Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugita, Yutaka; Ono, Hirokazu; Beese, S.*; Pan, P.*; Kim, M.*; Lee, C.*; Jove-Colon, C.*; Lopez, C. M.*; Liang, S.-Y.*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100668_1 - 100668_21, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)The international cooperative project DECOVALEX 2023 focused on the Horonobe EBS experiment in the Task D, which was undertaken to study, using numerical analyses, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (or thermo-hydro) interactions in bentonite based engineered barriers. One full-scale in-situ experiment and four laboratory experiments, largely complementary, were selected for modelling. The Horonobe EBS experiment is a temperature-controlled non-isothermal experiment combined with artificial groundwater injection. The Horonobe EBS experiment consists of the heating and cooling phases. Six research teams performed the THM or TH (depended on research team approach) numerical analyses using a variety of computer codes, formulations and constitutive laws.
Kim, M.*; Lee, C.*; Sugita, Yutaka; Kim, J.-S.*; Jeon, M.-K.*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 41, p.100628_1 - 100628_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)This study investigates the impact of primary variables selection on the modeling of non-isothermal two-phase flow, by using the numerical work on the full-scale Engineered Barrier System (EBS) experiment conducted at Horonobe URL as part of the DECOVALEX-2023 project. A validated numerical model is employed to simulate the coupled thermo-hydrological behavior of heterogeneous porous media within the EBS. Two different primary variable schemes are compared in discretizing the governing equations, revealing significant difference in results.

Chung, J.-H.*; Kwangwoo, S.*; Yokoo, Tetsuya R.; Ueta, Daichi*; Imai, Masaki; Kim, H.-S.; Kiem, D. H.; Han, M. J.*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Scientific Reports (Internet), 15, p.5978_1 - 5978_10, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Cho, S. H.*; Cho, S. W.*; Lv, Z.*; Sekine, Yurina; Liu, S.*; Zhou, M.*; Nuxoll, R. F.*; Kanatzidis, E. E.*; Ghaffari, R.*; Kim, D.*; et al.
Lab on a Chip, 9 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Biochemical Research Methods)Amino acids are essential for protein synthesis and metabolic processes in support of homeostatic balance and healthy body functions. This study quantitatively investigates eccrine sweat as a significant channel for loss of amino acids during exercise, to improve an understanding of amino acid turnover and to provide feedback to users on the need for supplement intake. The measurement platform consists of a soft, skin-interfaced microfluidic system for real-time analysis of amino acid content in eccrine sweat. This system relies on integrated fluorometric assays and smartphone-based imaging techniques for quantitative analysis.
 signatures in two-dimensional cone beam interferometry
signatures in two-dimensional cone beam interferometrySarenac, D.*; Gorbet, G.*; Clark, C. W.*; Cory, D. G.*; Ekinci, H.*; Henderson, M. E.*; Huber, M. G.*; Hussey, D. S.*; Kapahi, C.*; Kienzle, P. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(3), p.L032054_1 - L032054_8, 2024/09
Peri
 ez, R.*; Bezhenar, R.*; Maderych, V.*; Brovchenko, I.*; Liptak, L.*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Min, B.-I.*; Suh, K. S.*; Little, A.*; Iosjpe, M.*; et al.
ez, R.*; Bezhenar, R.*; Maderych, V.*; Brovchenko, I.*; Liptak, L.*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Min, B.-I.*; Suh, K. S.*; Little, A.*; Iosjpe, M.*; et al.
IAEA-TECDOC-2060, 55 Pages, 2024/07
This publication describes the work undertaken by Working Group 7, Assessment of Fate and Transport of Radionuclides Released in the Marine Environment of the IAEA's Modelling and Data for Radiological Impact Assessments (MODARIA II) programme (2016-2019). In MODARIA II, the degree of complexity of the models used was increased in order to effectively consider additional processes, specifically uptake by biota, and the spatiotemporal scales of the simulations were also expanded.
Kim, J.*; Thompson, B. R.*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Osawa, Takahito; Egami, Takeshi*; F rster, S.*; Ohl, M.*; Senses, E.*; Faraone, A.*; Wagner, N. J.*
rster, S.*; Ohl, M.*; Senses, E.*; Faraone, A.*; Wagner, N. J.*
ACS Macro Letters (Internet), 13(6), p.720 - 725, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:28.80(Polymer Science)The Rouse dynamics of polymer chains in model nanocomposite PolyEthylene Oxide (PEO)/Silica NanoParticles (NPs) was investigated using QuasiElastic Neutron Scattering (QENS). The apparent Rouse rate of the polymer chains decreases as the particle loading increases. However, there is no evidence of an immobile segment population on the probed time scale of tens of ps. The slowing down of the dynamics is interpreted in terms of modified Rouse models for the chains in the NP inter-phase region. Thus, two chain populations, one bulk like and the other characterized by a suppression of Rouse modes, are identified. The spatial extent of the interphase region is estimated to be about twice the adsorbed layer thickness, or about 2 nm. These findings provide a detailed description of the suppression of the chain dynamics on the surface of NPs. These results are relevant insights on surface effects and confinement and provide a foundation for the understanding of the rheological properties of Polymer NanoComposites (PNCs) with well-dispersed NPs.
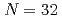
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Watabe, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yu, K. N.*; Zivkovic, M.*; Krstic, D.*; Nikezic, D.*; Kim, K. M.*; Yamaya, Taiga*; Kawachi, Naoki*; Tanaka, Hiroki*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(2), p.130 - 142, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Environmental Sciences)Previously, we have developed DynamicMC for modelling relative movement of ORNL phantom in a radiation field for MCNP. Using this software, 3-dimensional dose distributions in a phantom irradiated by a certain mono-energetic source can be deduced through its graphical user interface (GUI). In this study, we extended DynamicMC to be used in combination with the PHITS by providing it with a higher flexibility for dynamic movement for a less sophisticated anthropomorphic phantom. We anticipate that the present work and the developed open-source tools will be in the interest of nuclear radiation physics community for research and teaching purposes.
Kim, G.*; Cho, S.-M.*; Im, S.*; Suh, H.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Shobu, Takahisa; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Machida, Akihiko*; Bae, S.*
Construction and Building Materials, 411, p.134529_1 - 134529_18, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:67.40(Construction & Building Technology) TaS
TaS
Park, P.*; Cho, W.*; Kim, C.*; An, Y.*; Kang, Y.-G.*; Avdeev, M.*; Sibille, R.*; Iida, Kazuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Lee, K. H.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.8346_1 - 8346_9, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:86.45(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yang, D. S.*; Wu, Y.*; Kanatzidis, E. E.*; Avila, R.*; Zhou, M.*; Bai, Y.*; Chen, S.*; Sekine, Yurina; Kim, J.*; Deng, Y.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(11), p.4992 - 5003, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:78.05(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)This paper presents a set of findings that enhances the performance of these systems through the use of microfluidic networks, integrated valves and microscale optical cuvettes formed by three-dimensional printing in hard/soft hybrid materials systems, for accurate spectroscopic and fluorometric assays. Field studies demonstrate the capability of these microcuvette systems to evaluate the concentrations of copper, chloride, and glucose in sweat, along with the sweat pH, with laboratory grade accuracy and sensitivity.
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
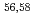 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:89.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 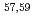 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 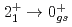 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 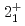 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 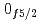 and
and 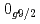 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:67.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Kwon, H.*; Sathiyamoorthi, P.*; Gangaraju, M. K.*; Zargaran, A.*; Wang, J.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Lee, B.-J.*; Kim, H. S.*
Acta Materialia, 248, p.118810_1 - 118810_12, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:99.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:87.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
Woo, W.*; Kim, Y. S.*; Chae, H. B.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Jeong, J. S.*; Lee, C. M.*; Won, J. W.*; Na, Y. S.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; et al.
Acta Materialia, 246, p.118699_1 - 118699_13, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:99.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)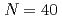 island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in
island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in  V and
V and  V
VElekes, Z.*; Juh sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064321_1 - 064321_10, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.00(Physics, Nuclear)The low-lying level structure of  V and
V and  V was investigated for the first time. The neutron knockout reaction and inelastic proton scattering were applied for
V was investigated for the first time. The neutron knockout reaction and inelastic proton scattering were applied for  V while the neutron knock-out reaction provided the data for
V while the neutron knock-out reaction provided the data for  V. Four and five new transitions were determined for
V. Four and five new transitions were determined for  V and
V and  V, respectively. Based on the comparison to our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS) interaction, three of the observed
V, respectively. Based on the comparison to our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS) interaction, three of the observed  rays for each isotope could be placed in the level scheme and assigned to the decay of the first 11/2
rays for each isotope could be placed in the level scheme and assigned to the decay of the first 11/2 and 9/2
and 9/2 levels. The (
levels. The ( ,
,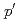 ) excitation cross sections for
) excitation cross sections for  V were analyzed by the coupled-channels formalism assuming quadrupole plus hexadecapole deformations. Due to the role of the hexadecapole deformation,
V were analyzed by the coupled-channels formalism assuming quadrupole plus hexadecapole deformations. Due to the role of the hexadecapole deformation,  V could not be unambiguously placed on the island of inversion.
V could not be unambiguously placed on the island of inversion.
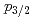 neutron orbital and the
neutron orbital and the 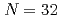 shell closure in
shell closure in  Ca
CaEnciu, M.*; Liu, H. N.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Poves, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 129(26), p.262501_1 - 262501_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:86.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The one-neutron knockout from  Ca was performed at
Ca was performed at  230 MeV/nucleon combined with prompt
230 MeV/nucleon combined with prompt  spectroscopy. The momentum distributions corresponding to the removal of
spectroscopy. The momentum distributions corresponding to the removal of 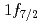 and
and 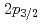 neutrons were measured. The cross sections are consistent with a shell closure at the neutron number
neutrons were measured. The cross sections are consistent with a shell closure at the neutron number 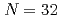 , found as strong as at
, found as strong as at 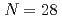 and
and 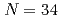 in Ca isotopes from the same observables. The analysis of the momentum distributions leads to a difference of the root-mean-square radii of the neutron
in Ca isotopes from the same observables. The analysis of the momentum distributions leads to a difference of the root-mean-square radii of the neutron 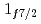 and
and 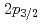 orbitals of 0.61(23) fm, in agreement with the modified-shell-model prediction of 0.7 fm suggesting that the large root-mean-square radius of the
orbitals of 0.61(23) fm, in agreement with the modified-shell-model prediction of 0.7 fm suggesting that the large root-mean-square radius of the 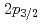 orbital in neutron-rich Ca isotopes is responsible for the unexpected linear increase of the charge radius with the neutron number.
orbital in neutron-rich Ca isotopes is responsible for the unexpected linear increase of the charge radius with the neutron number.