Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

 H
H O
OFujihara, Masayoshi; Hagihara, Masato; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Matsuo, Akira*; Kindo, Koichi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(1), p.014406_1 - 014406_9, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Honda, Fuminori*; Aoki, Dai*; Haga, Yoshinori; Kida, Takanori*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Karube, Kosuke*; Harima, Hisatomo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044708_1 - 044708_10, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) =1/2 Ising-like antiferromagnetic chain CsCoCl
=1/2 Ising-like antiferromagnetic chain CsCoCl in longitudinal magnetic fields studied by high-field ESR measurements
in longitudinal magnetic fields studied by high-field ESR measurementsKimura, Shojiro*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Okunishi, Koichi*; Akaki, Mitsuru*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Kikuchi, Hikomitsu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(9), p.094701_1 - 094701_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Zn
Zn
Kitazawa, Takafumi; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Matsuo, Akira*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kindo, Koichi*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(8), p.085105_1 - 085105_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sb
Sb
Kitaori, Aki*; Kanazawa, Naoya*; Kida, Takanori*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Nakamura, Ai*; Aoki, Dai*; Haga, Yoshinori; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(2), p.024702_1 - 024702_6, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg
O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain
chainFujihara, Masayoshi; Jeschke, H. O.*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Matsuo, Akira*; Kindo, Koichi*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(11), p.114408_1 - 114408_8, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)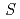 = 1/2 Heisenberg
= 1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd
chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and
O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and  SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the
SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the 
 -
-
 antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions
antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions 
 and
and 
 are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of
are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of 
 is two to three times larger than that of
is two to three times larger than that of 
 , thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of
, thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of 
 . The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K (
. The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K ( 0.036
0.036 
 ), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
 =
=  one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo
one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo V
V O
O
Kimura, Shojiro*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Okutani, Akira*; Akaki, Mitsuru*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Okunishi, Koichi*; Kindo, Koichi*; He, Z.*; Taniyama, Tomoyasu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(1), p.014417_1 - 014417_9, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.41(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) =1/2 one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo
=1/2 one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo V
V O
O in transverse magnetic fields
in transverse magnetic fieldsOkutani, Akira*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Kimura, Shojiro*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Kida, Takanori*; Mori, Michiyasu; Miyake, Atsushi*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Kindo, Koichi*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(4), p.044704_1 - 044704_9, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:38.65(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Fujihara, Masayoshi*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Mole, R.*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Toyama, Takami*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Yu, D.*; Sota, Shigetoshi*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.3429_1 - 3429_7, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:92.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)
Ikeda, Shugo*; Kaneko, Koji; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Nakao, Akiko*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Mochizuki, Kensei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(1), p.014707_1 - 014707_7, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary) symmetry in CeCu
symmetry in CeCu Ge
Ge ; Soft X-ray absorption and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy
; Soft X-ray absorption and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopyAratani, Hidekazu*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Kawada, Moeki*; Kanai-Nakata, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Fujioka, Shuhei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Kiss, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(12), p.121113_1 - 121113_6, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) axis
axisPosp
 il, J.*; Haga, Yoshinori; Kohama, Yoshimitsu*; Miyake, Atsushi*; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tateiwa, Naoyuki; Vali
il, J.*; Haga, Yoshinori; Kohama, Yoshimitsu*; Miyake, Atsushi*; Kambe, Shinsaku; Tateiwa, Naoyuki; Vali ka, M.*; Proschek, P.*; Prokle
ka, M.*; Proschek, P.*; Prokle ka, J.*; Sechovsk
ka, J.*; Sechovsk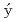 , V.*; et al.
, V.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(1), p.014430_1 - 014430_7, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:56.39(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) states in CeFe
states in CeFe revealed by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
revealed by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroismSaito, Yuji; Yasui, Akira*; Fuchimoto, Hiroto*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Imada, Shin*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Kindo, Koichi*; Takahashi, Minoru*; Ebihara, Takao*; et al.
Physical Review B, 96(3), p.035151_1 - 035151_5, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We revisit the delocalized character of the 4 states of CeFe
states of CeFe in the ferromagnetically ordered phase by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) in X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) with improved data quality using single crystals. Surprisingly, the Ce
in the ferromagnetically ordered phase by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) in X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) with improved data quality using single crystals. Surprisingly, the Ce 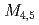 XMCD spectral shape changes significantly as a function of temperature and applied magnetic field, with no concomitant changes in the spectral shape of the Ce
XMCD spectral shape changes significantly as a function of temperature and applied magnetic field, with no concomitant changes in the spectral shape of the Ce 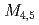 XAS as well as the Fe
XAS as well as the Fe 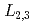 XAS and XMCD. This unusual behavior is characterized by the
XAS and XMCD. This unusual behavior is characterized by the 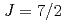 states in a 4
states in a 4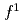 configuration mixed into the
configuration mixed into the 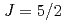 ground state. Such extreme sensitivity of the Ce 4
ground state. Such extreme sensitivity of the Ce 4 states to the external perturbations can be related to the magnetic instability toward an antiferromagnetic phase in CeFe
states to the external perturbations can be related to the magnetic instability toward an antiferromagnetic phase in CeFe . Our experimental data presented here provide valuable insights into the underlying physics in strongly-hybridized ferromagnetic Ce compounds.
. Our experimental data presented here provide valuable insights into the underlying physics in strongly-hybridized ferromagnetic Ce compounds.
 -YbAlB
-YbAlB at high magnetic fields
at high magnetic fieldsTerashima, Taku*; Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Suzuki, Shintaro*; Matsumoto, Yosuke*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Kondo, Akihiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(11), p.114715_1 - 114715_4, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -YbAl
-YbAl Fe
Fe B
B (
(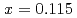 ) at low temperatures and high magnetic fields
) at low temperatures and high magnetic fieldsTerashima, Taku*; Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Suzuki, Shintaro*; Matsumoto, Yosuke*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Kondo, Akihiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 592(1), p.012020_1 - 012020_6, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.80(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Valence fluctuation phenomena in rare-earth intermetallic compounds have attracted attention because the quantum criticality of the valence transition has been proposed theoretically. Recently, it was found that  -YbAlB
-YbAlB shows quantum criticality without tuning and has a strong mixed-valence state. In this study, we measured the magnetization curve and X-ray magnetoabsorption in
shows quantum criticality without tuning and has a strong mixed-valence state. In this study, we measured the magnetization curve and X-ray magnetoabsorption in  -YbAl
-YbAl Fe
Fe B
B (
(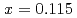 ), which is a locally isostructural polymorph of
), which is a locally isostructural polymorph of  -YbAlB
-YbAlB . The magnetization and X-ray experiments were performed in fields up to 55 and 40 T, respectively. A small increase in the Yb valence was observed at fields where the magnetization curve exhibited a change in slope.
. The magnetization and X-ray experiments were performed in fields up to 55 and 40 T, respectively. A small increase in the Yb valence was observed at fields where the magnetization curve exhibited a change in slope.
 Si
Si observed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy
observed by X-ray absorption spectroscopyNakai, Hirohito*; Ebihara, Takao*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Kondo, Akihiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(12), p.124712_1 - 124712_5, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The temperature and magnetic field dependences of Yb valence were observed in the heavy fermion compoundYbRh Si
Si by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The measurements revealed that the Yb valence decreases with decreasing temperature in the range from 200 to 2 K and increases with increasing magnetic field in the range from 0 to 33 T without showing an abrupt change in the Yb valence. The Yb valence is in the range from 2.92 to 2.96 depending on temperature and magnetic field. With respect to the valence being 2.92 at 0 T and 2.93 at 33 T in 2 K, YbRh
by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. The measurements revealed that the Yb valence decreases with decreasing temperature in the range from 200 to 2 K and increases with increasing magnetic field in the range from 0 to 33 T without showing an abrupt change in the Yb valence. The Yb valence is in the range from 2.92 to 2.96 depending on temperature and magnetic field. With respect to the valence being 2.92 at 0 T and 2.93 at 33 T in 2 K, YbRh Si
Si is a valence fluctuation compound and does not reach the integer trivalent state at high magnetic field. These results endorse the conventional knowledge that the valence of Yb is very close to the integer value of 3+, decreases with decreasing temperature, and becomes closer to 3+ with increasing magnetic field.
is a valence fluctuation compound and does not reach the integer trivalent state at high magnetic field. These results endorse the conventional knowledge that the valence of Yb is very close to the integer value of 3+, decreases with decreasing temperature, and becomes closer to 3+ with increasing magnetic field.

Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Her, J.-L.*; Kindo, Koichi*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Chen, B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(11), p.114702_1 - 114702_11, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.34(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The X-ray absorption and magnetic circular dichroism (MCD) spectra at the Yb L edge were measured in the mixed-valent heavy fermion compound YbAgCu
edge were measured in the mixed-valent heavy fermion compound YbAgCu at high magnetic fields and low temperatures. The magnetic-field-temperature (H-T) phase boundary determined by the valence state is in very good agreement with that determined by the magnetization. It is clearly found that the metamagnetism of this compound is due to the field induced valence transition. A distinctive positive peak of the XMCD spectra appears in the vicinity of the white line of the absorption due to Yb
at high magnetic fields and low temperatures. The magnetic-field-temperature (H-T) phase boundary determined by the valence state is in very good agreement with that determined by the magnetization. It is clearly found that the metamagnetism of this compound is due to the field induced valence transition. A distinctive positive peak of the XMCD spectra appears in the vicinity of the white line of the absorption due to Yb state, while no feature is observed in the XMCD spectra corresponding to the Yb
state, while no feature is observed in the XMCD spectra corresponding to the Yb state. A small negative XMCD peak was observed at a lower energy and was attributed to the quadrupole trasition from theoretical calcuration, which explains its peculicar magnetic field dependence.
state. A small negative XMCD peak was observed at a lower energy and was attributed to the quadrupole trasition from theoretical calcuration, which explains its peculicar magnetic field dependence.
 -electron itinerancy in CeRu
-electron itinerancy in CeRu Si
Si by a strong magnetic field
by a strong magnetic fieldMatsuda, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Her, J. L.*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Kindo, Koichi*; Ebihara, Takao*
Physical Review B, 86(4), p.041109_1 - 041109_4, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:36.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The valence state of Ce in a typical heavy fermion compound CeRu Si
Si has been investigated by synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy at 1.8 K in high magnetic fields of up to 40T. The valence was slightly larger than for the pure trivalent state, as expected in heavy fermion compounds, and it decreased toward the trivalent state as the magnetic field was increased. The field-induced valence reduction indicates that the itinerant character of the 4
has been investigated by synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy at 1.8 K in high magnetic fields of up to 40T. The valence was slightly larger than for the pure trivalent state, as expected in heavy fermion compounds, and it decreased toward the trivalent state as the magnetic field was increased. The field-induced valence reduction indicates that the itinerant character of the 4 electrons in CeRu
electrons in CeRu Si
Si was suppressed by a strong magnetic field. The suppression was gradual and showed a characteristic magnetic field dependence, which reflects the metamagnetism around
was suppressed by a strong magnetic field. The suppression was gradual and showed a characteristic magnetic field dependence, which reflects the metamagnetism around 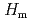
 8T.
8T.
 at high Magnetic fields
at high Magnetic fieldsMatsuda, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Her, J.-L.*; Kindo, Koichi*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Chen, B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(1), p.015002_1 - 015002_2, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.34(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The valence change of Yb ion in YbAgCu was measured by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy under high magnetic fields up to 35T. The valence state of Yb in YbAgCu
was measured by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy under high magnetic fields up to 35T. The valence state of Yb in YbAgCu at 4.8K significantly increases at the metamagnetic transition. The saturation value of
at 4.8K significantly increases at the metamagnetic transition. The saturation value of  at 55T is evaluated as 2.97 using the relation
at 55T is evaluated as 2.97 using the relation 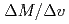 at 35T. This value is in good agreement with
at 35T. This value is in good agreement with  for the related compound YbInCu
for the related compound YbInCu at high temperatures and the Yb valence in the localized high-field phase. We conclude that the metamagnetic transition in YbAgCu
at high temperatures and the Yb valence in the localized high-field phase. We conclude that the metamagnetic transition in YbAgCu arises from the valence transition, as theoretically predicted.
arises from the valence transition, as theoretically predicted.
 Os
Os O
O studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroismMatsuda, Yasuhiro*; Her, J.-L.*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kindo, Koichi*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Hiroi, Zenji*
Physical Review B, 84(17), p.174431_1 - 174431_5, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:69.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) at the 
 -edge of Os has been investigated in the antiferromagneticphase of Cd
-edge of Os has been investigated in the antiferromagneticphase of Cd Os
Os O
O , which exhibits a metal-insulator transition around 227 K. According to the sum rule, the XMCD spectra at 10 and 37 T clearly show that the ratio between the orbital magnetic moment (
, which exhibits a metal-insulator transition around 227 K. According to the sum rule, the XMCD spectra at 10 and 37 T clearly show that the ratio between the orbital magnetic moment (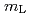 ) and spinmagnetic moment (
) and spinmagnetic moment (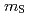 ) is
) is 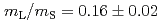 , and that
, and that 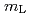 and
and 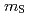 are coupled in parallel (
are coupled in parallel (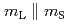 ). These phenomena are unusual in that the expected ground state of Os
). These phenomena are unusual in that the expected ground state of Os (5
(5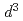 ) is an orbital singlet in a cubic crystal field, and
) is an orbital singlet in a cubic crystal field, and 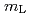 and
and 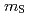 should be antiparallel for a less than half-filled system in accordance with Hund's third rule. It is likely that the spin-orbit coupling is important for explaining the observed orbital magnetism.
should be antiparallel for a less than half-filled system in accordance with Hund's third rule. It is likely that the spin-orbit coupling is important for explaining the observed orbital magnetism.