Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study山下 享介*; 古賀 紀光*; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 藤井 英俊*; 梅澤 修*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 941, p.148602_1 - 148602_11, 2025/09
被引用回数:0Ferrite-austenite duplex stainless steels offer excellent strength and ductility, making them suitable for extreme environments. In this study,  neutron diffraction during tensile testing at 293 K and 200 K was used to investigate stress partitioning and phase-specific deformation. Phase stress was calculated using a texture-compensated method. At both temperatures, ferrite showed higher phase stress than austenite, acting as the harder phase. At 200 K, both phases exhibited increased strength and work hardening. Austenite showed significant stacking fault formation alongside dislocation migration, while ferrite retained its dislocation-based deformation mode, becoming more effective. Stress contributions from both phases were comparable. No martensitic transformation occurred. Strengthening and enhanced work hardening in both phases led to high strength at 200 K, with ductility similar to that at 293 K.
neutron diffraction during tensile testing at 293 K and 200 K was used to investigate stress partitioning and phase-specific deformation. Phase stress was calculated using a texture-compensated method. At both temperatures, ferrite showed higher phase stress than austenite, acting as the harder phase. At 200 K, both phases exhibited increased strength and work hardening. Austenite showed significant stacking fault formation alongside dislocation migration, while ferrite retained its dislocation-based deformation mode, becoming more effective. Stress contributions from both phases were comparable. No martensitic transformation occurred. Strengthening and enhanced work hardening in both phases led to high strength at 200 K, with ductility similar to that at 293 K.
Cao, T.*; Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 他10名*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 940, p.148534_1 - 148534_16, 2025/09
The thermal stability of microstructure and mechanical performance is crucial for the industrial application of laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) superalloy components in gas turbines and jet engines. This work investigated the microstructural evolution and strengthening mechanism of LPBF Mar-M509 cobalt-based superalloy before and after thermal exposure at 1200  C using multi-scale microstructural characterization and in situ neutron diffraction tensile testing. The as-built Mar-M509 superalloy exhibited a heterogeneous microstructural features with coarse columnar and fine equiaxed grains, both containing dendritic and cellular substructures enriched with nanoscale carbides and high-density dislocations. The ultra high strength of the as-built sample was primarily attributed to dislocation-precipitation synergistic strengthening. After thermal exposure at 1200
C using multi-scale microstructural characterization and in situ neutron diffraction tensile testing. The as-built Mar-M509 superalloy exhibited a heterogeneous microstructural features with coarse columnar and fine equiaxed grains, both containing dendritic and cellular substructures enriched with nanoscale carbides and high-density dislocations. The ultra high strength of the as-built sample was primarily attributed to dislocation-precipitation synergistic strengthening. After thermal exposure at 1200  C for 4 h, the dendritic and cellular substructures disappeared and the dislocation density decreased significantly. This study reveals the microstructural evolution and instability of LPBF Mar-M509 superalloy under high-temperature exposure and the impacts on mechanical properties, which provides critical support for the development of cobalt-based superalloys in high-temperature application fields.
C for 4 h, the dendritic and cellular substructures disappeared and the dislocation density decreased significantly. This study reveals the microstructural evolution and instability of LPBF Mar-M509 superalloy under high-temperature exposure and the impacts on mechanical properties, which provides critical support for the development of cobalt-based superalloys in high-temperature application fields.
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Gao, S.*; 伊東 達矢; 山下 享介*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)An ultrafine-grained 304 austenitic stainless steel exhibited pronounced serrated Luders deformation at 20 K, with stress and temperature oscillations reaching 200 MPa and 20 K.  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction study伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Incorporating solute hydrogen into Fe-Cr-Ni-based austenitic stainless steels enhances both strength and ductility, providing a promising solution to hydrogen embrittlement by causing solid-solution strengthening and assisting deformation twinning. However, its impacts on the relevant lattice defects evolution ( , dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using
, dislocations, stacking faults, and twins) during deformation remains unclear. This study compared the tensile deformation behavior in an Fe-24Cr-19Ni (mass%) austenitic steel with 7600 atom ppm hydrogen-charged (H-charged) and without hydrogen-charged (non-charged) using  neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
neutron diffraction. Hydrogen effects on the lattice expansion, solid-solution strengthening, stacking fault probability, stacking fault energy, dislocation density, and strain/stress for twin evolution were quantitatively evaluated to link them with the macroscale mechanical properties. The H-charged sample showed improvements in yield stress, flow stress, and uniform elongation, consistent with earlier findings. However, solute hydrogen exhibited minimal influences on the evolution of dislocation and stacking fault. This fact contradicts the previous reports on hydrogen-enhanced dislocation and stacking fault evolutions, the latter of which can be responsible for the enhancement of twinning. The strain for twin evolution was smaller in the H-charged sample compared to the non-charged one. Nevertheless, when evaluated as the onset stress for twin evolution, there was minimal change between the two samples. These findings suggest that the increase in flow stress due to the solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen is a root cause of accelerated deformation twinning at a smaller strain, leading to an enhanced work-hardening rate and improved uniform elongation.
Pandian, K.*; Neikter, M.*; Ekh, M.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Woracek, R.*; Hansson, T.*; Pederson, R.*
JOM, 77(4), p.1803 - 1815, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To produce dense Ti-6Al-4V components, electron beam powder bed fusion is typically followed by post-heat treatment like hot isostatic pressing (HIP). Standard HIP at 920 C/100 MPa for 2 h coarsens the microstructure and reduces yield strength, while low-temp HIP at 800
C/100 MPa for 2 h coarsens the microstructure and reduces yield strength, while low-temp HIP at 800 C/200 MPa for 2 h limits coarsening and retains strength comparable to as-built material. A coarser microstructure negatively affects tensile properties. Tensile tests at various temperatures suggest that thermally activated slip systems may influence elongation, requiring further study. In situ neutron time-of-flight diffraction during tensile loading enables analysis of strain evolution and slip plane activity. A two-phase elastic-plastic self-consistent model was used to compare with experiments. Results show basal slip {0002} activated at 20
C/200 MPa for 2 h limits coarsening and retains strength comparable to as-built material. A coarser microstructure negatively affects tensile properties. Tensile tests at various temperatures suggest that thermally activated slip systems may influence elongation, requiring further study. In situ neutron time-of-flight diffraction during tensile loading enables analysis of strain evolution and slip plane activity. A two-phase elastic-plastic self-consistent model was used to compare with experiments. Results show basal slip {0002} activated at 20 C, pyramidal slip {10-11} at 350
C, pyramidal slip {10-11} at 350 C, and
C, and  phase carrying higher stress than
phase carrying higher stress than  in the plastic regime.
in the plastic regime.
川崎 卓郎; 福田 竜生; 山中 暁*; 村山 一郎*; 加藤 孝典*; 馬場 将亮*; 橋本 英樹*; Harjo, S.; 相澤 一也; 田中 裕久*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 137(9), p.094101_1 - 094101_7, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)Energy harvesting from waste heat can improve energy efficiency in society. This research investigated the structural behaviors of lead zirconate titanate-based ferroelectric ceramics using operando neutron diffraction measurements under the conditions of two energy-harvesting cycles that involve consideration of the temperature changes of automobile exhaust gas for achieving good harvesting efficiencies. Input and output electrical energies and neutron diffraction data were simultaneously collected. The obtained time-resolved neutron-diffraction intensity data indicate that the applied electric fields and temperature changes induced 90 domain rotation and lattice strain. These structural changes and their variations depending on cycle conditions, such as temperature changes, applied electric fields, and circuit switching, provide insight into the origins of the differences in the behaviors of electrical input/output energies in the cycles.
domain rotation and lattice strain. These structural changes and their variations depending on cycle conditions, such as temperature changes, applied electric fields, and circuit switching, provide insight into the origins of the differences in the behaviors of electrical input/output energies in the cycles.
Song, Y.*; Xu, S.*; 佐藤 駿介*; Lee, I.*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 長迫 実*; 川崎 卓郎; 鬼柳 亮嗣; Harjo, S.; et al.
Nature, 638, p.965 - 971, 2025/02
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:94.96(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In advanced applications like aerospace and space exploration, materials must balance lightness, functionality, and extreme thermal fluctuation resistance. Shape-memory alloys show promise with strength, toughness, and substantial strain recovery due to superelasticity, but maintaining low mass and effective operation at cryogenic temperatures is challenging. We hereby introduce a novel shape-memory alloy that adheres to these stringent criteria. Predominantly composed of Ti and Al with a chemical composition of Ti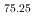 Al
Al Cr
Cr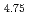 , this alloy 25 is characterized by a low density (4.36
, this alloy 25 is characterized by a low density (4.36 10
10 kg/m
kg/m ) and a high specific strength (185
) and a high specific strength (185 10
10 Pa
Pa m
m /kg) at room temperature, while exhibiting excellent superelasticity. The superelasticity, owing to a reversible stress-induced phase transformation from an ordered body-centered cubic parent phase to an ordered orthorhombic martensite, allows for a recoverable strain exceeding 7%. Remarkably, this functionality persists across a broad range of temperatures, from deep cryogenic 4.2 K to above room temperature, arising from an unconventional temperature dependence of transformation stresses. Below a certain threshold during cooling, the critical transformation stress inversely correlates with temperature. We interpret this behavior from the perspective of a temperature-dependent anomalous lattice instability of the parent phase. This alloy holds potential in everyday appliances requiring flexible strain accommodations, as well as components designed for extreme environmental conditions such as deep space and liquefied gases.
/kg) at room temperature, while exhibiting excellent superelasticity. The superelasticity, owing to a reversible stress-induced phase transformation from an ordered body-centered cubic parent phase to an ordered orthorhombic martensite, allows for a recoverable strain exceeding 7%. Remarkably, this functionality persists across a broad range of temperatures, from deep cryogenic 4.2 K to above room temperature, arising from an unconventional temperature dependence of transformation stresses. Below a certain threshold during cooling, the critical transformation stress inversely correlates with temperature. We interpret this behavior from the perspective of a temperature-dependent anomalous lattice instability of the parent phase. This alloy holds potential in everyday appliances requiring flexible strain accommodations, as well as components designed for extreme environmental conditions such as deep space and liquefied gases.
 neutron diffraction measurement during tensile deformation
neutron diffraction measurement during tensile deformation山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 北條 智彦*; 興津 貴隆*; 藤井 英俊*
ISIJ International, 64(14), p.2051 - 2060, 2024/12
被引用回数:0An Fe-0.15C-5Mn-0.5Si-0.05Nb steel annealed at 660 C and 685
C and 685 C showed L
C showed L ders deformation followed by high work hardening, with variations in L
ders deformation followed by high work hardening, with variations in L ders strain and hardening behavior.
ders strain and hardening behavior.  neutron diffraction during tensile tests analyzed phase stresses, strength contributions, and austenite orientation. Deformation-induced martensite contributed
neutron diffraction during tensile tests analyzed phase stresses, strength contributions, and austenite orientation. Deformation-induced martensite contributed  1000 MPa to strength near tensile failure, while austenite mainly enhanced ductility via transformation-induced plasticity. Austenite transformed to martensite during L
1000 MPa to strength near tensile failure, while austenite mainly enhanced ductility via transformation-induced plasticity. Austenite transformed to martensite during L ders deformation regardless of orientation, though 311-oriented grains tended to remain along the tensile direction.
ders deformation regardless of orientation, though 311-oriented grains tended to remain along the tensile direction.
 Sn strands in ITER central solenoid conductors of short and long twist pitch
Sn strands in ITER central solenoid conductors of short and long twist pitch諏訪 友音*; 礒野 高明*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 相澤 一也
Superconductor Science and Technology, 38(1), p.015008_1 - 015008_8, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)The ITER central solenoid (CS) conductors are composed of Nb Sn superconducting cables and stainless steel jackets. Approximately 60,000 electromagnetic loading cycles will be applied to the Nb
Sn superconducting cables and stainless steel jackets. Approximately 60,000 electromagnetic loading cycles will be applied to the Nb Sn strands in the CS conductor over the course of ITER tokamak operation, and the CS conductor is required to maintain the current sharing temperature (
Sn strands in the CS conductor over the course of ITER tokamak operation, and the CS conductor is required to maintain the current sharing temperature (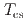 ) for these electromagnetic loading cycles. However, in CS conductor prototypes, degradation of
) for these electromagnetic loading cycles. However, in CS conductor prototypes, degradation of 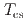 was observed after electromagnetic loading cycles. Visual inspections of the tested CS conductors revealed large bending and buckling of the Nb
was observed after electromagnetic loading cycles. Visual inspections of the tested CS conductors revealed large bending and buckling of the Nb Sn strands. These strand deformations were considered to be the cause of
Sn strands. These strand deformations were considered to be the cause of 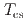 degradation because even a small amount of strain markedly affects the critical current of Nb
degradation because even a small amount of strain markedly affects the critical current of Nb Sn strands. To prevent the strands from bending and buckling, the twist pitch of the cable was shortened to improve stiffness. The stiffer cables did prevent
Sn strands. To prevent the strands from bending and buckling, the twist pitch of the cable was shortened to improve stiffness. The stiffer cables did prevent 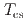 from degrading after electromagnetic loading cycles owing to the shortened twist pitch of the conductors, but a slight increase of
from degrading after electromagnetic loading cycles owing to the shortened twist pitch of the conductors, but a slight increase of 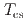 was observed. Visual inspections revealed no significant bent or buckled strands, but small deformations cannot be investigated visually. Thus, internal strain was measured by neutron diffraction and the internal strain states of the prototype CS conductors having long twist pitches and the improved short-twist-pitch (STP) CS conductors were evaluated. The results indicated that, after electromagnetic loading cycles, bending of the strands in the STP CS conductor was limited and compressive strain was reduced. Therefore, we determined that this STP is not only effective to prevent degradation caused by bent strands but it also increases
was observed. Visual inspections revealed no significant bent or buckled strands, but small deformations cannot be investigated visually. Thus, internal strain was measured by neutron diffraction and the internal strain states of the prototype CS conductors having long twist pitches and the improved short-twist-pitch (STP) CS conductors were evaluated. The results indicated that, after electromagnetic loading cycles, bending of the strands in the STP CS conductor was limited and compressive strain was reduced. Therefore, we determined that this STP is not only effective to prevent degradation caused by bent strands but it also increases 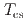 by reducing compressive strain.
by reducing compressive strain.
Harjo, S.; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.205 - 208, 2024/11
This study aimed to elucidate the effect of grain size on the deformation behavior of TRIP steel. We prepared metastable austenitic Fe-24Ni-0.3C steel samples with average grain sizes of 35 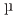 m (coarse grain: CG) and 0.5
m (coarse grain: CG) and 0.5 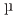 m (ultrafine-grain: UFG) for in situ neutron diffraction studies during tensile deformation at room temperature. Our observations revealed increases in dislocation density in both samples prior to DIMT, indicating that plastic deformation precedes DIMT regardless of grain size. In the UFG sample, a significant rise in dislocation density occurred just around the yielding point with minimal increases in macroscopic plastic strain. Additionally, the dislocations exhibited strong dipole arrangements.
m (ultrafine-grain: UFG) for in situ neutron diffraction studies during tensile deformation at room temperature. Our observations revealed increases in dislocation density in both samples prior to DIMT, indicating that plastic deformation precedes DIMT regardless of grain size. In the UFG sample, a significant rise in dislocation density occurred just around the yielding point with minimal increases in macroscopic plastic strain. Additionally, the dislocations exhibited strong dipole arrangements.
 neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel
neutron diffraction study to elucidate hydrogen effect on the deformation mechanism in Type 310S austenitic stainless steel伊東 達矢; 小川 祐平*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; 岡田 和歩*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Steel Science (ISSS 2024), p.237 - 240, 2024/11
Hydrogen embrittlement has long been an obstacle to the development of safe infrastructure. However, in contrast to hydrogen's embrittling effect, recent research has revealed that the addition of hydrogen improves both the strength and uniform elongation of AISI Type 310S austenitic stainless steel. A detailed understanding of how hydrogen affects the deformation mechanism of this steel could pave the way for the development of more advanced materials with superior properties. In the present study,  neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
neutron diffraction experiments were conducted on Type 310S steel with and without hydrogen-charged to investigate the effect of hydrogen on the deformation mechanism. In addition to the effect of solid-solution strengthening by hydrogen, the q-value, a parameter representing the proportion of edge and screw dislocations in the accumulated dislocations, was quantitatively evaluated using CMWP analysis on neutron diffraction patterns. The comparison of q-values between the hydrogen-charged and non-charged samples reveals that hydrogen has minimal effect on dislocation character in Type 310S steel.
Mao, W.*; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 278, p.120233_1 - 120233_13, 2024/10
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:96.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using a hybrid method of in situ neutron diffraction and digital image correlation, we found that ultrafine-grained 304 stainless steel exhibits Luders deformation after yielding, in which the deformation behavior changes from a cooperation mechanism involving dislocation slip and martensitic transformation to one primarily governed by martensitic transformation, as the temperature decreases from 295 K to 77 K. Such martensitic transformation-governed Luders deformation delays the activation of plastic deformation in both the austenite parent and martensite product, resulting in delayed strain hardening. This preserves the strain-hardening capability for the later stage of deformation, thereby maintaining a remarkable elongation of 29% while achieving a high tensile strength of 1.87 GPa at 77 K.
中島 多朗*; 齋藤 開*; 小林 尚暉*; 川崎 卓郎; 中村 龍也; 古川 はづき*; 浅井 晋一郎*; 益田 隆嗣*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.091002_1 - 091002_5, 2024/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutron scattering is a powerful tool to study magnetic structures and cross-correlated phenomena originated from symmetry of the magnetic structures in matter. Among a number of neutron scattering techniques, polarized neutron scattering is quite sensitive to the orientations of the magnetic moments, which are essential to understand microscopic mechanisms of the spin-driven emergent phenomena. Here, we present POlarized Neutron Triple-Axis spectrometer PONTA in the Japan Research Reactor 3 (JRR-3), and show the present capabilities of polarized and unpolarized neutron scattering by introducing recent results from the instrument.
 Sn wires with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement
Sn wires with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement中本 美緒*; 菅野 未知央*; 荻津 透*; 杉本 昌弘*; 谷口 諒*; 廣瀬 清慈*; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 淡路 智*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 34(5), p.8400806_1 - 8400806_6, 2024/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)For an accelerator magnet, a certain mechanical strength is required to sustain against a transverse compression stress due to Lorentz force. A bronze-route Nb Sn wire with Cu-Nb reinforcement was developed by Tohoku University and Furukawa Electric to enhance the strength against axial tension. The Cu-Nb reinforcement wire also exhibited some indication of strength improvement against transverse compression; however, the details of a reinforcement mechanism for the transverse compression stress have not been clarified. In this study, the internal strains of Nb
Sn wire with Cu-Nb reinforcement was developed by Tohoku University and Furukawa Electric to enhance the strength against axial tension. The Cu-Nb reinforcement wire also exhibited some indication of strength improvement against transverse compression; however, the details of a reinforcement mechanism for the transverse compression stress have not been clarified. In this study, the internal strains of Nb Sn bronze-route wires with and without the Cu-Nb reinforcement under transverse compression stress were evaluated by neutron diffraction at BL19 (TAKUMI) in J-PARC. The samples were attached to jig with solder only at the ends and compression was applied at the center of the samples with 30-mm anvil with 5-mm wide and 8- to 15-mm high beam. Since a critical current, Ic of a superconducting wire depends on the three-dimensional strain, internal strain of Nb
Sn bronze-route wires with and without the Cu-Nb reinforcement under transverse compression stress were evaluated by neutron diffraction at BL19 (TAKUMI) in J-PARC. The samples were attached to jig with solder only at the ends and compression was applied at the center of the samples with 30-mm anvil with 5-mm wide and 8- to 15-mm high beam. Since a critical current, Ic of a superconducting wire depends on the three-dimensional strain, internal strain of Nb Sn along the axial and two orthogonal radial directions were evaluated at room temperature (RT). In the different setup, Ic measurements of the wires under transverse compression stresses were also performed at 4.2 K and 14.5 T. Using 3-mm wide anvil, the transverse compression was applied at 4.2 K or RT. The neutron diffraction results indicated no significant differences in the internal strains of Nb
Sn along the axial and two orthogonal radial directions were evaluated at room temperature (RT). In the different setup, Ic measurements of the wires under transverse compression stresses were also performed at 4.2 K and 14.5 T. Using 3-mm wide anvil, the transverse compression was applied at 4.2 K or RT. The neutron diffraction results indicated no significant differences in the internal strains of Nb Sn under transverse compression between the samples with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement, while the Ic measurements showed potential increase in the irreversible stress (
Sn under transverse compression between the samples with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement, while the Ic measurements showed potential increase in the irreversible stress (
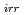 ) for Cu-Nb reinforced wires. The reason for this discrepancy was discussed based on the difference in the experimental setups for each measurement.
) for Cu-Nb reinforced wires. The reason for this discrepancy was discussed based on the difference in the experimental setups for each measurement.
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 相澤 一也; 山崎 倫昭*; 川崎 卓郎
日本材料学会第58回X線材料強度に関するシンポジウム講演論文集, p.58 - 60, 2024/07
The experiment and analysis procedures for a sample exhibiting multimodal structures were outlined. The sample, a Mg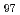 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy, initially comprised two phases: the HCP
alloy, initially comprised two phases: the HCP  matrix (
matrix ( Mg) and the long-period stacking ordered phase (LPSO), constituting approximately 25% of the volume. Through hot extrusion at 623 K with an extrusion ratio (R) of 5.0, the alloy was rendered multimodal. Specifically, at an R value of 5.0, dynamic recrystallization occurred partially within the
Mg) and the long-period stacking ordered phase (LPSO), constituting approximately 25% of the volume. Through hot extrusion at 623 K with an extrusion ratio (R) of 5.0, the alloy was rendered multimodal. Specifically, at an R value of 5.0, dynamic recrystallization occurred partially within the  Mg phase, resulting in a bimodal microstructure. This microstructure consisted of a deformed
Mg phase, resulting in a bimodal microstructure. This microstructure consisted of a deformed  Mg component and a recrystallized
Mg component and a recrystallized  Mg component. An analysis employing Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) data facilitated multimodal characterization, enabling successful determination of stresses within the individual
Mg component. An analysis employing Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) data facilitated multimodal characterization, enabling successful determination of stresses within the individual  Mg components, as well as the LPSO phase stress.
Mg components, as well as the LPSO phase stress.
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
日本材料学会第58回X線材料強度に関するシンポジウム講演論文集, p.51 - 54, 2024/07
In-situ neutron diffraction was used to study tensile deformation in an extruded AZ31 alloy. The aim was to validate existing methods and develop new ones for stress evaluation in magnesium alloys. Results showed varied increases in lattice strains among grains, posing challenges for conventional procedures. A new method, considering grain volume fraction and multiple orientations, proved highly accurate. When simultaneous hk.l peaks weren't available, the 12.1 peak was recommended for stress evaluation, showing a linear relationship with applied stress throughout deformation.
Ma, Y.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Sun, X.*; Yang, Z.*; He, F.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 270, p.119822_1 - 119822_13, 2024/05
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:94.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report an in situ neutron diffraction study of 316 L that reveals an extraordinary work-hardening rate (WHR) of  7 GPa at 15 K. Detailed analyses show that the major contribution to the excellent strength and ductility comes from the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, introduced by the austenite-to-martensite (
7 GPa at 15 K. Detailed analyses show that the major contribution to the excellent strength and ductility comes from the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, introduced by the austenite-to-martensite ( -to-
-to- ') phase transition. A dramatic increase in the WHR is observed along with the transformation; the WHR declined when the austenite phase is exhausted. During plastic deformation, the volume-fraction weighted phase stress and stress contribution from the
') phase transition. A dramatic increase in the WHR is observed along with the transformation; the WHR declined when the austenite phase is exhausted. During plastic deformation, the volume-fraction weighted phase stress and stress contribution from the  '-martensite increase significantly. The neutron diffraction data further suggest that the
'-martensite increase significantly. The neutron diffraction data further suggest that the  -to-
-to- ' phase transformation was mediated by the
' phase transformation was mediated by the  -martensite, as evidenced by the concurrent decline of the
-martensite, as evidenced by the concurrent decline of the  phase with the
phase with the  phase.
phase.
Kim, Y. S.*; Chae, H.*; Lee, D.-Y.*; Han, J. H.*; Hong, S.-K.*; Na, Y. S.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Woo, W.*; Lee, S.-Y.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 899, p.146453_1 - 146453_7, 2024/05
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:79.11(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)This work focused on the mechanical properties and serration-involved deformation behavior of advanced alloys at 15 K. Evolution of stacking faults and  -martensite improved the mechanical performance of CoCrNi alloys, and significant strain-induced martensite transformation of DED-SS316L led to superior strength and strain hardening. A magnitude in stress drop was governed by dislocation density, phase type, and lattice defects, irrespective of processing method. FCC {200} notably was influenced recovery behavior after stress drop, and the contribution of strain energy density by serration on tensile toughness was the greatest for HR-CoCrNi.
-martensite improved the mechanical performance of CoCrNi alloys, and significant strain-induced martensite transformation of DED-SS316L led to superior strength and strain hardening. A magnitude in stress drop was governed by dislocation density, phase type, and lattice defects, irrespective of processing method. FCC {200} notably was influenced recovery behavior after stress drop, and the contribution of strain energy density by serration on tensile toughness was the greatest for HR-CoCrNi.
Chae, H.*; Huang, E.-W.*; Jain, J.*; Lee, D.-H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Lee, S. Y.*
Metals and Materials International, 30(5), p.1321 - 1330, 2024/05
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:44.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In situ neutron diffraction during tensile deformation was performed for the stainless steels prepared by the additive manufacturing (AM) processes with two strategies: vertically built and horizontally built. The AM steels were further aged without solid solution treatment. As the results, the retained austenite was found to be more stable because the chemical composition became homogeneous by aging, and the onset of deformation induced martensitic transformation was delayed.
Liss, K.-D.*; Han, J.-K.*; Blankenburg, M.*; Lienert, U.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 徐 平光; 行武 栄太郎*; Kawasaki, M.*
Journal of Materials Science, 59(14), p.5831 - 5853, 2024/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:73.30(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The magnesium alloy AZ31, which has undergone high-pressure torsion processing, was subjected to in situ annealing micro-beam synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction and compared to the as-received rolled sheet material that was investigated through in situ neutron diffraction. While the latter only exhibits thermal expansion and minor recovery, the nanostructured specimen displays a complex evolution, including recovery, strong recrystallization, phase transformations, and various regimes of grain growth. Nanometer-scale grain sizes, determined using Williamson-Hall analysis, exhibit seamless growth, aligning with the transition to larger grains, as assessed through the occupancy of single grain reflections on the diffraction rings. The study uncovers strain anomalies resulting from thermal expansion, segregation of Al atoms, and the kinetics of vacancy creation and annihilation. Notably, a substantial number of excess vacancies were generated through high-pressure torsion, and maintained for driving the recrystallization and forming highly activated volumes for diffusion and phase precipitation during heating. The unsystematic scatter observed in the Williamson-Hall plot indicates high dislocation densities following severe plastic deformation, which significantly decreases during recrystallization. Subsequently, dislocations reappear during grain growth, likely in response to torque gradients in larger grains. It is worth noting that the characteristics of unsystematic scatter differ for dislocations created at high and low temperatures, underscoring the strong temperature dependence of slip system activation.