Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sb
Sb with a honeycomb network
with a honeycomb networkAdachi, Tadashi*; Ogawa, Taiki*; Komiyama, Yota*; Sumura, Takuya*; Saito-Tsuboi, Yuki*; Takeuchi, Takaaki*; Mano, Kohei*; Manabe, Kaoru*; Kawabata, Koki*; Imazu, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.L100508_1 - L100508_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Kida, Takashi; Sono, Hiroki; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/10
In the criticality experiment in the new STACY, pseudo fuel debris samples are used to acquire data for validation of the system used for 1F debris criticality safety assessment. The pseudo fuel debris is a pellet with a diameter of 8 mm and a height of 10 mm containing uranium oxide and structural materials (iron, silicon, zirconium, etc.). The pellets are made by mixing, pressing and sintering uranium dioxide powder and structural materials powder. The UO powder uses the same composition of uranium as the STACY driver fuel rods, in order to reduce the errors in fuel composition. The pseudo fuel debris fabrication devices and analysis equipment are installed at the BECKY in order to evaluate the critical properties of fuel debris with high accuracy in dimension and analysis. This equipment is located in the same laboratory and can quickly respond to experimental needs such as preparation of the pseudo fuel debris and analysis before and after irradiation.
powder uses the same composition of uranium as the STACY driver fuel rods, in order to reduce the errors in fuel composition. The pseudo fuel debris fabrication devices and analysis equipment are installed at the BECKY in order to evaluate the critical properties of fuel debris with high accuracy in dimension and analysis. This equipment is located in the same laboratory and can quickly respond to experimental needs such as preparation of the pseudo fuel debris and analysis before and after irradiation.
Inagawa, Jun; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Takano, Masahide; Akie, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Osamu; Komuro, Michiyasu; Oura, Hirofumi*; Nagai, Isao*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-001, 144 Pages, 2021/08
Plutonium Research Building No.1 (Pu1) was qualified as a facility to decommission, and preparatory operations for decommission were worked by the research groups users and the facility managers of Pu1. The operation of transportation of whole nuclear materials in Pu1 to Back-end Cycle Key Element Research Facility (BECKY) completed at Dec. 2020. In the operation included evaluation of criticality safety for changing permission of the license for use nuclear fuel materials in BECKY, cask of the transportation, the registration request of the cask at the institute, the test transportation, formulation of plan for whole nuclear materials transportation, and the main transportation. This report circumstantially shows all of those process to help prospective decommission.
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Sumiya, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Kokusen, Junya; Uchida, Shoji; Kaminaga, Jota; Oki, Keiichi; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Sono, Hiroki
JAEA-Technology 2016-025, 42 Pages, 2016/11
A preliminary test on MOX fuel dissolution for the STACY critical experiments had been conducted in 2000 through 2003 at Nuclear Science Research Institute of JAEA. Accordingly, the uranyl / plutonium nitrate solution should be reconverted into oxide powder to store the fuel for a long period. For this storage, the moisture content in the oxide powder should be controlled from the viewpoint of criticality safety. The stabilization of uranium / plutonium solution was carried out under a precipitation process using ammonia or oxalic acid solution, and a calcination process using a sintering furnace. As a result of the stabilization operation, recovery rate was 95.6% for uranium and 95.0% for plutonium. Further, the recovered oxide powder was calcined again in nitrogen atmosphere and sealed immediately with a plastic bag to keep its moisture content low and to prevent from reabsorbing atmospheric moisture.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Keyakida, Satoshi*; Uchimoto, Tetsuya*; Takaya, Shigeru; Tsukada, Takashi
International Journal of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics, 35(2), p.123 - 139, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.82(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)This paper presents a study conducted to develop a diagnostic system that can detect IASCC precursors in stainless steels by measuring the magnetic properties of the material. The eddy current method and alternating current (AC) magnetization method were used, as these will be more practical for use in actual reactors. Probes were developed for these measurement methods, providing sufficient tolerance for environments in nuclear reactors. An attempt was also made to improve spatial resolution by manufacturing a smaller probe. A sensor system was designed for remote control, performance tests were conducted by measuring neutron-irradiated specimens and mock specimens, and magnetic data were evaluated by comparing the IASCC susceptibility of the specimens. It was proved that the sensor system developed in this study is capable of detecting IASCC precursors. Further developments necessary for application in actual nuclear reactors and the mechanism of correlation between magnetic properties and IASCC susceptibility were also discussed.
Ishii, Junichi; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Uchida, Shoji; Sumiya, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Shirahashi, Koichi; Umeda, Miki; Sakuraba, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-068, 20 Pages, 2010/03
At Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety Engineering Research Facility, the cerium mediated electrolytic oxidation method which is a decontamination technique to decrease the radioactivity of TRU wastes to the clearance-level has been developed for the effective reduction of TRU wastes generated from the decommissioning of a nuclear fuel reprocessing facility and so on. This method corrodes the oxide layer and the surface of metallic TRU metal wastes by the strong oxidation power of Ce in nitric acid. In this study, parameter tests were conducted to optimize the solution condition of Ce
in nitric acid. In this study, parameter tests were conducted to optimize the solution condition of Ce initial concentrations and nitric acid concentrations. The target corrosion rate of metallic TRU wastes set to be 2
initial concentrations and nitric acid concentrations. The target corrosion rate of metallic TRU wastes set to be 2 4
4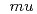 m/h for the practical use of this method. Under the optimized solution condition, a dissolution test of stainless steel simulating wastes was carried out. From the result of the dissolution test, the average corrosion rate was 3.3
m/h for the practical use of this method. Under the optimized solution condition, a dissolution test of stainless steel simulating wastes was carried out. From the result of the dissolution test, the average corrosion rate was 3.3  m/h during the test time of 90 hours. Based on the supposition that the corrosion depth of metallic TRU wastes was 20
m/h during the test time of 90 hours. Based on the supposition that the corrosion depth of metallic TRU wastes was 20  m enough to achieve the clearance-level, the treatment time for the decontamination was about 6 hours. It was confirmed from the result that the decontamination could be performed within one day and the decontamination solution could repeatedly reuse 15 times.
m enough to achieve the clearance-level, the treatment time for the decontamination was about 6 hours. It was confirmed from the result that the decontamination could be performed within one day and the decontamination solution could repeatedly reuse 15 times.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Keyakida, Satoshi*; Uchimoto, Tetsuya*; Takaya, Shigeru; Tsukada, Takashi
Hozengaku, 7(4), p.57 - 68, 2009/01
Authors previously reported leakage magnetic flux density measured by flux gate (FG) sensor seems to depend on irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) susceptibility of neutron irradiated austenitic stainless steels. This study aimed to evaluate possibility to develop diagnostic method to detect symptom of IASCC by more practical methods such as Eddy current method and AC magnetization method. Magnetic properties of neutron irradiated specimens and mockup specimens were studied and dependence on IASCC susceptibility was revealed. Microstructure observation using transmission electron microscope (TEM) was conducted to study magnetic phase formation by radiation induced segregation. It was shown that measurement of magnetic signal changed by magnetic phase formation along grain boundaries caused by radiation induced segregation would be a mechanism of the diagnostic method to detect symptom of IASCC.
Sugikawa, Susumu; Nakazaki, Masato; Kimura, Akihiro; Kida, Takashi*; Kihara, Takehiro*; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo; Suda, Kazuhiro*; Chikazawa, Takahiro*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 6(4), p.476 - 483, 2007/12
A one-step simple extraction chromatography method using TODGA (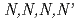 -tetraoctyl-diglycolamide) adsorbent column has been developed to separate the americium from plutonium-solvent extraction raffinate. The raffinate contained Am(
-tetraoctyl-diglycolamide) adsorbent column has been developed to separate the americium from plutonium-solvent extraction raffinate. The raffinate contained Am( 620 mg/
620 mg/ ), Np(
), Np( 107 mg/
107 mg/ ), Ag(
), Ag( 2000 mg/
2000 mg/ ), Fe(
), Fe( 290 mg/
290 mg/ ), Cr(
), Cr( 38 mg/
38 mg/ ), Ni(
), Ni( 52 mg/
52 mg/ ) and trace of TBP. Small-scale and scale-up tests for separation of americium and conversion to americium oxide were carried out in NUCEF. Efforts were made to increase yield and purity of americium. The americium was separated with 83-92% yields and 97-98% purities by small-scale tests and 85-95% yields and 98-99% purities by scale-up tests. The yields for conversion of americium nitrate solution to americium oxide were 89-100% by small-scale tests and 85-96 % by scale-up tests. Approximately 1.8 gram americium oxide was recovered from 6 litres of the raffinate and supplied for the research on the high-temperature chemistry of TRU.
) and trace of TBP. Small-scale and scale-up tests for separation of americium and conversion to americium oxide were carried out in NUCEF. Efforts were made to increase yield and purity of americium. The americium was separated with 83-92% yields and 97-98% purities by small-scale tests and 85-95% yields and 98-99% purities by scale-up tests. The yields for conversion of americium nitrate solution to americium oxide were 89-100% by small-scale tests and 85-96 % by scale-up tests. Approximately 1.8 gram americium oxide was recovered from 6 litres of the raffinate and supplied for the research on the high-temperature chemistry of TRU.
Kokusen, Junya; Seki, Masakazu; Abe, Masayuki; Nakazaki, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Umeda, Miki; Kihara, Takehiro; Sugikawa, Susumu
JAERI-Tech 2005-004, 53 Pages, 2005/03
This report presents operating records of dissolution of uranium dioxide and concentration of uranyl nitrate solution and acid removal, which have been performed from 1994 through 2003, for the purpose of feeding 10% and 6% enriched uranyl nitrate solution fuel to Static Experimental Critical Facility(STACY) and Transient Experimental Critical Facility(TRACY) in Nuclear Fuel Safety Engineering Facility(NUCEF).
Konomura, Mamoru; Ogawa, Takashi; Okano, Yasushi; Yamaguchi, Hiroyuki; Murakami, Tsutomu; Takaki, Naoyuki; Nishiguchi, Youhei; Sugino, Kazuteru; Naganuma, Masayuki; Hishida, Masahiko; et al.
JNC TN9400 2004-035, 2071 Pages, 2004/06
The attractive concepts for Sodium-, lead-bismuth-, helium- and water-cooled FBRs have been created through using typical plant features and employing advanced technologies. Efforts on evaluating technological prospects of feasibility have been paid for these concepts. Also, it was comfirmed if these concepts satisfy design requierments of capability and performance presumed in the feasibilty study on commertialization of Fast Breeder Reactor Systems. As results, it was concluded that the selection of sodium-cooled reactor was most rational for practical use of FBR technologies in 2015.
Kida, Takashi; Sugikawa, Susumu
JAERI-Tech 2004-019, 30 Pages, 2004/03
It is known that hydrazine nitrate used in nuclear fuel reprocessing plants is an unstable substance thermochemically like hydroxylamine nitrate. In order to take the basic data regarding the reaction of hydrazine nitrate with nitric acid, initiation temperatures and heats of this reaction, effect of impurity on initiation temperature and self-accelerating reaction when it holds at constant temperature for a long time were measured by the pressure vessel type reaction calorimeter etc. In this paper, the experimental data and evaluation of the safe handling of hydrazine nitrate in nuclear fuel reprocessing plants are described.
Umeda, Miki; Nakazaki, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Sato, Kenji; Kato, Tadahito; Kihara, Takehiro; Sugikawa, Susumu
JAERI-Tech 2003-024, 23 Pages, 2003/03
MOX dissolution with silver mediated electrolytic oxidation method is planned for the preparation of plutonium nitrate solution to be used for criticality safety experiments at Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety Engineering Research Facility (NUCEF). Silver mediated electrolytic oxidation method uses the strong oxidisation ability of Ag(II) ion. This method is thought to be effective for the dissolution of MOX, which is difficult to be dissolved with nitric acid.In this paper, the results of experiments on dissolution with 100 g of MOX are described. It was confirmed by the results that the MOX powder to be used at NUCEF was completely dissolved by silver mediated electrolytic oxidation method and that Pu(VI) ion in the obtained solution was reduced to tetravalent by means of NO purging.
purging.
Kida, Takashi; Umeda, Miki; Sugikawa, Susumu
JAERI-Data/Code 2003-001, 29 Pages, 2003/03
MOX dissolution using silver-mediated electrochemical method will be employed for the preparation of plutonium nitrate solution in the criticality safety experiments in NUCEF. A simulation code for the MOX dissolution has been developed for the operating support. In this report an outline of the simulation code is proposed and a comparison with the experimental data and a parameter study on the MOX dissolution rate are described.The principle of this code is based on Zundelevich's model for PuO dissolution using Ag
dissolution using Ag . The influence of nitrous acid on the material balance of Ag
. The influence of nitrous acid on the material balance of Ag and the surface area of MOX powder on the basis of particle size distribution are taken into consideration in this model. A comparison with experimental data was carried out to confirm a validity of this model. It was confirmed that the behavior of MOX dissolution could adequately be simulated using the appropriate MOX dissolution rate constant. The parameters affecting the dissolution rate were studied, it was found that MOX particle size was major governing factor on the dissolution rate.
and the surface area of MOX powder on the basis of particle size distribution are taken into consideration in this model. A comparison with experimental data was carried out to confirm a validity of this model. It was confirmed that the behavior of MOX dissolution could adequately be simulated using the appropriate MOX dissolution rate constant. The parameters affecting the dissolution rate were studied, it was found that MOX particle size was major governing factor on the dissolution rate.
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Sumiya, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Ogawa, Kazuhiko
no journal, ,
Towards the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Stations (1F), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has designed fabrication equipment of a pseudo fuel debris for the evaluation of the criticality characteristics of 1F fuel debris. In order to confirm the feasibility of the fabrication-method in designing, some fuel pellets mixed with uranium oxide and structural materials (iron, silicon, zirconium, etc.) were manufactured. The properties such as pressing and sintering condition were obtained by the prototyped fuel debris. The pseudo fuel debris fabricating equipment reflecting these properties is designed in 2016 and now constructed. The equipment will be installed in 2018 to start the fabrication.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Takaya, Shigeru; Ebine, Noriya; Tsukada, Takashi; Uchimoto, Tetsuya*; Keyakida, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Authors reported previously that magnetic parameter seems to depend on irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of high purity model austenitic stainless steels. This study aimed to investigate mechanism of the dependence. Electron diffraction patterns obtained by transmission electron microscopy were evaluated to study precipitation in irradiated specimens. Influence of element segregation on electro magnetic property of austenitic stainless steel was investigated applying mockup specimens. It was shown that magnetic phases were formed in irradiated austenitic stainless steels. Mockup experiments showed that radiation induced segregation can bring magnetic phase formation along grain boundaries. The magnetic phase was thought to involve with mechanism of magnetic parameter dependence on irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking susceptibility.
 in Reprocessing Solutions, 7; Measurement of hydrogen generation test using high active liquid waste
in Reprocessing Solutions, 7; Measurement of hydrogen generation test using high active liquid wasteHotoku, Shinobu; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Kumagai, Yuta; Inoue, Masao*; Suzuki, Sachiko*; Ban, Yasutoshi; Kida, Takashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Abe, Yuma*; Tamauchi, Yoshikazu*
no journal, ,
In order to evaluate the amount of hydrogen generated by radiolysis of water from the high active liquid waste in the reprocessing process, In this study a spent fuel solution was used and tests were conducted under the conditions of the solution temperature and the presence or absence of agitation and analyzed of the components in spent fuel solution. In this presentation, it is report on the outline of the test and the results obtained in the test.
Asano, Masaharu; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Maekawa, Yasunari; Yoshida, Masaru; Kanega, Jun*; Enokida, Takashi*
no journal, ,
The newly developed amorphous PFA was irradiated with  -rays under different conditions. It was found that the radiation crosslinking occurred even at temperatures ranging from 0 to 60
-rays under different conditions. It was found that the radiation crosslinking occurred even at temperatures ranging from 0 to 60 C, thereby significantly enhancing the mechanical properties. This can be attributed to high molecular mobility due to the glass translation temperature of the PFA as low as 12 to 42
C, thereby significantly enhancing the mechanical properties. This can be attributed to high molecular mobility due to the glass translation temperature of the PFA as low as 12 to 42 C.
C.
 -irradiation
-irradiationAsano, Masaharu; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Maekawa, Yasunari; Yoshida, Masaru; Kanega, Jun*; Enokida, Takashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Takaya, Shigeru; Ebine, Noriya; Tsukada, Takashi; Uchimoto, Tetsuya*; Keyakida, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Authors reported previously that magnetic parameter seems to depend on irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of high purity model austenitic stainless steels. This study aimed to investigate mechanism of the dependence. Electron diffraction patterns obtained by transmission electron microscopy were evaluated to study precipitation in irradiated specimens. Influence of element segregation on electro magnetic property of austenitic stainless steel was investigated applying mockup specimens. It was shown that magnetic phases were formed in irradiated austenitic stainless steels. Mockup experiments showed that radiation induced segregation can bring magnetic phase formation along grain boundaries. The magnetic phase was thought to involve with mechanism of magnetic parameter dependence on irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking susceptibility.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Takaya, Shigeru; Ebine, Noriya; Tsukada, Takashi; Uchimoto, Tetsuya*; Keyakida, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English