Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Kinjo, Katsuki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Matsumura, Hiroki*; Hori, Fumiya*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 9(30), p.2736_1 - 2736_6, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:88.25(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Te-NMR on the uranium-based superconductor UTe
Te-NMR on the uranium-based superconductor UTe
Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Nakamine, Genki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(5), p.053702_1 - 053702_5, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:77.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -axis knight shift on UTe
-axis knight shift on UTe with
with  = 2.1 K
= 2.1 KMatsumura, Hiroki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(6), p.063701_1 - 063701_5, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:98.12(Physics, Multidisciplinary) induced by magnetic field
induced by magnetic fieldKinjo, Katsuki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Physical Review B, 107(6), p.L060502_1 - L060502_5, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:92.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) under pressure revealed by
under pressure revealed by  Te-NMR
Te-NMRKinjo, Katsuki*; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Nakamine, Genki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(14), p.L140502_1 - L140502_5, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:63.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) determined by knight shift measurement
determined by knight shift measurementFujibayashi, Hiroki*; Nakamine, Genki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(4), p.043705_1 - 043705_4, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:97.07(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This study investigates the spin susceptibility in U-based superconductor UTe in the superconducting (SC) state by using Knight shift measurements for a magnetic field
in the superconducting (SC) state by using Knight shift measurements for a magnetic field  along the
along the  axis, which is the magnetic easy axis of UTe
axis, which is the magnetic easy axis of UTe . Although a tiny anomaly ascribed to the SC diamagnetic effect was observed just below the SC transition temperature
. Although a tiny anomaly ascribed to the SC diamagnetic effect was observed just below the SC transition temperature  , the
, the  -axis Knight shift in the SC state shows no significant decrease, following the extrapolation from the normal-state temperature dependence. This indicates that the spin susceptibility is nearly unchanged below
-axis Knight shift in the SC state shows no significant decrease, following the extrapolation from the normal-state temperature dependence. This indicates that the spin susceptibility is nearly unchanged below  . Considering the previous Knight shift results for
. Considering the previous Knight shift results for 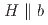 and
and 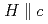 , the dominant SC state is determined to be
, the dominant SC state is determined to be 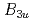 in the spin-triplet pairing, which is consistent with the spin anisotropy in the normal state. The present result shows that UTe
in the spin-triplet pairing, which is consistent with the spin anisotropy in the normal state. The present result shows that UTe is a spin-triplet superconductor with spin degrees of freedom.
is a spin-triplet superconductor with spin degrees of freedom.

Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Haga, Yoshinori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(2), p.023707_1 - 023707_5, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:91.89(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Te NMR experiments in field (
Te NMR experiments in field ( ) applied along the easy magnetization axis (the
) applied along the easy magnetization axis (the  -axis) revealed slow electronic dynamics developing in the paramagnetic state of UTe
-axis) revealed slow electronic dynamics developing in the paramagnetic state of UTe . The observed slow fluctuations are concerned with a successive growth of long-range electronic correlations below 30
. The observed slow fluctuations are concerned with a successive growth of long-range electronic correlations below 30 40 K, where the spin susceptibility along the hard magnetization axis (the
40 K, where the spin susceptibility along the hard magnetization axis (the  -axis) shows a broad maximum. The experiments also imply that tiny amounts of disorder or defects locally disturb the long-range electronic correlations and develop an inhomogeneous electronic state at low temperatures, leading to a low temperature upturn observed in the bulk-susceptibility in
-axis) shows a broad maximum. The experiments also imply that tiny amounts of disorder or defects locally disturb the long-range electronic correlations and develop an inhomogeneous electronic state at low temperatures, leading to a low temperature upturn observed in the bulk-susceptibility in 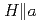 . We suggest that UTe
. We suggest that UTe would be located on the paramagnetic side near an electronic phase boundary, where either the magnetic or Fermi-surface instability would be the origin of the characteristic fluctuations.
would be located on the paramagnetic side near an electronic phase boundary, where either the magnetic or Fermi-surface instability would be the origin of the characteristic fluctuations.
 Te NMR on UTe
Te NMR on UTe
Nakamine, Genki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(6), p.064709_1 - 064709_7, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:87.29(Physics, Multidisciplinary) probed with
probed with  Te-NMR measurement
Te-NMR measurementNakamine, Genki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Nakamura, Ai*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(10), p.L100503_1 - L100503_5, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:93.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Si
Si
Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Haga, Yoshinori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Harima, Hisatomo*
no journal, ,
In this study, the local symmetry of Ru site is determined in the hidden order state under uni-axial stress along the [100] and [110] directions [4], by means of precise Ru-NQR measurements. These measurements again support the 4-fold symmetry at Ru site in the hidden order state without uni-axial stress. Furthermore, certain cases can be excluded from the previously proposed possible ones.
 Si
Si
Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Harima, Hisatomo*
no journal, ,
Consider the hidden order of URu Si
Si . Recent studies have limited the electronic state symmetry of hidden ordered states to some space groups. However, it is still difficult to distinguish because it has the same high symmetry. Therefore, it is necessary to see how the symmetry of the hidden ordered state is lowered by the external field such as uniaxial pressure. In this study, we discuss Ru-NQR when the uniaxial pressure is applied in the [100] direction to form an orthorhombic crystal.
. Recent studies have limited the electronic state symmetry of hidden ordered states to some space groups. However, it is still difficult to distinguish because it has the same high symmetry. Therefore, it is necessary to see how the symmetry of the hidden ordered state is lowered by the external field such as uniaxial pressure. In this study, we discuss Ru-NQR when the uniaxial pressure is applied in the [100] direction to form an orthorhombic crystal.

Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Haga, Yoshinori; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Opletal, P.; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; et al.
no journal, ,
 Si
Si under uniaxial stress, 2
under uniaxial stress, 2Kambe, Shinsaku; Haga, Yoshinori; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; Harima, Hisatomo*
no journal, ,
Consider the hidden order of URu Si
Si . Recent studies have shown that the electronic state symmetry of hidden ordered states is restricted to a few space groups. However, since they have the same high symmetry, their distinction remains difficult. Therefore, it is necessary to see how external fields such as uniaxial pressure lower the symmetry of hidden ordered states. In this study, we discuss the Ru-NQR when the uniaxial pressure is applied to the [100] and [110] directions to form orthorhombic crystals.
. Recent studies have shown that the electronic state symmetry of hidden ordered states is restricted to a few space groups. However, since they have the same high symmetry, their distinction remains difficult. Therefore, it is necessary to see how external fields such as uniaxial pressure lower the symmetry of hidden ordered states. In this study, we discuss the Ru-NQR when the uniaxial pressure is applied to the [100] and [110] directions to form orthorhombic crystals.

Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; Fujibayashi, Hiroki*; Kinjo, Katsuki*; Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Ishida, Kenji*; et al.
no journal, ,
We report the results of  Te NMR measurements in field (
Te NMR measurements in field ( ) applied along the easy magnetization axis (the
) applied along the easy magnetization axis (the  -axis). The experiments revealed slow electronic dynamics developing in the paramagnetic state of UTe
-axis). The experiments revealed slow electronic dynamics developing in the paramagnetic state of UTe . The observed slow fluctuations are concerned with a successive growth of long-range electronic correlations below 30
. The observed slow fluctuations are concerned with a successive growth of long-range electronic correlations below 30 40 K, where the spin susceptibility along the hard magnetization axis (the
40 K, where the spin susceptibility along the hard magnetization axis (the  -axis) shows a broad maximum. The experiments also imply that tiny amounts of disorder or defects locally disturb the long-range electronic correlations and develop an inhomogeneous electronic state at low temperatures, leading to a low temperature upturn observed in the bulk-susceptibility in
-axis) shows a broad maximum. The experiments also imply that tiny amounts of disorder or defects locally disturb the long-range electronic correlations and develop an inhomogeneous electronic state at low temperatures, leading to a low temperature upturn observed in the bulk-susceptibility in 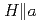 .
.