Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kimura, Takaumi; Kihara, Sorin*
Electrochimica Acta, 141, p.6 - 12, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:9.01(Electrochemistry)Reduction processes of U(VI) in weakly acidic solutions were investigated based on electrochemical and spectrophotometric measurements. A reversible one-electron reduction of U(VI) to U(V) and a further irreversible reduction of U(V) were observed voltammetrically at a gold microdisk electrode in solutions of pH from 2.0 to 3.5. Aggregates of U(IV) were formed as a deposit on the electrode and a colloid in the bulk solution, when the electrolysis was carried out at a gold gauze electrode, even though the potential applied was that available for the first one-electron reduction wave of U(VI) observed. It was elucidated that the aggregate was produced by the combination of the one-electron reduction to U(V) and the disproportionation of U(V) producing U(IV) and U(VI). The aggregate enhanced the rate of the disproportionation of U(V), and hence the reduction current of U(VI) increased abruptly when a definite amount of aggregate was formed on the electrode, in the solution, or both.
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kimura, Takaumi; Kihara, Sorin*
Electrochimica Acta, 74, p.215 - 221, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:4.99(Electrochemistry)Redox reactions of U, Np and Pu ions of various oxidation states were investigated by flow electrolysis at a column electrode (CE) equipped with a platinized glassy carbon (GC) fiber working electrode (Pt/GC-WE), and compared with those observed at the CE with an ordinary activated GC fiber working electrode (GC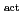 -WE). Since the overpotential for the reduction of NpO
-WE). Since the overpotential for the reduction of NpO
 and PuO
and PuO
 were decreased when Pt/GC-WE was employed, the one-electron reduction of NpO
were decreased when Pt/GC-WE was employed, the one-electron reduction of NpO
 to Np
to Np followed by that of Np
followed by that of Np to Np
to Np and the one-step three-electron reduction of PuO
and the one-step three-electron reduction of PuO
 to Pu
to Pu proceeded at the CE with Pt/GC-WE, different from the reduction processes of NpO
proceeded at the CE with Pt/GC-WE, different from the reduction processes of NpO
 and PuO
and PuO
 at the CE with GC
at the CE with GC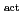 -WE. A rapid and precise method for the preparation of U, Np and Pu ion of a desired oxidation state was proposed by taking advantage of the unique characteristics of the CE with Pt/GC-WE.
-WE. A rapid and precise method for the preparation of U, Np and Pu ion of a desired oxidation state was proposed by taking advantage of the unique characteristics of the CE with Pt/GC-WE.
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Okugaki, Tomohiko*; Kasuno, Megumi*; Kubota, Hiroki*; Maeda, Koji*; Kimura, Takaumi; Yoshida, Zenko; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 43(6), p.844 - 851, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:28.93(Thermodynamics)Standard Gibbs energies for transfer ( G
G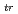
 ) of actinyl ions (AnO
) of actinyl ions (AnO
 ; z = 2 or 1; An: U, Np or Pu) between an aqueous solution and an organic solution were determined based on distribution method combined with voltammetry for ion transfer at the interface of two immiscible electrolyte solutions. The organic solutions examined were nitrobenzene, 1,2-dichloroethane, benzonitrile, acetophenone and 2-nitrophenyl octyl ether. Irrespective of the type of organic solutions,
; z = 2 or 1; An: U, Np or Pu) between an aqueous solution and an organic solution were determined based on distribution method combined with voltammetry for ion transfer at the interface of two immiscible electrolyte solutions. The organic solutions examined were nitrobenzene, 1,2-dichloroethane, benzonitrile, acetophenone and 2-nitrophenyl octyl ether. Irrespective of the type of organic solutions,  G
G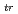
 of UO
of UO
 , NpO
, NpO
 and PuO
and PuO
 were nearly equal to each other and slightly larger than that of Mg
were nearly equal to each other and slightly larger than that of Mg . The
. The  G
G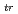
 of NpO
of NpO
 was extraordinary large compared with those of ordinary monovalent cations. The dependence of
was extraordinary large compared with those of ordinary monovalent cations. The dependence of  G
G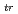
 of AnO
of AnO
 on the type of organic solutions was similar to that of H
on the type of organic solutions was similar to that of H or Mg
or Mg . The
. The  G
G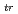
 of An
of An and An
and An were also discussed briefly.
were also discussed briefly.
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kimura, Takaumi; Kihara, Sorin*
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 9, p.012078_1 - 012078_7, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The behaviors of reduction of Np(V) by controlled potential electrolysis were studied, and a unique time course of electrolysis current was observed. It was conclude that Np(V) was reduced by two reduction processes that are the chemical reaction with Np(III) and the electrocatalytic reduction by adsorbed hydrogen atom on platinum electrode surface. The time course of current for controlled potential electrolysis of Np(V) under various condition of the solution was investigated, and the effects of the concentration of H and NO
and NO
 on electrolysis behaviour were shown.
on electrolysis behaviour were shown.
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kimura, Takaumi; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 641(1-2), p.83 - 89, 2010/03
Unique current-time relations were observed during the controlled potential electrolysis for the reduction of Np(V) to Np(IV) or Np(III) at a Au or Pt electrode. The reduction process of Np(V) was elucidated based on bulk electrolysis and voltammetry: Though Np(V) is not reduced directly at a Au electrode, it is reduced by chemical reaction with Np(III) which is produced by the electrode reduction of Np(IV). The reduction of Np(V) at a Pt electrode is initiated by the electrocatalytic reduction to Np(IV) with the hydrogen atom which is produced by the electrode reduction of H and adsorbed on the Pt electrode surface. The Np(IV) produced functions as an electron transfer mediator to reduce Np(V) similarly to the reaction at a Au electrode. The above described catalytic reduction processes of Np(V) were elucidated with the aid of digital simulation. Methods useful for the preparation of Np(IV) and Np(III) by bulk electrolysis were proposed based on the experimental results.
and adsorbed on the Pt electrode surface. The Np(IV) produced functions as an electron transfer mediator to reduce Np(V) similarly to the reaction at a Au electrode. The above described catalytic reduction processes of Np(V) were elucidated with the aid of digital simulation. Methods useful for the preparation of Np(IV) and Np(III) by bulk electrolysis were proposed based on the experimental results.
Okugaki, Tomohiko*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kasuno, Megumi*; Yoshizumi, Asuka*; Kubota, Hiroki*; Shibafuji, Yayoi*; Maeda, Koji*; Yoshida, Zenko; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 629(1-2), p.50 - 56, 2009/04
A high performance electrochemical solvent extraction method was developed based on the quantitative transfer of ions from an aqueous, W, to an organic solution, O. It was realized by applying a potential difference between W and O. The cell was composed of a porous Teflon tube immersed with O, a Ag wire inserted into the tube, a Pt wire placed outside the tube. When W containing ions was forced to flow through the narrow gap between the tube and Ag wire, and potential was applied, a very rapid quantitative ion transfer was attained. When O containing extractant, more than 99% of U(VI) in W was extracted during the residence (e.g., 40 s) in the cell. The fundamental feature of the extraction system was investigated, taking into account the application of the system to the extraction of actinide, lanthanide, Sr or Cs ions. The use of a column electrode system connected before the extraction system was examined in order to adjust the oxidation state of the element to that desired.
 organic solution interface in chelate extraction
organic solution interface in chelate extractionUehara, Akihiro*; Kasuno, Megumi*; Okugaki, Tomohiko*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Shirai, Osamu*; Yoshida, Zenko; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 604(2), p.115 - 124, 2007/06
The distribution ratio of a metal ion between an aqueous solution and an organic solution in solvent extraction with a chelating agent was evaluated by using physicochemical constants determined electrochemically such as standard Gibbs energies for transfers of the ions, the overall complex formation constants and the acid dissociation constants of the chelating agent. The distribution ratio thus evaluated agreed well with those determined by the distribution experiment.
Yoshizumi, Asuka*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Kasuno, Megumi*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Yoshida, Zenko; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 581(2), p.275 - 283, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Shirai, Osamu*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Yamana, Hajimu*; Onuki, Toshihiko; Yoshida, Yumi*; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 6(1), p.55 - 60, 2005/07
The ion transport from one aqueous phase (W1) to another (W2) across a bilayer lipid membrane (BLM) in a cell system in the presence of a hydrophobic ion or an ionophore was investigated by voltammetry. The hydrophobic ion was distributed into the BLM with the counter ion to hold the electroneutrality within the BLM. It was pointed out that the counter ion could transfer between W1 and W2 across the BLM since concentrations of the counter ion in W1, BLM and W2 were so high as to cause the ion transfer current while concentrations of the hydrophobic ion were very low. The facilitated transports of alkali ions across a BLM containing valinomycin (Val) used as an ionophore were also investigated by considering the hydrophobicity of both the objective cation and the counter anion and the formation of the alkali metal ion-Val complex..
Aoyagi, Hisao*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Yoshida, Zenko; Kihara, Sorin*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 538(1-2), p.283 - 289, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:40.83(Chemistry, Analytical)Redox behavior of Np(III), (IV), (V) and (VI) ions in aqueous perchloric, nitric and sulphuric acid solutions was elucidated by using column electrodes connected in series in a flow system. Using a glassy carbon fiber working electrode as the column electrode was found to be very useful for the investigation of current-potential relations of not only reversible redox processes such as Np(VI)/(V) or Np(IV)/(III) but also irreversible processes such as Np(V)/(IV) or Np(V)/(III), the latter not observed by conventional voltammetry which uses a glassy carbon or platinum electrode. Quantitative electrolysis could be executed even if the redox process was completely irreversible by the use of the column electrodes. By taking advantage of column electrode electrolysis, a novel method was developed for the rapid preparation of a neptunium species of a desired oxidation state, including unstable species. The multi-step column electrode system was demonstrated to be useful for the coulometric determination and speciation of Np(IV), (V) and (VI) in aqueous HNO solution as an example.
solution as an example.
Shirai, Osamu*; Yamada, Hajimu*; Onuki, Toshihiko; Yoshida, Yumi*; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 570(2), p.219 - 226, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:58.39(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Zenko; Kihara, Sorin*; Fujinaga, Taichiro*
Bunseki Kagaku, 53(4), p.195 - 205, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.80(Chemistry, Analytical)A quantitative electrolysis of an electro-active species in a sample solution can be achieved very rapidly when the solution is allowed to flow through and be electrolyzed at a column electrode. Complete electrolysis of the species is attained with a small over-voltage, even if the electrode reaction is slow. The electrolytic method using the column electrode is suitable for automated or remote-controlled operation. Because of unmatched advantages, the column-electrode electrolysis method has been widely applied to the coulometric determination of species in a flowing sample solution and to liquid chromatography as a coulometric detector. This technique is especially favorable for elucidating mechanism of such complicated reactions as that involving unstable intermediates. In the present article, a principle and a feature of the column-electrode electrolysis are presented and the advantages of these methods are reviewed based on recent works on its application to flow-injection analysis and to a study of the redox reaction of actinide ions or the reaction of short-lived radicals.
 organic solution interface
organic solution interfaceUehara, Akihiro*; Yoshida, Zenko; Yoshida, Yumi*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kasuno, Megumi*; Maeda, Koji*; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 563(2), p.257 - 267, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Aoyagi, Hisao; Kimura, Takaumi; Yoshida, Zenko; Kudo, Hiroshi*; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.3), p.259 - 262, 2002/11
Controlled-potential electrolysis (CPE) method for the transfer of an ion at the interface of two immiscible electrolyte solutions has been developed. The CPE method was applied to the transfer of actinide ions such as UO
 and Am
and Am between aqueous (W) and nitrobenzene (NB) solutions. The transfer of actinide ions from W to NB facilitated by bis(diphenyl-phosphoryl)methane (BDPPM) was studied, and it was found that CPE was successfully applied to the electrolytic separation of U(VI) and Am(III) from W to NB containing BDPPM.
between aqueous (W) and nitrobenzene (NB) solutions. The transfer of actinide ions from W to NB facilitated by bis(diphenyl-phosphoryl)methane (BDPPM) was studied, and it was found that CPE was successfully applied to the electrolytic separation of U(VI) and Am(III) from W to NB containing BDPPM.
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Yoshida, Zenko; Kudo, Hiroshi*; Kihara, Sorin*
Analytical Sciences (CD-ROM), 17(Suppl.), p.329 - 331, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Yoshida, Zenko; Kudo, Hiroshi*; Kihara, Sorin*
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 520(1-2), p.133 - 144, 2002/02
no abstracts in English
Takeishi, Hideyo; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kimura, Takaumi; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Yoshida, Zenko; Kihara, Sorin*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 431(1), p.69 - 80, 2001/03
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:67.29(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Kihara, Sorin*; Yoshida, Zenko; Aoyagi, Hisao; Maeda, Koji*; Shirai, Osamu; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Yoshida, Yumi*
Pure and Applied Chemistry, 71(9), p.1771 - 1807, 1999/09
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:83.60(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Aoyagi, Hisao; Yoshida, Zenko; Kihara, Sorin*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 387, p.181 - 187, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:39.32(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Shirai, Osamu; ; Kihara, Sorin*
Review of Polarography, 44(2), p.76 - 92, 1998/09
no abstracts in English