Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2024, P. 31, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
FeNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) rays in the
rays in the  La(
La(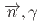 )
) La reaction
La reactionOkuizumi, Mao*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(3), p.034611_1 - 034611_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear) Er(n,
Er(n, )
)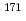 Er and
Er and  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reactions
Hf reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag, and
Ag, and  In
InNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(11), p.1415 - 1430, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron capture cross-sections of nuclides targeted for decommissioning are necessary to contribute to the evaluation of radioactivity produced. The present study,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag and
Ag and  In nuclides were selected as target ones, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured by an activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were obtained as follows: 27.18
In nuclides were selected as target ones, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured by an activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were obtained as follows: 27.18 0.28 barn for
0.28 barn for  Sc(n,
Sc(n,  )
)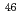 Sc, 4.34
Sc, 4.34 0.06 barn for
0.06 barn for  Cu(n,
Cu(n,  )
) Cu, 0.719
Cu, 0.719 0.011 barn for
0.011 barn for  Zn(n,
Zn(n,  )
) Zn, 4.05
Zn, 4.05 0.05 barn for
0.05 barn for  Ag(n,
Ag(n,  )
)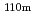 Ag and 8.53
Ag and 8.53 0.27 barn for
0.27 barn for  In(n,
In(n,  )
) 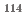 In
In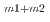 . The results for
. The results for  Sc and
Sc and  Zn nuclides supported evaluated values within the limits of uncertainties, while those for the other nuclides were slightly different from evaluated ones. The obtained results are useful not only for the evaluation of production amount, but also for the monitor selection other than Au and Co by considering those nuclides as flux monitors.
Zn nuclides supported evaluated values within the limits of uncertainties, while those for the other nuclides were slightly different from evaluated ones. The obtained results are useful not only for the evaluation of production amount, but also for the monitor selection other than Au and Co by considering those nuclides as flux monitors.
Ozaki, Yusuke; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ono, Hirokazu; Kimura, Shun
Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Coupled Processes in Fractured Geological Media; Observation, Modeling, and Application (CouFrac2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/11
Electrical resistivity tomography was repeatedly carried out to investigate the changes of the electrical resistivity distribution around 350m Niche No. 2 and No. 4 in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The electrical resistivity around Niche No. 2 did not change so much after the high resistive zone appeared around the tunnel by the excavation under opened condition during the studied period. Around Niche No. 4, the electrical resistivity was investigated under closed condition by engineered barrier system (EBS) where the EBS and surrounding rocks were disturbed artificially by water injection and heating. Our results could capture the change in the distribution of electrical resistivity due to the artificial disturbances in and around of Niche No. 4. These results would help us to understand the time lapse behavior of excavation damaged zone and re-saturation process in and around the EBS from the construction to the closure.
Endo, Shunsuke; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Ino, Takashi*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kawamura, Shiori*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Ryuju*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 60(8), p.166_1 - 166_10, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2023, P. 46, 2024/07
The present work is an attempt to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-sections for some nuclides which are of importance in decommissioning to evaluate produced radioactivity. This work selected some of objective nuclides for decommissioning, such as  Fe,
Fe,  Er and
Er and  Hf, and measured thermal-neutron capture cross-sections for these nuclides by a neutron activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The present results were obtained as follows:1.23
Hf, and measured thermal-neutron capture cross-sections for these nuclides by a neutron activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The present results were obtained as follows:1.23 0.03 barn for
0.03 barn for  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe reaction, 8.19
Fe reaction, 8.19 0.35 barn for
0.35 barn for  Er(n,
Er(n, )
)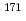 Er reaction and 13.57
Er reaction and 13.57 0.14 barn for
0.14 barn for  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reaction. As a by-product, the measurement of Hf sample also presented 0.427
Hf reaction. As a by-product, the measurement of Hf sample also presented 0.427 0.006 barn for
0.006 barn for 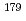 Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
)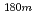 Hf reaction. It has been revealed that the data adopted in an evaluated data library differ from the present results by more than experimental uncertainties.
Hf reaction. It has been revealed that the data adopted in an evaluated data library differ from the present results by more than experimental uncertainties.
Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Uda, Toshiaki*; Hayashi, Daisuke*; Emori, Minoru*; Kimura, Shun
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 31(1), p.11 - 20, 2024/06
no abstracts in English
 I and
I and  I using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline at J-PARC
I using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline at J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*
European Physical Journal A, 60(5), p.120_1 - 120_14, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Kimura, Atsushi; Endo, Shunsuke; Nakamura, Shoji
EPJ Web of Conferences, 294, p.01002_1 - 01002_7, 2024/04
 Am neutron capture cross section measurement using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline of J-PARC
Am neutron capture cross section measurement using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline of J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; Sato, Yaoki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(4), p.459 - 477, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology) Ta
TaEndo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 198(4), p.786 - 803, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology) -odd/
-odd/ -odd interactions on the 0.75 eV
-odd interactions on the 0.75 eV  -wave resonance in
-wave resonance in 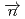 +
+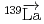 forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beam
forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beamNakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.L041602_1 - L041602_4, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.90(Physics, Nuclear)Saito, Shigeru; Meigo, Shinichiro; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Hirano, Yukinori*; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Technology 2023-025, 48 Pages, 2024/03
JAEA has been developing Accelerator-Driven Systems (ADS) for research and development of nuclear transmutation using accelerators in order to reduce the volume and hazardousness of high-level radioactive waste generated by nuclear power plants. In order to prepare the material irradiation database necessary for the design of ADS and to study the irradiation effects in Lead-Bismuth Eutectic (LBE) alloys, a proton irradiation facility is under consideration at J-PARC. In this proton irradiation facility, 250 kW proton beams will be injected into the LBE spallation target, and irradiation tests under LBE flow will be performed for candidate structural materials for ADS. Furthermore, semiconductor soft-error tests, medical RI production, and proton beam applications will be performed. Among these, Post Irradiation Examination (PIE) of irradiated samples and RI separation and purification will be carried out in the PIE facility to be constructed near the proton irradiation facility. In this PIE facility, PIE of the equipment and samples irradiated in other facilities in J-PARC will also be performed. This report describes the conceptual study of the PIE facility, including the items to be tested, the test flow, the facilities, the test equipment, etc., and the proposed layout of the facility.
 I and
I and  I using ANNRI at MLF/J-PARC
I using ANNRI at MLF/J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*
JAEA-Conf 2023-001, p.74 - 79, 2024/02
 La and evaluation of resonance parameters
La and evaluation of resonance parametersEndo, Shunsuke; Kawamura, Shiori*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Yoshikawa, Hiromoto*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki
European Physical Journal A, 59(12), p.288_1 - 288_12, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.87(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 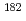 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Kimura, Atsushi; Endo, Shunsuke; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(9), p.1133 - 1142, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In recent years, research has been advanced on lead-cooled fast reactors and accelerator drive systems, and it is required to improve the accuracy of the neutron capture cross section of Pb isotopes. Although  Pb has a small natural abundance, it is of importance because it produces the long-lived radionuclide
Pb has a small natural abundance, it is of importance because it produces the long-lived radionuclide  Pb (17.3 million years) by neutron capture reaction. However, it is difficult to measure its cross section by a conventional activation method using a nuclear reactor because the induced radioactivity of
Pb (17.3 million years) by neutron capture reaction. However, it is difficult to measure its cross section by a conventional activation method using a nuclear reactor because the induced radioactivity of  Pb is weak. Hence, the cross-section measurement was performed by applying mass spectrometry. This presentation gives the details of the experiment and the results obtained in the neutron capture cross-section measurement of
Pb is weak. Hence, the cross-section measurement was performed by applying mass spectrometry. This presentation gives the details of the experiment and the results obtained in the neutron capture cross-section measurement of  Pb using mass spectroscopy.
Pb using mass spectroscopy.
Maeda, Makoto; Segawa, Mariko; Toh, Yosuke; Endo, Shunsuke; Nakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(8), p.2995 - 2999, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)