Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 revealed by inelastic X-ray and neutron scattering
revealed by inelastic X-ray and neutron scatteringKimura, Koji*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Yuta*; Nakano, Akitoshi*; Kawamura, Keisuke*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Martin, A.*; Webber, K. G.*; Kakimoto, Kenichi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 110(13), p.134314_1 - 134314_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nagai, Yuki; Iwasaki, Yutaka*; Kitahara, Koichi*; Takagiwa, Yoshiki*; Kimura, Kaoru*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Physical Review Letters, 132(19), p.196301_1 - 196301_6, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:82.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasicrystal is an ordered but non-periodic structure understood as a projection from a higher dimensional periodic structure. An anomalous increase in heat capacity at high temperatures has been discussed for over two decades as a manifestation of a hidden high dimensionality of quasicrystals. A theoretical study of the heat capacity of realistic quasicrystals or their approximants has yet to be conducted because of the huge computational complexity. To bridge this gap between experiment and theory, we show experiments and cutting-edge machine-learning molecular simulations on the same material, an Al-Pd-Ru quasicrystal, and its approximants. We show that at high temperatures, aluminum atoms diffuse with discontinuous-like jumps, and the diffusion paths of the aluminum can be understood in terms of jumps corresponding to hyperatomic fluctuations in six-dimensional space.
 =1/2 Ising-like antiferromagnetic chain CsCoCl
=1/2 Ising-like antiferromagnetic chain CsCoCl in longitudinal magnetic fields studied by high-field ESR measurements
in longitudinal magnetic fields studied by high-field ESR measurementsKimura, Shojiro*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Okunishi, Koichi*; Akaki, Mitsuru*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Kikuchi, Hikomitsu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(9), p.094701_1 - 094701_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -Mo
-Mo O
O revealed by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy and first-principles calculation
revealed by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy and first-principles calculationSumida, Kazuki; Higaki, Sota*; Sato, Hitoshi*; Tsuru, Daichi*; Miyamoto, Koji*; Okuda, Taichi*; Kuroiwa, Yoshihiro*; Moriyoshi, Chikako*; Takase, Koichi*; Oguchi, Tamio*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(8), p.084706_1 - 084706_6, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.15(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
Yasue, Ayumu*; Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Yoshioka, Masahiro*; Noma, Takashi*; Okuno, Koichi*; Tanaka, Seiichiro*; Hirata, Yoshikazu*; Ooka, Tokunao*; Kimura, Yoshiharu*; Nagai, Tomoya*; et al.
Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 21(5), p.337 - 350, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)The purpose of this study was to evaluate the use of resin injection to repair cracks in ultra-high-strength concrete (UHSC) members. As a preliminary step, the applicability of the neutron diffraction method (NDM) to investigate the effect of repairs in UHSC specimens was examined. The experimental results showed that the NDM can measure stresses in rebars in UHSC and normal concrete specimens. Therefore, in this experiment, the NDM was used to measure the bond performance of repairs with epoxy resin around the slit in normal concrete and UHSC specimens and examine the effect of repair on the UHSC specimens. Displacement around the slit was measured using a PI-shape displacement transducer. The evaluation confirmed that the bond performance of the repaired area was recovered by resin injection regardless of the concrete strength. In addition, the displacement around the slit was smaller for the injected specimens than the noninjected specimens. These experimental results clarified that by injecting resin, the same bond repair effect could be obtained in UHSC and normal concrete specimens.
 =
=  one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo
one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo V
V O
O
Kimura, Shojiro*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Okutani, Akira*; Akaki, Mitsuru*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Okunishi, Koichi*; Kindo, Koichi*; He, Z.*; Taniyama, Tomoyasu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(1), p.014417_1 - 014417_9, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) =1/2 one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo
=1/2 one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo V
V O
O in transverse magnetic fields
in transverse magnetic fieldsOkutani, Akira*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Kimura, Shojiro*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Kida, Takanori*; Mori, Michiyasu; Miyake, Atsushi*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Kindo, Koichi*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(4), p.044704_1 - 044704_9, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:38.13(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Te
Te
Shikin, A. M.*; Estyunin, D. A.*; Klimovskikh, I. I.*; Filnov, S. O.*; Kumar, S.*; Schwier, E. F.*; Miyamoto, Koji*; Okuda, Taichi*; Kimura, Akio*; Kuroda, Kenta*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.13226_1 - 13226_13, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:95.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences) -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
 Am neutron capture and total cross sections with ANNRI at J-PARC
Am neutron capture and total cross sections with ANNRI at J-PARCKimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Terada, Kazushi*; Nakao, Taro*; Mizuyama, Kazuhito*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.479 - 492, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:79.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakamura, Shoji; Terada, Kazushi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakao, Taro*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Uehara, Akihiro*; Takamiya, Koichi*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(1), p.123 - 129, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)Accurate data of  -ray emission probabilities are frequently needed when one quantitatively determines the amount of isotope by
-ray emission probabilities are frequently needed when one quantitatively determines the amount of isotope by  -ray measurements or obtains neutron capture cross-sections using them. Americium-243, one of the most important minor actinides, produces
-ray measurements or obtains neutron capture cross-sections using them. Americium-243, one of the most important minor actinides, produces  Am after neutron capture. The 744-keV
Am after neutron capture. The 744-keV  -ray decaying from the ground state of
-ray decaying from the ground state of  Am has a relatively large
Am has a relatively large  -ray emission probability c.a. 66%, however, its uncertainty is as large as 29%. The uncertainty of the
-ray emission probability c.a. 66%, however, its uncertainty is as large as 29%. The uncertainty of the  -ray emission probability leads to a major factor of the systematic uncertainty on determining an amount of isotope, and therefore the
-ray emission probability leads to a major factor of the systematic uncertainty on determining an amount of isotope, and therefore the  -ray emission probability was measured by using an activation method and an examined level structure of
-ray emission probability was measured by using an activation method and an examined level structure of  Cm. In this study, the emission probability of 744-keV
Cm. In this study, the emission probability of 744-keV  ray was derived as 66.5
ray was derived as 66.5 1.1%, and its uncertainty was improved from 29% to 2%.
1.1%, and its uncertainty was improved from 29% to 2%.
Lustikova, J.*; Shiomi, Yuki*; Yokoi, Naoto*; Kabeya, Noriyuki*; Kimura, Noriaki*; Ienaga, Koichiro*; Kaneko, Shinichi*; Okuma, Satoshi*; Takahashi, Saburo*; Saito, Eiji
Nature Communications (Internet), 9, p.4922_1 - 4922_6, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:86.60(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Am with ANNRI at J-PARC
Am with ANNRI at J-PARCTerada, Kazushi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakao, Taro*; Nakamura, Shoji; Mizuyama, Kazuhito*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(10), p.1198 - 1211, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:83.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kimura, Atsushi; Terada, Kazushi; Nakao, Taro; Nakamura, Shoji; Mizuyama, Kazuhito; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.11001_1 - 11001_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Terada, Kazushi; Nakao, Taro; Nakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Takamiya, Koichi*; Hori, Junichi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.03019_1 - 03019_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:83.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)The research project entitled "Research and development for Accuracy Improvement of neutron nuclear data on Minor ACtinides (AIMAC)" has been started to improve the reliability of the neutron cross section date of MAs. In order to obtain accurate cross section data, it is indispensable to determine the amount of MA sample accurately and non-destructively. However, the uncertainty concerning the amount of sample is not assured in some cases. Therefore, as a part of the AIMAC project, this study is aimed to development the technique for accurate determination of the amount of samples by two different methods:  -ray spectroscopic method and calorimetric method. This contribution presents the developed techniques together with results obtained by two independent techniques.
-ray spectroscopic method and calorimetric method. This contribution presents the developed techniques together with results obtained by two independent techniques.
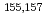 Gd
GdMizuyama, Kazuhito; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hasemi, Hiroyuki*; Kino, Koichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.11042_1 - 11042_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Gadolinium has been used as neutron-absorbing material in a thermal reactor since 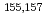 have large thermal neutron capture cross sections. Nevertheless, there is a discrepancy between RPI data and JENDL-4.0 data for
have large thermal neutron capture cross sections. Nevertheless, there is a discrepancy between RPI data and JENDL-4.0 data for  Gd. The criticality in the reactor is very sensitive to the capture cross section. The RPI data made the criticality of Gd-loaded thermal systems in ICSBEP overestimated. Recently, the neutron capture cross sections of
Gd. The criticality in the reactor is very sensitive to the capture cross section. The RPI data made the criticality of Gd-loaded thermal systems in ICSBEP overestimated. Recently, the neutron capture cross sections of 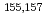 Gd were measured by the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method using the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI) in the J-PARC/MLF. The pulsed neutron beam from the Japan Spallation Neutron Source (JSNS) was used with a double-bunch structure in this measurement, since the incident proton beam is normally delivered in a double-bunch scheme in the J-PARC. In addition to this, it is necessary to take into account the energy resolution of the pulsed neutron beam at the JSNS for the accurate derivation of resolved resonance parameters. In this study, using the least-squares multilevel R-matrix code REFIT modified to include the double bunch structure and the resolution function for the ANNRI, we fitted the calculated capture cross sections of
Gd were measured by the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method using the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI) in the J-PARC/MLF. The pulsed neutron beam from the Japan Spallation Neutron Source (JSNS) was used with a double-bunch structure in this measurement, since the incident proton beam is normally delivered in a double-bunch scheme in the J-PARC. In addition to this, it is necessary to take into account the energy resolution of the pulsed neutron beam at the JSNS for the accurate derivation of resolved resonance parameters. In this study, using the least-squares multilevel R-matrix code REFIT modified to include the double bunch structure and the resolution function for the ANNRI, we fitted the calculated capture cross sections of 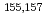 Gd to the experimental data at the ANNRI. We derived the resonance parameters for some low-lying resonances of the two Gd isotopes.
Gd to the experimental data at the ANNRI. We derived the resonance parameters for some low-lying resonances of the two Gd isotopes.
 =1/2 quasi-one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo
=1/2 quasi-one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo V
V O
O in a transverse magnetic field
in a transverse magnetic fieldMatsuda, Masaaki*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Okutani, Akira*; Ma, J.*; Agrawal, H.*; Hong, T.*; Pajerowski, D. M.*; Copley, J. R. D.*; Okunishi, Koichi*; Mori, Michiyasu; et al.
Physical Review B, 96(2), p.024439_1 - 024439_8, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:51.97(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Higemoto, Wataru; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Koda, Akihiro*; Kojima, Kenji*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Matoba, Shiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Strasser, P.*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(1), p.11_1 - 11_24, 2017/06
A muon experimental facility, known as the Muon Science Establishment (MUSE), is one of the user facilities at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, along with those for neutrons, hadrons, and neutrinos. The MUSE facility is integrated into the Materials and Life Science Facility building in which a high-energy proton beam that is shared with a neutron experiment facility delivers a variety of muon beams for research covering diverse scientific fields. In this review, we present the current status of MUSE, which is still in the process of being developed into its fully fledged form.
 -ray emission probabilities of
-ray emission probabilities of 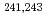 Am and
Am and  Np
NpTerada, Kazushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Nakao, Taro; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Takamiya, Koichi*; Hori, Junichi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(11), p.1881 - 1888, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.92(Nuclear Science & Technology) -ray emission probabilities of
-ray emission probabilities of 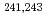 Am and
Am and  Np have been precisely measured with
Np have been precisely measured with  - and
- and  -ray spectroscopic methods. The activities of
-ray spectroscopic methods. The activities of  Am samples were determined by measuring alpha particles using a Si semiconductor detector.
Am samples were determined by measuring alpha particles using a Si semiconductor detector.  -rays emitted from the samples were measured with a planar type High-Purity Germanium (HPGe) detector. An efficiency curve of the Ge detector was derived with uncertainties of 0.7% from 50 to 1332 keV and 1.3% below 50 keV by combining measured efficiencies and Monte Carlo simulation. The
-rays emitted from the samples were measured with a planar type High-Purity Germanium (HPGe) detector. An efficiency curve of the Ge detector was derived with uncertainties of 0.7% from 50 to 1332 keV and 1.3% below 50 keV by combining measured efficiencies and Monte Carlo simulation. The  -ray emission probabilities for the major
-ray emission probabilities for the major  -rays of these nuclides were determined with uncertainties less than 1.2%.
-rays of these nuclides were determined with uncertainties less than 1.2%.