Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Namie, Masanari; Saito, Junichi; Oka, Ryotaro*; Kim, J.-H.*
Vacuum, 234, p.114038_1 - 114038_9, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Namie, Masanari; Saito, Junichi; Ikeda, Asuka; Oka, Ryotaro*; Kim, J.-H.*
Surfaces (Internet), 7(3), p.550 - 559, 2024/09
 TaS
TaS
Park, P.*; Cho, W.*; Kim, C.*; An, Y.*; Avdeev, M.*; Iida, Kazuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Park, J.-G.*
Physical Review B, 109(6), p.L060403_1 - L060403_7, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Liao, L.*; Puebla, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Kim, J.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Hwang, Y.*; Ba, Y.*; Otani, Yoshichika*
Physical Review Letters, 131(17), p.176701_1 - 176701_6, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:79.13(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Mun, M.-H.*; Shin, I. J.*; Paeng, W.-G.*; Harada, Masayasu*; Kim, Y.*
European Physical Journal A, 59(7), p.149_1 - 149_6, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:67.28(Physics, Nuclear)Yasue, Ayumu*; Kawakami, Mayu*; Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Kim, J.*; Miyazu, Yuji*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Mukai, Tomohisa*; Morooka, Satoshi; Kanematsu, Manabu*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.15_1 - 15_14, 2023/05
Hosokawa, Takayuki*; Yasue, Ayumu*; Kim, J.*; Kurita, Keisuke; Kanematsu, Manabu*
Konkurito Kozobutsu No Hoshu, Hokyo, Appuguredo Rombun Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 22, p.113 - 118, 2022/10
no abstracts in English
Fukaya, Yuki; Zhao, Y.*; Kim, H.-W.*; Ahn, J.-R.*; Fukidome, Hirokazu*; Matsuda, Iwao*
Physical Review B, 104(18), p.L180202_1 - L180202_5, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:70.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of nuclear facilities being decommissioned has been increasing worldwide, in particular following the accident of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011. In these nuclear facilities, proper management of radioactive materials is required. Then, A  -ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr
-ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr scintillators with a dimension of
scintillators with a dimension of 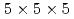
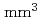 was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the
was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the  -ray exposure study under
-ray exposure study under  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields. Under the
Co radiation fields. Under the  Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2
Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0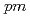 0.03%, and 9.0
0.03%, and 9.0 0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioningKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:84.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)An increasing number of nuclear facilities have been decommissioned worldwide following the 2011 accident of the TEPCO' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. During the decommissioning, radioactive materials have to be retrieved under proper management. In this study, a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm was manufactured to perform
5 mm was manufactured to perform  -ray spectroscopy under intense
-ray spectroscopy under intense  -ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform
-ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform  -ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a
-ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a  Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a
Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a  Co radiation field, which suggested to realize
Co radiation field, which suggested to realize  -ray assessment of
-ray assessment of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Gens, A.*; Alcoverro, J.*; Blaheta, R.*; Hasal, M.*; Michalec, Z.*; Takayama, Yusuke; Lee, C.*; Lee, J.*; Kim, G. Y.*; Kuo, C.-W.*; et al.
International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 137, p.104572_1 - 104572_19, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:87.36(Engineering, Geological)Bentonite-based engineered barriers are a key component of many repository designs for the confinement of high-level radioactive waste and spent fuel. Given the complexity and interaction of the phenomena affecting the barrier, coupled hydro-mechanical (HM) and thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) numerical analyses are a potentially useful tool for a better understanding of their behaviour. In this context, a Task (INBEB) was undertaken to study, using numerical analyses, the hydro-mechanical and thermohydro-mechanical Interactions in Bentonite Engineered Barriers within the international cooperative project DECOVALEX 2019. Two large scale tests, largely complementary, were selected for modelling: EB and FEBEX. The EB experiment was carried out under isothermal conditions and artificial hydration and it was dismantled after 10.7 years. The FEBEX test was a temperature-controlled non-isothermal test combined with natural hydration that underwent two dismantling operations, a partial one after 5 years of heating and a final one after a total of 18.4 years of heating. Direct observation of the state of the barriers was possible during the dismantling operations. Four teams performed the HM and THM numerical analyses using a variety of computer codes, formulations and constitutive laws. For each experiment, the basic features of the analyses are described and the comparison between calculations and field observations are presented and discussed. Comparisons involve measurements performed during the performance of the test and data gathered during dismantling. A final evaluation of the performance of the modelling closes the paper.
Gens, A.*; Alcoverro, J.*; Blaheta, R.*; Hasal, M.*; Michalec, Z.*; Takayama, Yusuke; Lee, C.*; Lee, J.*; Kim, G. Y.*; Kuo, C.-W.*; et al.
LBNL-2001267 (Internet), 210 Pages, 2020/10
This document is the final report of Task D of the DECOVALEX-2019 project, presenting the definitions of the problems studied, approaches applied, achievements made and outstanding issues identified for future research. Task D of the DECOVALEX 2019 project is devoted to the study of the hydro-mechanical and thermo-hydro-mechanical Interactions in Bentonite Engineered Barriers. The Task is structured around two large scale in situ experiments that were subjected to well managed dismantling operations that provided direct observations of the state of the barrier after long test periods. Four teams carried out the modelling of the two experiments: Institute of Geonics, of the Czech Academy of Sciences (IGN), supported by SURAO, Czech Republic, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI) and National Central University of Taiwan (NCU), supported by the Taipower.
 gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Otaka, Yutaka*; Uenomachi, Mizuki*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 971, p.164118_1 - 164118_8, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:60.25(Instruments & Instrumentation) meson with finite momentum in a dense medium
meson with finite momentum in a dense mediumKim, H.-J.*; Gubler, P.
Physics Letters B, 805, p.135412_1 - 135412_8, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:87.95(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The dispersion relation of the  meson in nuclear matter is studied in a QCD sum rule approach. In a dense medium, longitudinal and transverse modes of vector particles can have independently modified dispersion relations due to broken Lorentz invariance. Employing the full set of independent operators and corresponding Wilson coefficients up to operator dimension-6, the
meson in nuclear matter is studied in a QCD sum rule approach. In a dense medium, longitudinal and transverse modes of vector particles can have independently modified dispersion relations due to broken Lorentz invariance. Employing the full set of independent operators and corresponding Wilson coefficients up to operator dimension-6, the  meson QCD sum rules are analyzed with changing densities and momenta. The non-trivial momentum dependence of the
meson QCD sum rules are analyzed with changing densities and momenta. The non-trivial momentum dependence of the  meson mass is found to have opposite signs for the longitudinal and transverse modes. Specifically, the mass is reduced by 5 MeV for the longitudinal mode, while its increase amounts to 7 MeV for the transverse mode, both at a momentum scale of 1 GeV. In an experiment which does not distinguish between longitudinal and transverse polarizations, this could in principle be seen as two separated peaks at large momenta.
meson mass is found to have opposite signs for the longitudinal and transverse modes. Specifically, the mass is reduced by 5 MeV for the longitudinal mode, while its increase amounts to 7 MeV for the transverse mode, both at a momentum scale of 1 GeV. In an experiment which does not distinguish between longitudinal and transverse polarizations, this could in principle be seen as two separated peaks at large momenta.
 dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy
dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopySong, C.*; Seo, O.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Hiroi, Satoshi*; Cui, Y.-T.*; Kim, J.*; Chen, Y.*; Tayal, A.*; Kusada, Kohei*; Kobayashi, Hirokazu*; et al.
RSC Advances (Internet), 10(34), p.19751 - 19758, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kim, J.*; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Murayama, Ichiro*; Kato, Takanori*; Sakamoto, Tomokazu*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Sekino, Toru*; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Takeda, Masatoshi*; et al.
Sustainable Energy & Fuels (Internet), 4(3), p.1143 - 1149, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:63.45(Chemistry, Physical)Hasegawa, Kunio; Li, Y.; Kim, Y.-J.*; Lacroix, V.*; Strnadel, B.*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 141(3), p.031201_1 - 031201_5, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.80(Engineering, Mechanical)When discrete multiple flaws are in the same plane, and they are close to each other, it can be determined whether they are combined or standalone in accordance with combination rules provided by Fitness-For-Service (FFS) codes. However, specific criteria of the rules are different amongst these FFS codes. On the other hand, plastic collapse bending stresses for stainless steel pipes with two circumferential similar flaws were obtained by experiments and the prediction procedure for collapse stresses for pipes with two similar flaws were developed analytically. Using the experimental data and the analytical procedure, plastic collapse stresses for pipes with two similar flaws are compared with the stresses in compliance with the flaw combination criteria. It is shown that the calculated plastic collapse stresses based on the flaw combination criteria are significantly different from the experimental and analytical stresses.
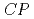 violation with kinematic asymmetries in the
violation with kinematic asymmetries in the 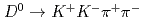 decay
decayKim, J. B.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 182 of others*
Physical Review D, 99(1), p.011104_1 - 011104_7, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Kim, B.-J.*; Sasaki, Miyuki; Sanada, Yukihisa
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.130 - 133, 2019/01
Kim, J.*; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Nakajima, Akira*; Kato, Takanori*; Kim, Y.*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yoshii, Kenji; Nishihata, Yasuo; Baba, Masaaki*; Takeda, Masatoshi*; et al.
Advanced Sustainable Systems (Internet), 2(11), p.1800067_1 - 1800067_8, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:26.72(Green & Sustainable Science & Technology)