Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Aoki, Dai*; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(14), p.L140502_1 - L140502_6, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:86.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The normal-conducting state of the superconductor UTe is studied by entropy analysis for magnetic fields along the
is studied by entropy analysis for magnetic fields along the  -axis, obtained from magnetization using the relation
-axis, obtained from magnetization using the relation 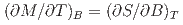 . We observe a strong increase in entropy with magnetic field due to metamagnetic fluctuations (spatially uniform,
. We observe a strong increase in entropy with magnetic field due to metamagnetic fluctuations (spatially uniform, 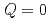 ). The field dependence is well described by the Hertz-Millis-Moriya theory for quantum criticality of itinerant metamagnetism. Notably, the lower bound of the quantum-critical region coincides well with the position of the minimum in the superconducting transition temperature
). The field dependence is well described by the Hertz-Millis-Moriya theory for quantum criticality of itinerant metamagnetism. Notably, the lower bound of the quantum-critical region coincides well with the position of the minimum in the superconducting transition temperature 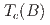 . Hence, our results suggest that
. Hence, our results suggest that 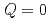 fluctuations reinforce the superconductivity.
fluctuations reinforce the superconductivity.

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Opletal, P.; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Yanase, Yoichi*; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(14), p.144502_1 - 144502_5, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:64.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The vortex dynamics in the spin-triplet superconductor, UTe , are studied by measuring the DC electrical resistivity with currents along the
, are studied by measuring the DC electrical resistivity with currents along the  -axis under magnetic fields along the
-axis under magnetic fields along the  -axis. Surprisingly, we have discovered an island region of low critical current deep inside the superconducting (SC) state, well below the SC upper critical field, attributed to a weakening of vortex pinning. Notably, this region coincides with the recently proposed intermediate-field SC state. We discuss the possibility of nonsingular vortices in the intermediate state, where SC order parameter does not vanish entirely in the vortex cores due to the mixing of multiple SC components.
-axis. Surprisingly, we have discovered an island region of low critical current deep inside the superconducting (SC) state, well below the SC upper critical field, attributed to a weakening of vortex pinning. Notably, this region coincides with the recently proposed intermediate-field SC state. We discuss the possibility of nonsingular vortices in the intermediate state, where SC order parameter does not vanish entirely in the vortex cores due to the mixing of multiple SC components.
 along hard magnetic axis
along hard magnetic axisSakai, Hironori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Aoki, Dai*; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori
Physical Review Letters, 130(19), p.196002_1 - 196002_6, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:96.14(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The superconducting (SC) phase diagram in uranium ditelluride is explored under magnetic fields ( ) along the hard magnetic
) along the hard magnetic  -axis using a high-quality single crystal with
-axis using a high-quality single crystal with  = 2.1 K. Simultaneous electrical resistivity and AC magnetic susceptibility measurements discern low- and high-field SC (LFSC and HFSC, respectively) phases with contrasting field-angular dependence. Crystal quality increases the upper critical field of the LFSC phase, but the
= 2.1 K. Simultaneous electrical resistivity and AC magnetic susceptibility measurements discern low- and high-field SC (LFSC and HFSC, respectively) phases with contrasting field-angular dependence. Crystal quality increases the upper critical field of the LFSC phase, but the 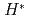 of
of 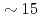 T, at which the HFSC phase appears, is always the same through the various crystals. A phase boundary signature is also observed inside the LFSC phase near
T, at which the HFSC phase appears, is always the same through the various crystals. A phase boundary signature is also observed inside the LFSC phase near 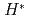 , indicating an intermediate SC phase characterized by small flux pinning forces.
, indicating an intermediate SC phase characterized by small flux pinning forces.
 induced by magnetic field
induced by magnetic fieldKinjo, Katsuki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Physical Review B, 107(6), p.L060502_1 - L060502_5, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:92.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) anisotropic triangular antiferromagnet Ca
anisotropic triangular antiferromagnet Ca ReO
ReO Cl
Cl
Nawa, Kazuhiro*; Hirai, Daigoro*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Murasaki, Ryo*; Kogane, Satoshi*; Kimata, Motoi*; Nojiri, Hiroyuki*; Hiroi, Zenji*; Sato, Taku*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(4), p.043121_1 - 043121_11, 2020/12
The spin excitations of the  =
=  anisotropic triangular antiferromagnet Ca
anisotropic triangular antiferromagnet Ca ReO
ReO Cl
Cl were investigated by inelastic neutron-scattering experiments. The spin excitation spectrum exhibits sharp dispersive modes in addition to a spinonlike continuum. The consistency with the simulated spectrum based on the random-phase approximation is better for Ca
were investigated by inelastic neutron-scattering experiments. The spin excitation spectrum exhibits sharp dispersive modes in addition to a spinonlike continuum. The consistency with the simulated spectrum based on the random-phase approximation is better for Ca ReO
ReO Cl
Cl than for Cs
than for Cs CuCl
CuCl , indicating that the spin system in the former remains closer to a Tomonaga-Luttinger liquidlike disordered state.
, indicating that the spin system in the former remains closer to a Tomonaga-Luttinger liquidlike disordered state.
Niimi, Yasuhiro*; Kimata, Motoi*; Omori, Yasutomo*; Gu, B.; Ziman, T.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Fert, A.*; Otani, Yoshichika*
Physical Review Letters, 115(19), p.196602_1 - 196602_5, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Haga, Yoshinori; Sakai, Hironori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Kimata, Motoi*; Nakamura, Shintaro*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Aoki, Dai*; Kambe, Shinsaku; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
In unconventional superconductors, there are cases of vortex liquid-like state. When the pinning is strong, vortices do not move, and thus, the formation of such abnormal states requires pure and pristine crystals. Recently, the growth of pure single crystals of the spin-triplet superconductor UTe using a molten salt flux has been reported. In this study, we report research on vortices in UTe
using a molten salt flux has been reported. In this study, we report research on vortices in UTe using such pure single crystals. As a result, in the magnetic field range of 15 T to 22 T, the critical current showed a maximum in temperature dependence, and a low-temperature region with a low critical current was observed deep in the superconducting state. This low critical current region matches the recently reported intermediate field superconducting phase. This suggests a weakening of the pinning force and a decrease in the critical current in the intermediate field superconducting phase.
using such pure single crystals. As a result, in the magnetic field range of 15 T to 22 T, the critical current showed a maximum in temperature dependence, and a low-temperature region with a low critical current was observed deep in the superconducting state. This low critical current region matches the recently reported intermediate field superconducting phase. This suggests a weakening of the pinning force and a decrease in the critical current in the intermediate field superconducting phase.

Sakai, Hironori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Aoki, Dai*; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
We have recently developed and optimized a molten salt flux method for growing high-purity single crystals of the superconductor UTe . The obtained crystals show a remarkably large residual resistivity ratio to the room temperature value and a small residual electronic contribution in specific heat well below
. The obtained crystals show a remarkably large residual resistivity ratio to the room temperature value and a small residual electronic contribution in specific heat well below  . Using the high-quality single crystal of UTe
. Using the high-quality single crystal of UTe , we have explored the superconducting phase diagram under magnetic fields along the hard magnetic
, we have explored the superconducting phase diagram under magnetic fields along the hard magnetic  -axis. Simultaneous electrical resistivity and AC magnetic susceptibility measurements discern low- and high-field SC (LFSC and HFSC, respectively) phases with contrasting field-angular dependence. Crystal quality increases the upper critical field of the LFSC phase, but the characteristic field of
-axis. Simultaneous electrical resistivity and AC magnetic susceptibility measurements discern low- and high-field SC (LFSC and HFSC, respectively) phases with contrasting field-angular dependence. Crystal quality increases the upper critical field of the LFSC phase, but the characteristic field of  15 T, at which the HFSC phase appears, is always the same through the various crystals. A phase boundary signature is also observed inside the LFSC phase near the characteristic field of 15 T, indicating an intermediate SC phase characterized by small flux pinning forces.
15 T, at which the HFSC phase appears, is always the same through the various crystals. A phase boundary signature is also observed inside the LFSC phase near the characteristic field of 15 T, indicating an intermediate SC phase characterized by small flux pinning forces.

Sakai, Hironori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Aoki, Dai*; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
For a paramagnetic superconductor UTe , a "field-reionforced superconducting state" in which
, a "field-reionforced superconducting state" in which  increases with magnetic field above 15 T emerges when a magnetic field is applied "exactly" in the direction of the magnetically hard
increases with magnetic field above 15 T emerges when a magnetic field is applied "exactly" in the direction of the magnetically hard  axis. In order to investigate this high-field superconducting phase, we have attempted to determine the magnetic field-temperature phase diagram of ultra-clean single crystals using a cryogen-free 25 T superconducting magnet (25T-CSM) at the High Field Laboratory for Superconducting Materials, Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University. In this presentation, we will report the obtained results.
axis. In order to investigate this high-field superconducting phase, we have attempted to determine the magnetic field-temperature phase diagram of ultra-clean single crystals using a cryogen-free 25 T superconducting magnet (25T-CSM) at the High Field Laboratory for Superconducting Materials, Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University. In this presentation, we will report the obtained results.

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
In unconventional superconductivity, magnetism is considered to be the origin of the superconducting interaction, and the relationship between magnetism and superconductivity is a central theme of research. UTe has attracted much attention due to its potential for reentrant superconductivity and spin-triplet superconductivity in magnetic fields. In this material, when a magnetic field is applied along the a-axis, a weak metamagnetism occurs near 6T due to Fermi surface instability. In the initial crystals synthesized by the vapor phase epitaxy, superconductivity disappeared in the magnetic field where metamagnetism was generated because
has attracted much attention due to its potential for reentrant superconductivity and spin-triplet superconductivity in magnetic fields. In this material, when a magnetic field is applied along the a-axis, a weak metamagnetism occurs near 6T due to Fermi surface instability. In the initial crystals synthesized by the vapor phase epitaxy, superconductivity disappeared in the magnetic field where metamagnetism was generated because  = 1.6K and upper critical magnetic field
= 1.6K and upper critical magnetic field 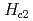 = 6T, and superconductivity was not affected. In the pure single crystal synthesized by the molten salt flux method,
= 6T, and superconductivity was not affected. In the pure single crystal synthesized by the molten salt flux method,  =2.1K is 25% stronger than the initial
=2.1K is 25% stronger than the initial  while
while 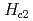 =12T is doubled. In this study, we revealed that this metamagnetism enhances
=12T is doubled. In this study, we revealed that this metamagnetism enhances 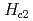 .
.
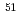 V nuclear magnetic resonance study of the triangular Kondo lattice system YbV
V nuclear magnetic resonance study of the triangular Kondo lattice system YbV Sn
Sn
Sakai, Hironori; Park, S.*; Dioguardi, A. P.*; Furukawa, Tetsuya*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Kimata, Motoi; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Thomas, S. M.*; Thompson, J. D.*; et al.
no journal, ,
YbV Sn
Sn has a HfFe
has a HfFe Ge
Ge -type structure, in which V atoms form a Kagome lattice and Yb atoms form a triangular lattice. This rare Yb-based Kondo triangular lattice system has attracted much attention as an essential model to explore the relationship between quantum magnetism and topological properties. To microscopically clarify the quantum criticality of this system, we have performed
-type structure, in which V atoms form a Kagome lattice and Yb atoms form a triangular lattice. This rare Yb-based Kondo triangular lattice system has attracted much attention as an essential model to explore the relationship between quantum magnetism and topological properties. To microscopically clarify the quantum criticality of this system, we have performed 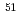 V nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) studies using a single crystal of YbV
V nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) studies using a single crystal of YbV Sn
Sn . In this talk, I will report on the spectral assignments of
. In this talk, I will report on the spectral assignments of 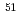 V nuclei revealed from
V nuclei revealed from 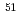 V NMR measurements in the paramagnetic state.
V NMR measurements in the paramagnetic state.
Sakai, Hironori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Kimata, Motoi; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
We investigated the angular dependence of the superconducting phase diagram in UTe using magnetic fields up to 25 T. Precise measurements of ac susceptibility and resistivity were performed with a two-axis rotator. The results show that the low-field (LFSC) and high-field (HFSC) superconducting phases respond differently to field orientation. Notably, the HFSC phase emerges only within a narrow angle near the
using magnetic fields up to 25 T. Precise measurements of ac susceptibility and resistivity were performed with a two-axis rotator. The results show that the low-field (LFSC) and high-field (HFSC) superconducting phases respond differently to field orientation. Notably, the HFSC phase emerges only within a narrow angle near the  axis and disappears rapidly with tilting, suggesting strong anisotropy. We will discuss how the HFSC phase vanishes as the field tilts.
axis and disappears rapidly with tilting, suggesting strong anisotropy. We will discuss how the HFSC phase vanishes as the field tilts.

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.*; Sakai, Hironori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kubo, Katsunori; Kimata, Motoi; Awaji, Satoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We investigate the effect of easy-axis metamagnetic crossover on superconductivity in UTe along the
along the  -axis through measurements of AC susceptibility, magnetization, and the magnetocaloric effect. In ultra-clean single crystals, we identify a field-induced phase transition within the superconducting state at 5.6 T, driven by metamagnetism. This transition leads to a high-field superconducting state, significantly increasing the upper critical field to 12 T. A sudden increase in entropy at the transition suggests a self-reconstruction of the order parameter, enabling multi-component superconducting states to adapt to external perturbations.
-axis through measurements of AC susceptibility, magnetization, and the magnetocaloric effect. In ultra-clean single crystals, we identify a field-induced phase transition within the superconducting state at 5.6 T, driven by metamagnetism. This transition leads to a high-field superconducting state, significantly increasing the upper critical field to 12 T. A sudden increase in entropy at the transition suggests a self-reconstruction of the order parameter, enabling multi-component superconducting states to adapt to external perturbations.

Haga, Yoshinori; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Kimata, Motoi*; Nakamura, Shintaro*; Awaji, Satoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
In unconventional superconductivity, magnetism is considered to be the origin of the superconducting interaction, and the relationship between magnetism and superconductivity is a central theme of research. UTe2 has attracted much attention due to its potential for reentrant superconductivity and spin-triplet superconductivity in magnetic fields. In this material, when a magnetic field is applied along the a-axis, a weak metamagnetism occurs near 6T due to Fermi surface instability. In the initial crystals synthesized by the vapor phase epitaxy, superconductivity disappeared in the magnetic field where metamagnetism was generated because  = 1.6K and upper critical magnetic field
= 1.6K and upper critical magnetic field 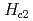 = 6T, and superconductivity was not affected. In the pure single crystal synthesized by the molten salt flux method,
= 6T, and superconductivity was not affected. In the pure single crystal synthesized by the molten salt flux method,  =2.1K is 25% stronger than the initial Tc, while
=2.1K is 25% stronger than the initial Tc, while 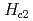 =12T is doubled. In this study, we revealed that this metamagnetism enhances
=12T is doubled. In this study, we revealed that this metamagnetism enhances 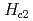 .
.

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
In unconventional superconductivity, magnetism is considered to be the origin of the superconducting interaction, and the relationship between magnetism and superconductivity is a central theme of research. UTe has attracted much attention due to its potential for reentrant superconductivity and spin-triplet superconductivity in magnetic fields. In this material, when a magnetic field is applied along the a-axis, a weak metamagnetism occurs near 6T due to Fermi surface instability. In the initial crystals synthesized by the vapor phase epitaxy, superconductivity disappeared in the magnetic field where metamagnetism was generated because
has attracted much attention due to its potential for reentrant superconductivity and spin-triplet superconductivity in magnetic fields. In this material, when a magnetic field is applied along the a-axis, a weak metamagnetism occurs near 6T due to Fermi surface instability. In the initial crystals synthesized by the vapor phase epitaxy, superconductivity disappeared in the magnetic field where metamagnetism was generated because  = 1.6K and upper critical magnetic field
= 1.6K and upper critical magnetic field 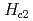 = 6T, and superconductivity was not affected. In the pure single crystal synthesized by the molten salt flux method,
= 6T, and superconductivity was not affected. In the pure single crystal synthesized by the molten salt flux method,  =2.1K is 25% stronger than the initial
=2.1K is 25% stronger than the initial  while
while 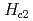 =12T is doubled. In this study, we revealed that this metamagnetism enhances
=12T is doubled. In this study, we revealed that this metamagnetism enhances 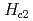 .
.

Sakai, Hironori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Aoki, Dai*; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
High-quality UTe single crystals were grown using a molten salt flux method with the highest reported superconducting (SC) transition temperature. The crystals had a small residual electronic contribution in specific heat and a large residual resistivity ratio. The SC phase diagram of UTe
single crystals were grown using a molten salt flux method with the highest reported superconducting (SC) transition temperature. The crystals had a small residual electronic contribution in specific heat and a large residual resistivity ratio. The SC phase diagram of UTe was studied, revealing contrasting field-angular dependence of low and high-field SC phases. An intermediate SC state was also found. The high-field SC phase appeared consistently at about 15 T, while crystal quality increased the upper critical field of the low-field superconducting phase. The MSF method facilitated the observation of quantum oscillations and progress in Fermi surface research for this spin-triplet superconductor.
was studied, revealing contrasting field-angular dependence of low and high-field SC phases. An intermediate SC state was also found. The high-field SC phase appeared consistently at about 15 T, while crystal quality increased the upper critical field of the low-field superconducting phase. The MSF method facilitated the observation of quantum oscillations and progress in Fermi surface research for this spin-triplet superconductor.

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
In unconventional superconductors, there are cases of vortex liquid-like state. When the pinning is strong, vortices do not move, and thus, the formation of such abnormal states requires pure and pristine crystals. Recently, the growth of pure single crystals of the spin-triplet superconductor UTe using a molten salt flux has been reported. In this study, we report research on vortices in UTe
using a molten salt flux has been reported. In this study, we report research on vortices in UTe using such pure single crystals. As a result, in the magnetic field range of 15 T to 22 T, the critical current showed a maximum in temperature dependence, and a low-temperature region with a low critical current was observed deep in the superconducting state. This low critical current region matches the recently reported intermediate field superconducting phase. This suggests a weakening of the pinning force and a decrease in the critical current in the intermediate field superconducting phase.
using such pure single crystals. As a result, in the magnetic field range of 15 T to 22 T, the critical current showed a maximum in temperature dependence, and a low-temperature region with a low critical current was observed deep in the superconducting state. This low critical current region matches the recently reported intermediate field superconducting phase. This suggests a weakening of the pinning force and a decrease in the critical current in the intermediate field superconducting phase.
 under magnetic field along the easy a-axis
under magnetic field along the easy a-axisTokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
We study the interplay between superconductivity and metamagnetism of Ute under magnetic field along the easy a-axis by analyzing the entropy, obtained from measurements of magnetization and magnetocaloric effect. Due to the weak metamagnetism around 8T the entropy in the normal-conducting state at high temperautres above the superconducting transition temperature, Tc, exhibits an anomalous enhancement as a function of the field at the metamagnetism. Suprisingly the anomaly persists even inside the superconducting state and transforms into a sharp anomaly. The anomaly is a step-wise increase of entropy with increasing magnetic field, corresponding to a heat absorbtion. Thus, we found an unprecedented phenomenon of a metamagnetism inducing a first-order phase transition within a superconducting state. We discuss that a transition within the same symmetry of
under magnetic field along the easy a-axis by analyzing the entropy, obtained from measurements of magnetization and magnetocaloric effect. Due to the weak metamagnetism around 8T the entropy in the normal-conducting state at high temperautres above the superconducting transition temperature, Tc, exhibits an anomalous enhancement as a function of the field at the metamagnetism. Suprisingly the anomaly persists even inside the superconducting state and transforms into a sharp anomaly. The anomaly is a step-wise increase of entropy with increasing magnetic field, corresponding to a heat absorbtion. Thus, we found an unprecedented phenomenon of a metamagnetism inducing a first-order phase transition within a superconducting state. We discuss that a transition within the same symmetry of 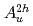 with a step-wise increase of
with a step-wise increase of 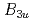 weight would be consistent with our observations.
weight would be consistent with our observations.

Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kimata, Motoi*; Awaji, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
UTe has attracted much attention due to the possibility of reentrant superconductivity and spin triplet superconductivity in a magnetic field. In this material, when a magnetic field is applied in the b-axis direction, Tc decreases once due to the magnetic field, but Tc increases under a magnetic field of about 16T or more. In this field direction, there is a metamagnetic transition at 34T. The relationship between this metamagnetism and the anomalous enhancement of Tc has been discussed. Many unconventional superconductors exhibit an unusual metallic state in the normal phase. It is believed that magnetic fluctuations, which are the cause of this phenomenon, generate superconducting electron pairs. Entropy is a direct measure of fluctuations, as entropy exhibits a maximum at the quantum critical point. Therefore, the relationship between fluctuations and superconductivity can be clarified by entropy measurements in the normal state. In this study, we performed precise magnetization measurements at temperatures up to 2 K and magnetic fields up to 24 T using cryogen-free superconducting magnets at the Research Center for High Magnetic Field Superconducting Materials, IMR, Tohoku University. We used a thermodynamic relation to map the entropy in the magnetic field-temperature parameter space. In this talk, we discuss the relationship between the entropy increase due to metamagnetic fluctuations and superconductivity.
has attracted much attention due to the possibility of reentrant superconductivity and spin triplet superconductivity in a magnetic field. In this material, when a magnetic field is applied in the b-axis direction, Tc decreases once due to the magnetic field, but Tc increases under a magnetic field of about 16T or more. In this field direction, there is a metamagnetic transition at 34T. The relationship between this metamagnetism and the anomalous enhancement of Tc has been discussed. Many unconventional superconductors exhibit an unusual metallic state in the normal phase. It is believed that magnetic fluctuations, which are the cause of this phenomenon, generate superconducting electron pairs. Entropy is a direct measure of fluctuations, as entropy exhibits a maximum at the quantum critical point. Therefore, the relationship between fluctuations and superconductivity can be clarified by entropy measurements in the normal state. In this study, we performed precise magnetization measurements at temperatures up to 2 K and magnetic fields up to 24 T using cryogen-free superconducting magnets at the Research Center for High Magnetic Field Superconducting Materials, IMR, Tohoku University. We used a thermodynamic relation to map the entropy in the magnetic field-temperature parameter space. In this talk, we discuss the relationship between the entropy increase due to metamagnetic fluctuations and superconductivity.