Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Taira, Yoshitaka*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kawamura, Shiori*; Nambu, Taro*; Okuizumi, Mao*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Omer, M.; Zen, H.*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*
Physical Review A, 107(6), p.063503_1 - 063503_10, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Optics)no abstracts in English
Endo, Shunsuke; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Zen, H.*; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Omer, M.; Kawamura, Shiori*; Abe, Ryota*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*
UVSOR-49, P. 38, 2022/08
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:79.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Naito, Fujio*; Anami, Shozo*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Uota, Masahiko*; Ouchi, Toshikatsu*; Onishi, Takahiro*; Oba, Toshiyuki*; Obina, Takashi*; Kawamura, Masato*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1244 - 1246, 2016/11
The proton linac installed in the Ibaraki Neutron Medical Research Center is used for production of the intense neutron flux for the Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). The linac consists of the 3-MeV RFQ and the 8-MeV DTL. Design average beam current is 10mA. Target is made of Beryllium. First neutron production from the Beryllium target was observed at the end of 2015 with the low intensity beam as a demonstration. After the observation of neutron production, a lot of improvement s was carried out in order to increase the proton beam intensity for the real beam commissioning. The beam commissioning has been started on May 2016. The status of the commissioning is summarized in this report.
Kawamura, Takuma; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Miyamura, Hiroko; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Takemiya, Hiroshi
Shisutemu Seigyo Joho Gakkai Rombunshi, 28(5), p.221 - 227, 2015/05
However remote volume visualization is important to obtain knowledge from complicated large-scale simulation results on supercomputer, the rendering speed and data transfer speed becomes bottleneck of the conventional Client/Server volume visualization techniques. Client/Server visualization system using particle-based volume rendering enables interactive volume visualization, which converts the original volume data to small size light particle data utilizing the supercomputer and transfer the data to Client PC. This system generated the particle data at a few seconds using parallel process on supercomputer Kei with strong scaling till 1000 processers.
Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya; Nishikawa, Shiro*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Usui, Norihisa*; Kamachi, Masafumi*; Aso, Noriko*; Tanaka, Yusuke*; Awaji, Toshiyuki*
Global Environmental Research (Internet), 18(1), p.81 - 96, 2014/09
A drift simulation of tsunami debris flushed out from the Tohoku district, Japan, into the North Pacific due to the tsunami on March 11, 2011, has been conducted to monitor and forecast the drift path over the North Pacific. Results showed that tsunami debris was first transported eastward by the intense Kuroshio Extension and westerly, spreading in the north and south directions by both an energetic ocean eddy and a storm track over the ocean. Tsunami debris with larger windage was transported over the North Pacific by ocean surface wind rather than ocean current and arrived at the west coast of the North American Continent in the fall of 2011. Tsunami debris located near the North American Continent migrated, associated with the basin-scale seasonal change in the atmospheric pressure pattern. Our forecast run suggested that the tsunami debris belt will be formed from the North American Continent in the east to the Philippines in the west.
 Si
Si observed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy
observed by X-ray absorption spectroscopyNakai, Hirohito*; Ebihara, Takao*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Kondo, Akihiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(12), p.124712_1 - 124712_5, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.63(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The temperature and magnetic field dependences of Yb valence were observed in the heavy fermion compoundYbRh Si
Si by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The measurements revealed that the Yb valence decreases with decreasing temperature in the range from 200 to 2 K and increases with increasing magnetic field in the range from 0 to 33 T without showing an abrupt change in the Yb valence. The Yb valence is in the range from 2.92 to 2.96 depending on temperature and magnetic field. With respect to the valence being 2.92 at 0 T and 2.93 at 33 T in 2 K, YbRh
by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The measurements revealed that the Yb valence decreases with decreasing temperature in the range from 200 to 2 K and increases with increasing magnetic field in the range from 0 to 33 T without showing an abrupt change in the Yb valence. The Yb valence is in the range from 2.92 to 2.96 depending on temperature and magnetic field. With respect to the valence being 2.92 at 0 T and 2.93 at 33 T in 2 K, YbRh Si
Si is a valence fluctuation compound and does not reach the integer trivalent state at high magnetic field. These results endorse the conventional knowledge that the valence of Yb is very close to the integer value of 3+, decreases with decreasing temperature, and becomes closer to 3+ with increasing magnetic field.
is a valence fluctuation compound and does not reach the integer trivalent state at high magnetic field. These results endorse the conventional knowledge that the valence of Yb is very close to the integer value of 3+, decreases with decreasing temperature, and becomes closer to 3+ with increasing magnetic field.
 - and
- and  -TbAlB
-TbAlB at low temperature and high magnetic fields
at low temperature and high magnetic fieldsMatsuda, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Kawamura, Naomi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 62(12), p.1778 - 1781, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.98(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The valence state of Yb ions in  - and
- and  -YbAlB
-YbAlB has been investigated by X-ray absorption and emission spectroscopy at temperatures from 2 to 280 K. It is found that the valence gradually increases with increasing temperature toward 3+ and that the characteristic temperature of the valence fluctuations is about 290 K. We also observe a small increase in the Yb valence (
has been investigated by X-ray absorption and emission spectroscopy at temperatures from 2 to 280 K. It is found that the valence gradually increases with increasing temperature toward 3+ and that the characteristic temperature of the valence fluctuations is about 290 K. We also observe a small increase in the Yb valence ( 0.002) in
0.002) in  -YbAlB
-YbAlB by a magnetic field of 32 T at 40 K.
by a magnetic field of 32 T at 40 K.

Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Her, J.-L.*; Kindo, Koichi*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Chen, B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(11), p.114702_1 - 114702_11, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.56(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The X-ray absorption and magnetic circular dichroism (MCD) spectra at the Yb L edge were measured in the mixed-valent heavy fermion compound YbAgCu
edge were measured in the mixed-valent heavy fermion compound YbAgCu at high magnetic fields and low temperatures. The magnetic-field-temperature (H-T) phase boundary determined by the valence state is in very good agreement with that determined by the magnetization. It is clearly found that the metamagnetism of this compound is due to the field induced valence transition. A distinctive positive peak of the XMCD spectra appears in the vicinity of the white line of the absorption due to Yb
at high magnetic fields and low temperatures. The magnetic-field-temperature (H-T) phase boundary determined by the valence state is in very good agreement with that determined by the magnetization. It is clearly found that the metamagnetism of this compound is due to the field induced valence transition. A distinctive positive peak of the XMCD spectra appears in the vicinity of the white line of the absorption due to Yb state, while no feature is observed in the XMCD spectra corresponding to the Yb
state, while no feature is observed in the XMCD spectra corresponding to the Yb state. A small negative XMCD peak was observed at a lower energy and was attributed to the quadrupole trasition from theoretical calcuration, which explains its peculicar magnetic field dependence.
state. A small negative XMCD peak was observed at a lower energy and was attributed to the quadrupole trasition from theoretical calcuration, which explains its peculicar magnetic field dependence.
Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya; Furuno, Akiko; In, Teiji*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Nakayama, Tomoharu*; Shima, Shigeki*; Awaji, Toshiyuki*
Reports of Research Institute for Applied Mechanics, Kyushu University, (143), p.111 - 117, 2012/09
Because of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant disaster, some radionuclides were released into the ocean from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant. In response to this situation, numerical experiments were carried out at Japan Atomic Energy Agency using an oceanic dispersion model and an ocean general circulation model to estimate an effect of the radionuclides on marine environment. It was suggested that the radionuclides deposited from the atmosphere mainly in the middle of March after the disaster spread over a comparatively wide area of the Pacific Ocean east of Japan. On the other hand the radionuclides directly released into the ocean from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant were carried along the coast and then spread along the Kuroshio extension.
 at high Magnetic fields
at high Magnetic fieldsMatsuda, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Her, J.-L.*; Kindo, Koichi*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Chen, B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(1), p.015002_1 - 015002_2, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.56(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The valence change of Yb ion in YbAgCu was measured by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy under high magnetic fields up to 35T. The valence state of Yb in YbAgCu
was measured by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy under high magnetic fields up to 35T. The valence state of Yb in YbAgCu at 4.8K significantly increases at the metamagnetic transition. The saturation value of
at 4.8K significantly increases at the metamagnetic transition. The saturation value of  at 55T is evaluated as 2.97 using the relation
at 55T is evaluated as 2.97 using the relation 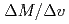 at 35T. This value is in good agreement with
at 35T. This value is in good agreement with  for the related compound YbInCu
for the related compound YbInCu at high temperatures and the Yb valence in the localized high-field phase. We conclude that the metamagnetic transition in YbAgCu
at high temperatures and the Yb valence in the localized high-field phase. We conclude that the metamagnetic transition in YbAgCu arises from the valence transition, as theoretically predicted.
arises from the valence transition, as theoretically predicted.
 I and
I and  Cs discharged into the ocean because of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant disaster
Cs discharged into the ocean because of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant disasterKawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya; Furuno, Akiko; In, Teiji*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Nakayama, Tomoharu*; Shima, Shigeki*; Awaji, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(11), p.1349 - 1356, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:180 Percentile:99.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)Numerical experiments were carried out to predict the spreading of  I and
I and  Cs released into the ocean due to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant incident. Results in the numerical experiments were in good agreement with the concentrations of
Cs released into the ocean due to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant incident. Results in the numerical experiments were in good agreement with the concentrations of  I and
I and  Cs in the monitoring data. It was suggested that the high
Cs in the monitoring data. It was suggested that the high  I concentration detected in the young lancefish caught off Kitaibaraki city was due to the deposition from the atmosphere. The numerical experiments suggest that the deposition of radionuclides released into the atmosphere in the middle March largely effected the concentrations of radionuclides east of Japan in the Pacific Ocean.
I concentration detected in the young lancefish caught off Kitaibaraki city was due to the deposition from the atmosphere. The numerical experiments suggest that the deposition of radionuclides released into the atmosphere in the middle March largely effected the concentrations of radionuclides east of Japan in the Pacific Ocean.
Kobayashi, Takuya; In, Teiji*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Nakayama, Tomoharu*; Shima, Shigeki*; Awaji, Toshiyuki*; Togawa, Orihiko
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.682 - 687, 2011/10
When the reprocessing plant is in routine operation, radionuclides are released to the coastal ocean as scheduled. Released radionuclides migrate in the ocean by physical, chemical and biological processes. Thus, for environmental safety, it is important to understand the migration behavior due to routine releases of radionuclides to the coastal ocean from the reprocessing plant. A numerical simulation model system that consists of an ocean general circulation model and a particle random-walk model to describe the radionuclide migration behavior in Rokkasho coastal region has been developed. The particle random-walk model, SEA-GEARN, calculates the radionuclides migration in the ocean. The system has been applied to simulate the nowcast of Rokkasho coastal region in 2007 and hypothetical radionuclide release has been carried out.
Kobayashi, Takuya; In, Teiji*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Matsuura, Yasutaka*; Shima, Shigeki*; Nakayama, Tomoharu*; Awaji, Toshiyuki*; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Togawa, Orihiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 7(2), p.112 - 126, 2008/06
The radionuclides migration forecasting system in the off Shimokita region has been developed to predict the routine and accidental releases of liquid radioactive wastes during the operations of a spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in Aomori prefecture, Japan. The results obtained from the case studies are as follows; (1) The ocean general circulation model by using the techniques of data assimilation and nesting reproduced well the flow pattern of a coastal area. (2) The estimated internal dose due to ingestion of marine products from hypothetical release of  H was 0.45
H was 0.45  Sv/y. (3) The results of hypothetical release of
Sv/y. (3) The results of hypothetical release of  Cs showed that about four percent of the whole deposited on the seabed after a 60-day calculation. The concentration of
Cs showed that about four percent of the whole deposited on the seabed after a 60-day calculation. The concentration of  Cs of hypothetical release from the off Shimokita region is the same or less than that of global fallout measured at the same area.
Cs of hypothetical release from the off Shimokita region is the same or less than that of global fallout measured at the same area.
Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:71.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
In, Teiji*; Nakayama, Tomoharu*; Matsuura, Yasutaka*; Shima, Shigeki*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Awaji, Toshiyuki*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Togawa, Orihiko; Toyoda, Takahiro*
Proceedings of International Symposium on Environmental Modeling and Radioecology, p.58 - 64, 2007/03
The northwestern part of the Pacific Ocean off the Shimokita Peninsula assumes a complex water mass structure. It is necessary to accurately reproduce the striking circulation patterns and the complicated water mass structures in this area with an ocean general circulation model. We have planned to make use of a one-way nesting method. To initialize the forecast system, we use a 4-dimensional variational method of data assimilation. The assimilated data consist of hydrographic observations collected through the Global Temperature-Salinity Profile Program, sea surface temperature and sea surface height data observed by satellites. A forecast experiment on the basis of oceanographic observations made in 2003 illustrates the good performance of our system. We shall focus, in particular, on the shift from the coastal mode to the gyre mode and vice versa.
Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kabutomori, Toshiyuki*; Kawamura, Hiroshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 58-59, p.401 - 405, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:59.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Ni
Ni alloy by adding third transition metals for tritium recovery
alloy by adding third transition metals for tritium recoveryKabutomori, Toshiyuki*; *; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kawamura, Hiroshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 258-263, p.481 - 487, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:74.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Ni
Ni particle packed bed
particle packed bedTsuchiya, Kunihiko; Imaizumi, Hideki*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Kabutomori, Toshiyuki*; *;
Fusion Technology, 2, p.1225 - 1228, 1996/00
no abstracts in English