Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Takeshi; Muto, Shigeo; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Aoki, Kazufumi; Okamoto, Akiko; Kawakami, Takeshi; Kume, Nobuhide; Nakanishi, Chika; Koie, Masahiro; Kawamata, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-048, 69 Pages, 2015/02
JAEA was assigned as a designated public institution under the Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act and under the Armed Attack Situations Response Act. Based on these Acts, the JAEA has the responsibility of providing technical support to the national government and/or local governments in case of disaster responses or response in the event of a military attack, etc. In order to fulfill the tasks, the JAEA has established the Emergency Action Plan and the Civil Protection Action Plan. In case of a nuclear emergency, NEAT dispatches specialists of JAEA, supplies the national government and local governments with emergency equipment and materials, and gives technical advice and information. In normal time, NEAT provides various exercises and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention to those personnel taking an active part in emergency response institutions of the national and local governments, police, fire fighters, self-defense forces, etc. in addition to the JAEA itself. The NEAT also researches nuclear disaster preparedness and response, and cooperates with international organizations. In the FY2013, the NEAT accomplished the following tasks: (1) Technical support activities as a designated public institution in cooperation with the national and local governments, etc. (2) Human resource development, exercise and training of nuclear emergency response personnel for the national and local governments, etc. (3) Researches on nuclear disaster preparedness and response, and sending useful information (4) International contributions to Asian countries on nuclear disaster preparedness and response in collaboration with the international organizations

Oba, Hirofumi; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Sghaier, H.; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 57, 2008/11
no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Hanada, Masaya; Kamada, Masaki; Kobayashi, Kaoru; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Inoue, Takashi; Honda, Atsushi; Kawai, Mikito; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1519 - 1529, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:41.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The JT-60SA N-NBI system is required to inject 10 MW for 100 s at 500 keV. Three key issues should be solved for the JT-60SA N-NBI ion source. One is to improve the voltage holding capability. Recent R&D tests suggested that the accelerator with a large area of grids may need a high margin in the design of electric field and a long time for conditioning. The second issue is to reduce the grid power loading. It was found that some beamlets were strongly deflected due to beamlet-beamlet interaction and strike on the grounded grid. The grids are to be designed by taking account of beamlet-beamlet interaction in three-dimensional simulation. Third is to maintain the D- production for 100 s. A simple cooling structure is proposed for the active cooled plasma grid, where a key is the temperature gradient on the plasma grid for uniform D- production. The modified N-NBI ion source will start on JT-60SA in 2015.
Kikuchi, Katsumi; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Seki, Norikazu*; Takenouchi, Tadashi; Tanai, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2008-034, 25 Pages, 2008/04
The control system for auxiliary pumping facility and primary water cooling facility in JT-60 NBI was updated. To realize the cost reduction, the control system with many input and outputs of 2000 was updated by JAEA itself using commercial Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC's). JAEA also made software with 3600 ladder lines by JAEA itself based on commercial basic programs. In addition to the simple replacement of the hardware and software, the function of remote operation has been newly added. At present, the auxiliary pumping facility and the primary water cooling facility have been stably operated without troubles. The remote operation enables to collect the detailed information on the trouble more easily, resulting in a quick countermeasure for the trouble.
Honda, Atsushi; Okano, Fuminori; Oshima, Katsumi; Akino, Noboru; Kikuchi, Katsumi; Tanai, Yutaka; Takenouchi, Tadashi; Numazawa, Susumu*; Ikeda, Yoshitaka
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(2-3), p.276 - 279, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)The control system of the cryogenic facility in the JT-60 NBI system has been renewed by employing the PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) system. The original control system was constructed about 20 years ago by specifying the DCS (Distributed Control System) computer to deal with 400 feedback loops. Recently, troubles on this control system have increased due to its aged deterioration. To maintain a high reliability of the cryogenic facility, a new control system has been intended with PLC and SCADA system. By optimizing the function blocks and connecting them in the FBD language, the feedback loops in the new control system have been successfully replaced from DCS to PLC without software developer. At present, the new control system has worked well. This is the first application of the marketable PLC to the actual system with feedback loops of  400 produced by the user itself.
400 produced by the user itself.
 ion beams in the JT-60 negative ion source
ion beams in the JT-60 negative ion sourceHanada, Masaya; Kamada, Masaki; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Honda, Atsushi; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 79(2), p.02A519_1 - 02A519_4, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:32.32(Instruments & Instrumentation)A long pulse production of high-current, high-energy D ion beams was studied in the JT-60U negative ion source that was designed to produce 22 A, 500 keV D
ion beams was studied in the JT-60U negative ion source that was designed to produce 22 A, 500 keV D ion beams. Prior to the long pulse production, the short pulse beams were produced to examine operational ranges for a stable voltage holding capability and an allowable grid power loading. From a correlation between the voltage holding capability and a light intensity of cathodoluminescence from the insulator made of Fiber Reinforced Plastic insulator, the voltage holding was found to be stable at
ion beams. Prior to the long pulse production, the short pulse beams were produced to examine operational ranges for a stable voltage holding capability and an allowable grid power loading. From a correlation between the voltage holding capability and a light intensity of cathodoluminescence from the insulator made of Fiber Reinforced Plastic insulator, the voltage holding was found to be stable at  340 kV where the light was sufficiently suppressed. The grid power loading for the long pulse operation was also decreased to the allowable level of
340 kV where the light was sufficiently suppressed. The grid power loading for the long pulse operation was also decreased to the allowable level of  1 MW without a significant reduction of the beam power by tuning the extraction voltage (Vext) and the arc power (Parc). These allow the production of 30 A D
1 MW without a significant reduction of the beam power by tuning the extraction voltage (Vext) and the arc power (Parc). These allow the production of 30 A D ion beams at 340 keV from two ion sources at Vacc = 340 kV. The pulse length was extended step by step, and finally reached up to 21 s, where the beam pulse length was limited by the surface temperature of the beam scraper without water cooling. The D
ion beams at 340 keV from two ion sources at Vacc = 340 kV. The pulse length was extended step by step, and finally reached up to 21 s, where the beam pulse length was limited by the surface temperature of the beam scraper without water cooling. The D ion beams were neutralized to via a gas cell, resulting in a long pulse injection of 3.2 MW D
ion beams were neutralized to via a gas cell, resulting in a long pulse injection of 3.2 MW D beams for 21 s. This is the first long injection of
beams for 21 s. This is the first long injection of  20 s in a power range of
20 s in a power range of  3 MW.
3 MW.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Hanada, Masaya; Inoue, Takashi; Honda, Atsushi; Kamada, Masaki; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(5-14), p.791 - 797, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:80.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Modification of JT-60U to a superconducting device (so called JT-60SA) has been planned to contribute to ITER and DEMO. The NBI system is required to inject 34 MW for 100 s. The upgraded NBI system consists of twelve positive ion based NBI (P-NBI) units and one negative ion based NBI (N-NBI) unit. The injection power of the P-NBI units are 2 MW each at 85 keV, and the N-NBI unit will be 10 MW at 500 keV, respectively. On JT-60U, the long pulse operation of 30 s at 2 MW (85 keV) and 20 s at 3.2 MW (320 keV) have been achieved on P-NBI and N-NBI units, respectively. Since the temperature increase of the cooling water in both ion sources is saturated within 20 s, further pulse extension up to 100 s is expected to mainly modify the power supply systems in addition to modification of the N-NBI ion source for high acceleration voltage. The detailed technical design of the NBI system for JT-60SA is presented.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Grisham, L. R.*; Hanada, Masaya; Honda, Atsushi; Inoue, Takashi; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(6), p.S211 - S219, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:87.2(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recently, the extension of the pulse duration up to 30 sec has been intended to study quasi-steady state plasma on JT-60U N-NBI system. The most serious issue is to reduce the heat load on the grids for long pulse operation. Two modifications have been proposed to reduce the heat load. One is to suppress the beam spread which may be caused by beamlet-beamlet interaction in the multi-aperture grid due to the space charge force. Thin plates were attached on the extraction grid to modify the local electric field. The plate thickness was optimized to steer the beamlet deflection. The other is to reduce the stripping loss, where the electron of the negative ion beam is stripped and accelerated in the ion source and then collides with the grids. The ion source was modified to reduce the pressure in the accelerator column to suppress the beam-ion stripping loss. Up to now, long pulse injection of 17 sec for 1.6 MW and 25 sec for  1 MW has been obtained by one ion source with these modifications.
1 MW has been obtained by one ion source with these modifications.
Honda, Atsushi; Okano, Fuminori; Oshima, Katsumi; Akino, Noboru; Kikuchi, Katsumi; Tanai, Yutaka; Takenouchi, Tadashi; Numazawa, Susumu*
JAEA-Technology 2006-020, 20 Pages, 2006/03
no abstracts in English
Kikuchi, Katsumi*; Akino, Noboru; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Oga, Tokumichi; Oshima, Katsumi*; Okano, Fuminori; Takenouchi, Tadashi*; Tanai, Yutaka*; Honda, Atsushi
Heisei-16-Nendo Osaka Daigaku Sogo Gijutsu Kenkyukai Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
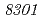 in the radioresistant bacterium
in the radioresistant bacterium 
Islam, M. S.*; Hua, Y.*; Oba, Hirofumi; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Narumi, Issei
Genes and Genetic Systems, 78(5), p.319 - 327, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:27.6(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English
Li, J.-F.*; Kawai, Masayoshi*; Kikuchi, Kenji; Igarashi, Tadashi*; Kurishita, Hiroaki*; Watanabe, Ryuzo*; Kawasaki, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 321(2-3), p.129 - 134, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:66.94(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)For the development of tantalum-clad tungsten targets for spallation neutron sources, the bonding strength of tantalum-tungsten interface was investigated by means of an easy-to-use and miniaturized small punch (SP) test, in which a punching load is vertically applied to the center of a jointed disk. Cracks initiated and propagated in the tungsten side for all the samples hot-isostatically pressed (HIPed) at temperatures from 1673 to 2073 K, whereas nocrack and debonding were observed in the interface, indicating that the jointed interface is strongly bonded. The re-crystallization of tungsten occurs and results in its strength reduction, consequently the crack-initiating load decreases with HIPing temperature. The finite element analysis of the measured SP testing results shows that the maximum bonding strength can exceed 1000 MPa. The present study shows that SP test is suitable for the strength evaluation of jointed tantalum-tungsten interfaces.
Kawai, Masayoshi*; Furusaka, Michihiro; Li, J.-F.*; Kawasaki, Akira*; Yamamura, Tsutomu*; Mehmood, M.*; Kurishita, Hiroaki*; Kikuchi, Kenji; Takenaka, Nobuyuki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 3, p.1087 - 1096, 2003/07
In order to establish the technique fabricating a thin target slab with a real size, thin tantalum-clad tungsten slab with a hole for a thermocouple was fabricated with the high-precision machinery techniques and the HIP'ing method. The ultrasonic diagnostic showed that tantalum and tungsten bond was perfect. The HIP optimum condition was certified by means of the small punch test as already reported. The electrolytic coating technique in a molten salt was developed to make a thinner tantalum cladding on a tungsten target with a complicated shape, in order to reduce radioactivity from tantalum in an irradiated target.
Kawai, Masayoshi*; Furusaka, Michihiro*; Kikuchi, Kenji; Kurishita, Hiroaki*; Watanabe, Ryuzo*; Li, J.*; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*; Yamamura, Tsutomu*; Hiraoka, Yutaka*; Abe, Katsunori*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 318, p.35 - 55, 2003/05
R&D works for MW class solid target composed of tungsten to produce pulsed intense neutron source has been made in order to construct a future scattering facility. Three methods were investigated to prevent corrosion of tungsten from water; those are hipping, brazing and electric coating in molten salt bath. Hipping condition was optimized to be 1500 degree C in the previous work: here small punch test shows highest load for crack initiation of hipped materials at the boundary of W/Ta. The basic techniques for the other two methods were developed. Erosion test showed that uncovered W is susceptible of flowing water velocity. At high velocity w is easy to be eroded. For solid target design slab type and rod type targets were studied. As long as the optimized neutron performance is concerned, 1MW solid target is better than mercury target.
Kawai, Masayoshi*; Li, J.*; Watanabe, Ryuzo*; Kurishita, Hiroaki*; Kikuchi, Kenji; Igarashi, Tadashi*; Kato, Masahiro*
Dai-23-Kai Nihon Netsu Bussei Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.313 - 315, 2002/11
The objective of the present study is to develop the stainless-steel-bonded tungsten alloys by powder metallurgy processes. Commercially available tungsten powders and stainless steel (SUS304L) powder were used as the raw materials and mixed by ball milling at the ratios of 97mass% W -3% SUS and 93mass% W -7mass% SUS. Powder compacts were formed by die pressing and cold isostatic pressing (CIP), then sintered mainly in vacuum at the temperatures above the melting point of the stainless steel phase. Some samples were fabricated by glass-encapsulated hot isostatic pressing (HIPing) at lower temperatures. The microstructural observation was made by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The thermal properties of the produced alloy and various tungsten materials supplied from Allied Material Corp. was measured with the laser-frash method. It was found that stable liquid-phase-sintered microstructures were not easily formed in the tungsten-stainless steel system. The electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) revealed that tungsten was considerably dissolved in the stainless steel phase during sintering. Therefore, thermal conductivity of the W/7 mass% SUS alloy was 22.8-53.5 W/m/K that was very lower than theoretical value calculated from those of pure tungsten and stainless steel. Its temperature dependence is resembled to that of stainless steel, i.e., thermal conductivity increased with the specimen temperature as like stainless steel. The diffusivity of pure tungsten is compared with those of tungsten alloys.

Sato, Katsuya; Narumi, Issei; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kitayama, Shigeru; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Yamamoto, Kazuo; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Journal of Biochemistry, 131(1), p.121 - 129, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:38.61(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)RecA protein is considered to be the most important participant in the radiation resistance of  . We identified a new
. We identified a new  mutation (
mutation (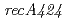 ) in the DNA-repair deficient mutant strain KI696, the phenotype of which is remarkably different from mutant strain rec30 carrying
) in the DNA-repair deficient mutant strain KI696, the phenotype of which is remarkably different from mutant strain rec30 carrying 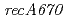 . In vitro, neither RecA424 nor RecA670 could promote DNA strand exchange, indicating that both RecA424 and Rec670 are defective in recombination activity. RecA424 promoted the autocleavage reaction of LexA in vitro, whereas RecA670 did not. The LexA level in KI696 was decreased following
. In vitro, neither RecA424 nor RecA670 could promote DNA strand exchange, indicating that both RecA424 and Rec670 are defective in recombination activity. RecA424 promoted the autocleavage reaction of LexA in vitro, whereas RecA670 did not. The LexA level in KI696 was decreased following  -irradiation. However, the LexA level in strain rec30 was constant irrespective of irradiation. These results indicate that RecA424 retains co-protease activity, whereas RecA670 does not. While strain rec30 is extremely radiation sensitive, strain KI696 is only slightly sensitive. Together, these observations suggest that the co-protease activity rather than the recombination activity of RecA contributes to the radiation resistance in
-irradiation. However, the LexA level in strain rec30 was constant irrespective of irradiation. These results indicate that RecA424 retains co-protease activity, whereas RecA670 does not. While strain rec30 is extremely radiation sensitive, strain KI696 is only slightly sensitive. Together, these observations suggest that the co-protease activity rather than the recombination activity of RecA contributes to the radiation resistance in  .
.
 is not involved in RecA induction following
is not involved in RecA induction following  irradiation
irradiationNarumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Journal of Bacteriology, 183(23), p.6951 - 6956, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:89 Percentile:83.76(Microbiology)The involvement of LexA in induction of RecA was investigated in  . As in the wild-type strain, an increase in RecA protein synthesis following
. As in the wild-type strain, an increase in RecA protein synthesis following  irradiation was detected in a
irradiation was detected in a 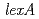 disruptant, indicating that LexA is not involved in the induction of RecA in
disruptant, indicating that LexA is not involved in the induction of RecA in  .
.
Sato, Toshinori; Kikuchi, Tadashi; Sugihara, Kozo
Engineering Geology, 56(1-2), p.97 - 108, 2000/00
Times Cited Count:103 Percentile:90.38(Engineering, Geological)None
Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Kitayama, Shigeru; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Mutation Research; DNA Repair, 435(3), p.233 - 243, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Sato, Toshinori; Matsui, Hiroya; Kikuchi, Tadashi; Sugihara, Kozo
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.506, p.813 - 820, 1998/00
None