. By using a large  Li-enriched single crystal sample, a QENS signal was clearly observed along the three principal axes [110], [111], and [001] at a temperature (
Li-enriched single crystal sample, a QENS signal was clearly observed along the three principal axes [110], [111], and [001] at a temperature ( ) of 600 K. Wave vector dependence of the linewidth of the QENS signal along each direction was explained well using the Chudley-Elliot model for jumps between the A sites of the perovskite lattice through the bottleneck square, which was also supported by molecular dynamics calculations. The estimated self-diffusion coefficient of Li
) of 600 K. Wave vector dependence of the linewidth of the QENS signal along each direction was explained well using the Chudley-Elliot model for jumps between the A sites of the perovskite lattice through the bottleneck square, which was also supported by molecular dynamics calculations. The estimated self-diffusion coefficient of Li (
(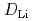 ) in the ab plane was slightly larger than that along the c axis, suggesting quasi-isotropic diffusion, that is, the three-dimensional diffusion of Li
) in the ab plane was slightly larger than that along the c axis, suggesting quasi-isotropic diffusion, that is, the three-dimensional diffusion of Li ions. The decrease in
ions. The decrease in 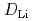 with decreasing
with decreasing  was reasonably explained by a thermal activation process with the activation energy determined from ionic-conductivity measurements. Furthermore, the estimated values of the self-diffusion coefficient are comparable to those in the sulfide-based Li
was reasonably explained by a thermal activation process with the activation energy determined from ionic-conductivity measurements. Furthermore, the estimated values of the self-diffusion coefficient are comparable to those in the sulfide-based Li ion conductor, Li
ion conductor, Li P
P S
S , with 10 times larger ionic conductivity, which clarifies how to understand the Li conduction mechanism in LLTO and Li
, with 10 times larger ionic conductivity, which clarifies how to understand the Li conduction mechanism in LLTO and Li P
P S
S in a unified manner.
in a unified manner.
中川 洋; 齋尾 智英*; 長尾 道弘*; 井上 倫太郎*; 杉山 正明*; 味戸 聡志; 富永 大輝*; 川北 至信
Biophysical Journal, 120(16), p.3341 - 3354, 2021/08
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:43.91(Biophysics)マルチドメインタンパク質は、溶液中で様々な構造を持つことができる。他の分子との相互作用により、そのうちの1つの構造が安定化し、ドメインダイナミクスが変化することが知られている。マルチドメインタンパク質の溶液中での構造を解明するためには、小角散乱法を用いることができる。中性子スピンエコー法は、ナノ秒・ナノメートルスケールでのドメインダイナミクスを解析するための有望な技術であるが、まだ開発途上である。本研究では、非干渉性散乱を用いて中性子スピンエコー法のデータから拡散運動や流体力学的相互作用の寄与を定量的に除去し、マルチドメインタンパク質MurDの3つの機能状態のドメインダイナミクスの違いを明らかにした。3つの状態間の違いは、2つのドメインモードによって説明できた。
富永 大輝*; 川北 至信; 中川 洋; 山田 武*; 柴田 薫
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011086_1 - 011086_5, 2021/03
後方散乱型中性子分光器、特にJ-PARC MLFのBL02(DNA)分光器用に最適化された二重円筒型石英試料セルを開発した。一端を閉じられた石英ガラス管を0.55mmの厚みまで削り、内筒を底部の突起によって外筒に同芯になるように挿入する。この石英セルは、標準的に用いられているアルミセルの表面に触れさせたくない試料に用いられる。石英セルと標準アルミセルの容器散乱の効果を重水バッファ試料を使って中性子準弾性散乱実験(QENS)により確かめた。Qが1[1/A]未満の領域では石英セルとアルミ容器の弾性散乱プロファイルはほぼ同一であった。一方Qが1[1/A]以上の領域では、石英ガラスのFSDPのために、プロファイルが異なることが分かった。この領域では、吸収補正や石英セルの個々の厚みの差を考慮した解析が必要である。
富永 大輝*; 佐原 雅恵*; 川北 至信; 中川 洋; 島本 直伸*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011094_1 - 011094_5, 2021/03
中性子準弾性散乱研究では、しばしばアルミもしくはアルミ合金製の試料容器が使われる。入射中性子の強度増大に伴って、研究領域は拡がり続けており、希薄な試料環境でもデータ取得は以前より速くなっている。そうした研究分野の一つに水を含むシステムが挙げられる。この研究では、アルミに関する温度効果を調べ、低温環境下でもアルミの腐食が起きることが分かった。その理由は、母材としてのアルミニウムと不動態フィルムとしての酸化アルミニウムの膨張係数の差による。
富永 大輝*; 小林 誠*; 山田 武*; 松浦 直人*; 川北 至信; 笠井 聡*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011095_1 - 011095_5, 2021/03
トップローディング型冷凍機用の垂直移動型試料交換機が、J-PARC MLFのBL02に設置された中性子分光器の利用支援のために開発された。PEACEと名付けられたこの試料交換機は、中性子照射位置での試料位置の再現性を、PEEKと呼ぶ物質でできたガイドを利用して制御している。3つの試料位置でのバックグラウンド散乱のプロファイルの変化は 1.6%以内であることが分かった。この結果は、垂直軸からの試料位置の偏差が
1.6%以内であることが分かった。この結果は、垂直軸からの試料位置の偏差が 0.3mmであることを考えると妥当である。
0.3mmであることを考えると妥当である。