Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Masatoshi*; Ishimaru, Sora*; Yamauchi, Sara*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Watanabe, Masao; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011010_1 - 011010_7, 2024/05
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kawamura, Seiko; Komine, Ryota
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011003_1 - 011003_5, 2024/03
Kofu, Maiko; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Ishii, Rieko*; Hirai, Daigoro*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013006_1 - 013006_9, 2024/01

Sala, G.*; Stone, M. B.*; Hal sz, G. B.*; Lumsden, M. D.*; Fay, A, F,*; Pajerowski, D. M.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kaneko, Koji; Mazzone, D. G.*; Simutis, G.*; et al.
sz, G. B.*; Lumsden, M. D.*; Fay, A, F,*; Pajerowski, D. M.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kaneko, Koji; Mazzone, D. G.*; Simutis, G.*; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 6, p.234_1 - 234_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kawamura, Seiko
Neutron News, 34(2), p.2 - 3, 2023/04
Kawamura, Seiko
Hamon, 33(1), P. 33, 2023/02
no abstracts in English
 Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Suyama, Kazuya*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Raymond, S.*; Steffens, P.*; Yamada, Akira*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*; Kawasaki, Ikuto; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kambara, Wataru*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 272, p.02012_1 - 02012_8, 2022/11
We will present some of attempts on AMATEAS, a cold-neutron chopper spectrometer at a pulsed source, to increase time-windows at a single-measurement condition. One of ways is that, by allowing interveined trajectories on the time-of-flight diagram, the usable width selectable for 
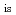 is can be increased. Based on our experiences, the conditions of pulse repetition rate multiplication based polychromatic
is can be increased. Based on our experiences, the conditions of pulse repetition rate multiplication based polychromatic 
 measurements on chopper spectrometers at pulsed sources will be discussed. Optimization of wide-band polychromatic
measurements on chopper spectrometers at pulsed sources will be discussed. Optimization of wide-band polychromatic 
 measurements and a generalized formulated condition will be proposed. Application of our idea to existing spectrometers and to the criteria design of an optimized chopper spectrometer will be also discussed with suggesting further possibility to improve efficiency by modifying the pulse shaping chopper.
measurements and a generalized formulated condition will be proposed. Application of our idea to existing spectrometers and to the criteria design of an optimized chopper spectrometer will be also discussed with suggesting further possibility to improve efficiency by modifying the pulse shaping chopper.
Ishii, Yui*; Yamamoto, Arisa*; Sato, Naoki*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Ohara, Koji*; Kawaguchi, Shogo*; Mori, Takao*; Mori, Shigeo*
Physical Review B, 106(13), p.134111_1 - 134111_7, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) O
O
Soda, Minoru*; Kofu, Maiko; Kawamura, Seiko; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Furukawa, Hazuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(9), p.094707_1 - 094707_5, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Mattan, K.*; Ono, Toshio*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Nambu, Yusuke*; Sato, Taku*
Physical Review B, 105(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_8, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:48.5(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Spin dynamics of the spin-1/2 kagome-lattice antiferromagnet Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF was studied using high-resolution, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The flat mode, a characteristic of the frustrated kagome antiferromagnet, and the low-energy dispersive mode, which is dominated by magnons, can be well described by the linear spin-wave theory. However, the theory fails to describe three weakly dispersive modes between 9 and 14 meV. These modes could be attributed to two-spinon bound states, which decay into free spinons away from the zone center and at a high temperature, giving rise to continuum scattering.
was studied using high-resolution, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. The flat mode, a characteristic of the frustrated kagome antiferromagnet, and the low-energy dispersive mode, which is dominated by magnons, can be well described by the linear spin-wave theory. However, the theory fails to describe three weakly dispersive modes between 9 and 14 meV. These modes could be attributed to two-spinon bound states, which decay into free spinons away from the zone center and at a high temperature, giving rise to continuum scattering.
Shamoto, Shinichi*; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Matsuura, Masato*; Kawamura, Seiko; Harii, Kazuya*; Ono, Masao*; Chang, L.-J.*; Ito, Takashi; Nemoto, Yuichi*; Ieda, Junichi
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(1), p.013245_1 - 013245_7, 2022/03
Ultrasound injection effect on a magnetic Bragg peak of yttrium iron garnet has been studied by quasielastic neutron scattering. The magnetic Bragg peak is vastly enhanced with decreasing temperature. The energy width increases proportionally to the square root of the sample temperature increase induced by the ultrasound injection. Because the magnetic Bragg peak is enhanced by the lattice vibration, the enhancement is expected to relate to the spin-lattice coupling closely. An observed sharp drop above 100 K in the longitudinal mode suggests the degradation of the spin-lattice coupling. It is consistent with the decline of spin Seebeck effect with increasing temperature above 100 K, proving the degradation mechanism by the spin-lattice coupling.
Hattori, Takanori; Kawamura, Seiko; Kawasaki, Takuro
High Pressure Research, 42(2), p.226 - 235, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have developed a hybrid piston cylinder cell for quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) experiments up to about 1 GPa. It consists of a fretted cylinder made of the high tensile steel (SNCM439) liner and the Al alloy (NA700) jacket. Performance tests revealed that the cell can withstand a pressure of 0.8 GPa without irreversible damage and has 4.4 times larger neutron transmission at 3.14 meV (5.10 in wavelength) than that of a conventional CuBe monobloc cylinder. Combined with the sample assembly devised for suppressing multiple scattering, high quality QENS spectra of water were obtained up to 0.8 GPa. This study illustrates the efficacy of the hybrid cylinders not only for increasing maximum available pressure but also manipulating the available pressure and the signal intensity, depending on the purpose of the experiments.
in wavelength) than that of a conventional CuBe monobloc cylinder. Combined with the sample assembly devised for suppressing multiple scattering, high quality QENS spectra of water were obtained up to 0.8 GPa. This study illustrates the efficacy of the hybrid cylinders not only for increasing maximum available pressure but also manipulating the available pressure and the signal intensity, depending on the purpose of the experiments.
Kofu, Maiko; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Matsuura, Masato*; Ueki, Takeshi*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.12098_1 - 12098_8, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:56.02(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Tahara, Shuta*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Maruyama, Kenji*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011071_1 - 011071_6, 2021/03
CuI is a well-known superionic conductor in a high temperature solid phase where the mobile cations migrate between interstitial sites in the f.c.c. sublattice formed by iodine ions. Even in the molten state, it shows several features suggesting collective or cooperative ionic motion. MD results show that Cu diffuses much faster than I. The Cu-Cu partial structure factor have a FSDP which indicates a medium-range ordering of Cu ions. Moreover the Cu-Cu partial pair distribution deeply penetrates into the nearest neighboring Cu-I shell. To reveal origin such anomalous behaviors of molten CuI, we performed quaiselastic neutron scattering (QENS) by the disk-chopper spectrometer AMATERAS at MLF, J-PARC. To interpret the total dynamic structure factor obtained from coherent QENS, the mode distribution analysis was applied. It is found that the motion of iodine is a kind of fluctuating within an almost local area while Cu ions diffuse much faster than iodine ions.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kofu, Maiko; Murai, Naoki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Wakai, Daisuke*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011089_1 - 011089_7, 2021/03
The recent update of AMATERAS, a cold-neutron disk-chopper spectrometer at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reported. AMATERAS has been operating for a decade. Since 2017, some updates have been done or are underway, which include installing new detectors, replacing the vacuum system of the scattering chamber, and other works. We are also working on the re-investigation of the resolution function. Demonstration measurements were carried out at 1MW test operations done in 2018 and 2019. Plans of upgrading the spectrometer are currently being considered.
Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yonetani, Yoshiteru*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kataoka, Mikio*; Kono, Hidetoshi*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011101_1 - 011101_6, 2021/03
Hydration water dynamics were measured by quasi-elastic neutron scattering with Hn O/D
O/D O contrast for two DNA dodecamers, 5'CGCG
O contrast for two DNA dodecamers, 5'CGCG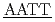 CGCG'3 and 5'CGCG
CGCG'3 and 5'CGCG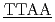 CGCG'3, which have been computationally shown to be structurally rigid and flexible, respectively. The dynamical transitions of the hydration water as well as DNA were observed for both sequences at approximately 240 K. Above the transition temperature, the mean square displacements of the hydration water for the rigid sequence were smaller than those for the flexible one. Furthermore, the relaxation time of the hydration water was longer in the rigid DNA than in the flexible DNA. We suggest that hydration water dynamics on the picosecond timescale are associated with sequence-dependent deformability of DNA.
CGCG'3, which have been computationally shown to be structurally rigid and flexible, respectively. The dynamical transitions of the hydration water as well as DNA were observed for both sequences at approximately 240 K. Above the transition temperature, the mean square displacements of the hydration water for the rigid sequence were smaller than those for the flexible one. Furthermore, the relaxation time of the hydration water was longer in the rigid DNA than in the flexible DNA. We suggest that hydration water dynamics on the picosecond timescale are associated with sequence-dependent deformability of DNA.
Fujihara, Masayoshi*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Mole, R.*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Toyama, Takami*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Yu, D.*; Sota, Shigetoshi*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3429_1 - 3429_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:90.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences) =0 long-range magnetic order in centennialite CaCu
=0 long-range magnetic order in centennialite CaCu (OD)
(OD) Cl
Cl
 0.6D
0.6D O; A Spin-
O; A Spin- perfect kagome antiferromagnet with
perfect kagome antiferromagnet with 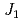 -
-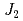 -
-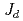
Iida, Kazuki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Jeschke, H. O.*; Iqbal, Y.*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Munakata, Koji*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Murai, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(22), p.220408_1 - 220408_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:80.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Crystal and magnetic structures of the mineral centennialite CaCu (OD)
(OD) Cl
Cl
 0.6D
0.6D O are investigated by means of synchrotron X-ray diffraction and neutron diffraction measurements complemented by density functional theory (DFT) and pseudofermion functional renormalization group (PFFRG) calculations. In CaCu
O are investigated by means of synchrotron X-ray diffraction and neutron diffraction measurements complemented by density functional theory (DFT) and pseudofermion functional renormalization group (PFFRG) calculations. In CaCu (OD)
(OD) Cl
Cl
 0.6D
0.6D O, Cu
O, Cu ions form a geometrically perfect kagome network with antiferromagnetic
ions form a geometrically perfect kagome network with antiferromagnetic 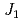 . No intersite disorder between Cu
. No intersite disorder between Cu and Ca
and Ca ions is detected. CaCu
ions is detected. CaCu (OD)
(OD) Cl
Cl
 0.6D
0.6D O enters a magnetic long-range ordered state below
O enters a magnetic long-range ordered state below  = 7.2 K, and the
= 7.2 K, and the  =0 magnetic structure with negative vector spin chirality is obtained. The ordered moment at 0.3 K is suppressed to 0.58(2)
=0 magnetic structure with negative vector spin chirality is obtained. The ordered moment at 0.3 K is suppressed to 0.58(2) B. Our DFT calculations indicate the presence of antiferromagnetic
B. Our DFT calculations indicate the presence of antiferromagnetic 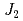 and ferromagnetic
and ferromagnetic 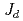 superexchange couplings of a strength which places the system at the crossroads of three magnetic orders (at the classical level) and a spin-
superexchange couplings of a strength which places the system at the crossroads of three magnetic orders (at the classical level) and a spin- PFFRG analysis shows a dominance of
PFFRG analysis shows a dominance of  =0 type magnetic correlations, consistent with and indicating proximity to the observed
=0 type magnetic correlations, consistent with and indicating proximity to the observed  =0 spin structure. The results suggest that this material is located close to a quantum critical point and is a good realization of a
=0 spin structure. The results suggest that this material is located close to a quantum critical point and is a good realization of a 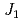 -
-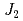 -
-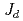 kagome antiferromagnet.
kagome antiferromagnet.
 PdSi
PdSi
Hirschberger, M.*; Nakajima, Taro*; Kriener, M.*; Kurumaji, Takashi*; Spitz, L.*; Gao, S.*; Kikkawa, Akiko*; Yamasaki, Yuichi*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Nakao, Hironori*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(22), p.220401_1 - 220401_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:91.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)