Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyHosomi, Kenji; Ma, Y.*; Ajimura, Shuhei*; Aoki, Kanae*; Dairaku, Seishi*; Fu, Y.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Imoto, Wataru*; Kakiguchi, Yutaka*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:64.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Level structure of the  C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of
C hypernucleus was precisely determined by means of  -ray spectroscopy. We identified four
-ray spectroscopy. We identified four  -ray transitions via the
-ray transitions via the  C
C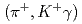 reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet
reaction using a germanium detector array, Hyperball2. The spacing of the ground-state doublet 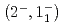 was measured to be
was measured to be 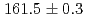 (stat)
(stat)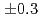 (syst)keV from the direct
(syst)keV from the direct  transition. Excitation energies of the
transition. Excitation energies of the 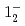 and
and 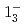 states were measured to be
states were measured to be 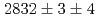 , keV and
, keV and 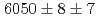 , keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of
, keV, respectively. The obtained level energies provide definitive references for the reaction spectroscopy of  hypernuclei.
hypernuclei.
Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Fukamoto, Kana; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 49(1), p.71 - 82, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:78.07(Biology)Research concerning cellular responses to low dose irradiation, radiation-induced bystander effects, and the biological track structure of charged particles has recently received particular attention in the field of radiation biology. Target irradiation employing a microbeam represents a useful means of advancing this research by obviating some of the disadvantages associated with the conventional irradiation strategies. The heavy-ion microbeam system at JAEA-Takasaki can provide target irradiation of heavy charged particles to biological material at atmospheric pressure using a minimum beam size 5  m in diameter. The system can be applied to the investigation of mechanisms within biological organisms not only in the context of radiation biology, but also in the fields of general biology such as physiology, developmental biology and neurobiology, and should help to establish and contribute to the field of "microbeam biology".
m in diameter. The system can be applied to the investigation of mechanisms within biological organisms not only in the context of radiation biology, but also in the fields of general biology such as physiology, developmental biology and neurobiology, and should help to establish and contribute to the field of "microbeam biology".
Fukamoto, Kana; Shirai, Koji*; Sakata, Toshiyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Shimura, Sachiko*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 48(3), p.247 - 253, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:46.75(Biology)To carry out the radio-microsurgery study using silkworm,  , we have already developed the specific irradiation systems for eggs and third to fifth instar larvae. In this study, a modified application consisting of the first instar silkworm larvae was further developed using heavy-ion microbeams. This system includes aluminum plates with holes specially designed to fix the first instar silkworm larvae during irradiation, and Mylar films were used to adjust energy deposited for planning radiation doses at certain depth. Using this system, the suppression of abnormal proliferation of epidermal cells in the knob mutant was examined. Following target irradiation of the knob-forming region at the first instar stage with 180-mum-diameter microbeam of 220 MeV carbon (
, we have already developed the specific irradiation systems for eggs and third to fifth instar larvae. In this study, a modified application consisting of the first instar silkworm larvae was further developed using heavy-ion microbeams. This system includes aluminum plates with holes specially designed to fix the first instar silkworm larvae during irradiation, and Mylar films were used to adjust energy deposited for planning radiation doses at certain depth. Using this system, the suppression of abnormal proliferation of epidermal cells in the knob mutant was examined. Following target irradiation of the knob-forming region at the first instar stage with 180-mum-diameter microbeam of 220 MeV carbon ( C) ions, larvae were reared to evaluate the effects of irradiation. The results indicated that the knob formation at the irradiated segment was specially suppressed in 5.9, 56.4, 66.7 and 73.6 % of larvae irradiated with 120, 250, 400 and 600 Gy, respectively, but the other knob formations at the non-irradiated segments were not suppressed in either irradiation. Although some larva did not survive undesired non-targeted exposure, our present results indicate that this method would be useful to investigate the irradiation effect on a long developmental period of time. Moreover, our system could also be applied to other species by targeting tissues, or organs during development and metamorphosis in insect and animals.
C) ions, larvae were reared to evaluate the effects of irradiation. The results indicated that the knob formation at the irradiated segment was specially suppressed in 5.9, 56.4, 66.7 and 73.6 % of larvae irradiated with 120, 250, 400 and 600 Gy, respectively, but the other knob formations at the non-irradiated segments were not suppressed in either irradiation. Although some larva did not survive undesired non-targeted exposure, our present results indicate that this method would be useful to investigate the irradiation effect on a long developmental period of time. Moreover, our system could also be applied to other species by targeting tissues, or organs during development and metamorphosis in insect and animals.
 , after heavy-ion irradiation; Analysis by transplantation of the irradiated organs using a transgenic silkworm strain
, after heavy-ion irradiation; Analysis by transplantation of the irradiated organs using a transgenic silkworm strainKiguchi, Kenji*; Shirai, Koji*; Sakata, Toshiyuki*; Fukamoto, Kana; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Wada, Seiichi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 117, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
 cyst formation from the implanted larval integument in the sweet potato hornworm,
cyst formation from the implanted larval integument in the sweet potato hornworm,  ; A Simple model for studying wound healing
; A Simple model for studying wound healingFukamoto, Kana; Shirai, Koji*; Sato, Shigeru*; Kanekatsu, Rensuke*; Kiguchi, Kenji*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Journal of Insect Biotechnology and Sericology, 75(3), p.99 - 106, 2006/10
no abstracts in English
Fukamoto, Kana; Shimura, Sachiko*; Shirai, Koji*; Kanekatsu, Rensuke*; Kiguchi, Kenji*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Journal of Insect Biotechnology and Sericology, 75(3), p.107 - 114, 2006/10
no abstracts in English
Shimoyama, Iwao; Miyauchi, Hideo*; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Hirao, Norie*; Okuno, Kenji*
JAEA-Research 2006-039, 33 Pages, 2006/06
Boron nitride (BN) ultrathin film attracts much attention as a coating material for Si cathode due to the chemical stability, heat resistance, and negative electron affinity. In order to study the oxidation resistance of BN ultrathin film coating, thermal dry oxidation is applied to BN coated Si and non-coated Si at various temperatures. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy is devoted to clarify the modification of chemical state of the samples. The XPS spectra change by the thermal oxidation for the non-coated Si. On the other hand, it scarcely change by the thermal oxidation for the BN coated Si. The oxidation resistance in ambient air is also investigated for BN coated Si. After the several days exposure of air, the O 1s photoelectron peak is drastically enhanced. These results mean that BN ultrathin film works as protective coating for dry thermal oxidation, however it does not work in ambient air.
 C
C ) irradiated hematopoietic organs in the silkworm,
) irradiated hematopoietic organs in the silkworm,  , through the way of phagocytosis of injured cells after invasion
, through the way of phagocytosis of injured cells after invasionLing, E.*; Shirai, Koji*; Kanekatsu, Rensuke*; Kiguchi, Kenji*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 30(6), p.531 - 543, 2006/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:52.70(Fisheries)no abstracts in English
Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Nath, K. G.; Sasaki, Masayoshi*; Okuno, Kenji*
Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology A, 21(6), p.1843 - 1848, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.75(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)Ion implantation method is applied to synthesize B-C-N hybrids and their electronic structures are characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. A boron nitride film is deposited on a graphite target by borazine plasma implantation. At the interface between the BN film and the graphite, variety of bonding combinations including B-N, B-C, and C-N are observed. This proved that B-C-N hybrids is formed by this method.
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Kiguchi, Kenji*
Isotope News, (593), p.9 - 12, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
 ?
?Ling, E.*; Shirai, Koji*; Kanekatsu, Rensuke*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tu, Z.; Funayama, Tomoo; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Kiguchi, Kenji*
Journal of Insect Biotechnology and Sericology, 72(2), p.101 - 109, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
 , after locally targeted irradiation with heavy ion beams
, after locally targeted irradiation with heavy ion beamsLing, E.*; Fukamoto, Kana*; Xu, S.*; Shirai, Koji*; Kanekatsu, Rensuke*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tu, Z.; Funayama, Tomoo; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Kiguchi, Kenji*
Journal of Insect Biotechnology and Sericology, 72(2), p.95 - 100, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
Tu, Z.; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Kiguchi, Kenji*; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.591 - 595, 2003/05
no abstracts in English
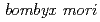
Tu, Z.; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Kiguchi, Kenji*; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.591 - 595, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
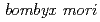
Tu, Z.; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Kiguchi, Kenji*; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo*
Journal of Radiation Research, 43(3), p.269 - 275, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:31.57(Biology)no abstracts in English
Tu, Z.; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Kiguchi, Kenji*; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 41(3), p.231 - 234, 2002/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.42(Biology)no abstracts in English
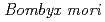 , by localized irradiation of heavy ion microbeams
, by localized irradiation of heavy ion microbeamsKiguchi, Kenji*; Kinjo, Y.*; Masahashi, K.*; Tu, Z.; Tamura, Hajime*; Shirai, K.*; Kanekatsu, Rensuke*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Watanabe, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 2000-024, TIARA Annual Report 1999, p.51 - 53, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Kiguchi, Kenji*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (85), p.30 - 36, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo*; Yamasaki, Shuhei*; Tu, Z. L.*; Kinjo, Y.*; Kiguchi, Kenji*
Proceedings of 11th International Congress of Radiation Research (ICRR-11), 2, p.182 - 186, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
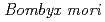 ; Morphological changes of the nuclei and cells after spot irradiation
; Morphological changes of the nuclei and cells after spot irradiationKiguchi, Kenji*; Shima, T.*; Kinjo, Y.*; Tu, Z. L.*; Yamasaki, Shuhei*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Watanabe, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.53 - 55, 1999/10
no abstracts in English