Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe and
Fe and  Pu deposited on Earth constrain the r-process yields of recent nearby supernovae
Pu deposited on Earth constrain the r-process yields of recent nearby supernovaeWallner, A.*; Froehlich, M. B.*; Hotchkis, M. A. C.*; Kinoshita, N.*; Paul, M.*; Martschini, M.*; Pavetich, S.*; Tims, S. G.*; Kivel, N.*; Schumann, D.*; et al.
Science, 372(6543), p.742 - 745, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:96.93(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Half of the chemical elements heavier than iron are produced by the rapid neutron capture process (r-process). The sites and yields of this process are disputed, with candidates including some types of supernovae (SNe) and mergers of neutron stars. We search for two isotopic signatures in a sample of Pacific Ocean crust-iron-60 ( Fe) (half-life, 2.6 million years), which is predominantly produced in massive stars and ejected in supernova explosions, and
Fe) (half-life, 2.6 million years), which is predominantly produced in massive stars and ejected in supernova explosions, and  Pu (half-life, 80.6 million years), which is produced solely in r-process events. We detect two distinct influxes of
Pu (half-life, 80.6 million years), which is produced solely in r-process events. We detect two distinct influxes of  Fe to Earth in the last 10 million years and accompanying lower quantities of
Fe to Earth in the last 10 million years and accompanying lower quantities of  Pu. The
Pu. The  Pu/
Pu/ Fe influx ratios are similar for both events. The
Fe influx ratios are similar for both events. The  Pu influx is lower than expected if SNe dominate r-process nucleosynthesis, which implies some contribution from other sources.
Pu influx is lower than expected if SNe dominate r-process nucleosynthesis, which implies some contribution from other sources.
Koarashi, Jun; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Nagano, Hirohiko*; Sugiharto, U.*; Saengkorakot, C.*; Suzuki, Takashi; Kokubu, Yoko; Fujita, Natsuko; Kinoshita, Naoki; Nagai, Haruyasu; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2020-012, 53 Pages, 2020/10
There is growing concern that recent rapid changes in climate and environment could have a significant influence on carbon cycling in terrestrial ecosystems (especially forest ecosystems) and could consequently lead to a positive feedback for global warming. The magnitude and timing of this feedback remain highly uncertain largely due to a lack of quantitative understanding of the dynamics of organic carbon stored in soils and its responses to changes in climate and environment. The tracing of radiocarbon (natural and bomb-derived  C) and stable carbon (
C) and stable carbon ( C) isotopes through terrestrial ecosystems can be a powerful tool for studying soil organic carbon (SOC) dynamics. The primary aim of this guide is to promote the use of isotope-based approaches to improve our understanding of the carbon cycling in soils, particularly in the Asian region. The guide covers practical methods of soil sampling; treatment and fractionation of soil samples; preparation of soil samples for
C) isotopes through terrestrial ecosystems can be a powerful tool for studying soil organic carbon (SOC) dynamics. The primary aim of this guide is to promote the use of isotope-based approaches to improve our understanding of the carbon cycling in soils, particularly in the Asian region. The guide covers practical methods of soil sampling; treatment and fractionation of soil samples; preparation of soil samples for  C (and stable nitrogen isotope,
C (and stable nitrogen isotope,  N) and
N) and  C analyses; and
C analyses; and  C,
C,  N, and
N, and  C measurements by the use of isotope ratio mass spectrometry and accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS). The guide briefly introduces ways to report
C measurements by the use of isotope ratio mass spectrometry and accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS). The guide briefly introduces ways to report  C data, which are frequently used for soil carbon cycling studies. The guide also reports results of a case study conducted in a Japanese forest ecosystem, as a practical application of the use of isotope-based approaches. This guide is mainly intended for researchers who are interested but are not experienced in this research field. The guide will hopefully encourage readers to participate in soil carbon cycling studies, including field works, laboratory experiments, isotope analyses, and discussions with great interest.
C data, which are frequently used for soil carbon cycling studies. The guide also reports results of a case study conducted in a Japanese forest ecosystem, as a practical application of the use of isotope-based approaches. This guide is mainly intended for researchers who are interested but are not experienced in this research field. The guide will hopefully encourage readers to participate in soil carbon cycling studies, including field works, laboratory experiments, isotope analyses, and discussions with great interest.
Kuroda, Kenta*; Arai, Yosuke*; Rezaei, N.*; Kunisada, So*; Sakuragi, Shunsuke*; Alaei, M.*; Kinoshita, Yuto*; Bareille, C.*; Noguchi, Ryo*; Nakayama, Mitsuhiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.2888_1 - 2888_9, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:75.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Hirayama, Hideo*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Mokhov, N.*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.2055 - 2058, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)It is important to obtain neutron spectra and its intensity on shielding experiment. Deduction of high-energy neutron spectra were done using fitting and unfolding methods based on the shielding data obtained at the anti-proton (pbar) target station in Fermilab. The neutron spectra for fitting method is useful to be easily obtained and the values gave reasonable results compared with nuclear data. Therefore, that for unfolding methods included inconsistency. Furthermore, the deduced neutron spectra were verified through the calculation analyses by PHITS code.
Yashima, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Boehnlein, D.*; Lautenschlager, G.*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.2051 - 2054, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The experiment was performed at the anti-proton (pbar) production target station in Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. At the pbar target station, an anti-proton production target, consisted of Inconel and copper disks, were irradiated by 120 GeV proton beam. The beam intensity was 2.0  10
10 proton per second. Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were set around the target to investigate the spatial and energy distribution of secondary particles emitted from the target. After irradiation, induced activities of samples were measured by using HPGe detector. The reaction rates of 30 nuclides induced in Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were obtained. The reaction rates of these nuclides increase for samples placed on forward angle position. The angle dependence of these reaction rates becomes larger for increasing threshold energy. These experimental results compared with the calculation. The calculated results generally agree with the experimental results within a factor of 3.
proton per second. Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were set around the target to investigate the spatial and energy distribution of secondary particles emitted from the target. After irradiation, induced activities of samples were measured by using HPGe detector. The reaction rates of 30 nuclides induced in Al, Nb, Cu, Au samples were obtained. The reaction rates of these nuclides increase for samples placed on forward angle position. The angle dependence of these reaction rates becomes larger for increasing threshold energy. These experimental results compared with the calculation. The calculated results generally agree with the experimental results within a factor of 3.
Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Toyoda, Akihiro*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Sakamoto, Yukio; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Mokhov, N.*; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.2059 - 2062, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In an antiproton production (Pbar) target station of the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL), the secondary particles produced by bombarding a target with 120-GeV protons are shielded by a thick iron shield. In order to obtain experimental data on high-energy proton accelerator facilities, we indirectly measured  100-MeV neutrons at the outside of the iron shield. The measurement was performed by using the Au activation method coupled with a low-background
100-MeV neutrons at the outside of the iron shield. The measurement was performed by using the Au activation method coupled with a low-background  -ray counting system. As an indicator for the neutron flux, we determined the production rates of 8 spallation nuclides (
-ray counting system. As an indicator for the neutron flux, we determined the production rates of 8 spallation nuclides (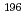 Au,
Au,  Pt,
Pt, 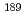 Ir,
Ir,  Os,
Os, 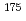 Hf,
Hf, 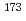 Lu,
Lu, 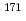 Lu, and
Lu, and 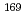 Yb) in the Au activation detector. The measured production rates were compared with the theoretical production rates calculated using PHITS. We proved that the Au activation method can serve as a powerful tool for indirect measurements of
Yb) in the Au activation detector. The measured production rates were compared with the theoretical production rates calculated using PHITS. We proved that the Au activation method can serve as a powerful tool for indirect measurements of  100-MeV neutrons that play a vital role in neutron transport.
100-MeV neutrons that play a vital role in neutron transport.
Yashima, Hiroshi*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; Vaziri, K.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.48 - 51, 2011/02
The shielding experiment was performed at the anti-proton production target station in Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. Aluminum, Bismath, Niobium, Copper and Indium samples were placed behind the shields. After irradiation, induced activities of samples were measured by using HPGe detector. The spatial distribution of reaction rate of samples which were placed behind the iron and concrete shields were obtained. The measured data shows that the reaction rates on the outer surfaces of the iron and concrete shields increases toward the downstream of the target. The obtained reaction rates were also fitted to Moyer's formula, and the attenuation lengths for iron and concrete shields were obtained.
Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.57 - 60, 2011/02
The anti-proton (pbar) production target in Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory can be produced a wide variety of secondary particles including of anti-protons, by bombarding with protons accelerated to 120 GeV. The shielding experimental data, which was obtained around the pbar target, make possible to validate the accuracies of the general-purpose Monte Carlo simulation codes. In this paper, spatial distribution of reaction rates were calculated with two-dimensional (r-z) geometry simplified the real pbar target station using the PHITS, MARS and MCNPX code. These experimental data in iron shield were compared with the calculated data. The comparison for attenuation length of iron were good agreement between the experiments and calculations.
Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Masukawa, Fumihiro; Mokhov, N.*; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 168(2), p.482 - 486, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental studies of shielding and radiation effects have been started using 120-GeV proton synchrotron at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) under collaboration between FNAL and Japan. The first campaign of the experiment was carried out at the Pbar target station and Numi experimental station at FNAL, using antiproton and neutrino production targets irradiated by 120-GeV protons. The generated secondary particles passing through steel, concrete and rock were measured by activation methods as well as by other detectors such as scintillator with a veto counter, phoswich detector and a Bonner ball counter on trial. Preliminary experimental results are presented.
Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Kinoshita, Kenichi*; Watanabe, Takahiro*; Sugahara, Jun*; Ueda, Toru*; Yoshii, Koji*; Kobayashi, Tetsuya*; Halz, N.*; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Sakai, Fumio*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 28(4), p.1133 - 1142, 2000/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:41.8(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Arakawa, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
A gold activation detector was studied as a high energy neutron detector at high radiation field in a series of shielding experiment at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. We could measure spallation residual nuclei with wide threshold energy by using a combination method with radiological chemical separation and X-X- coincidence detection methods. It was shown the detector was effective for high energy neutron detector.
coincidence detection methods. It was shown the detector was effective for high energy neutron detector.
Kasugai, Yoshimi; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kinoshita, Norikazu*; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Hirayama, Hideo*; Ishibashi, Kenji*; et al.
no journal, ,
On the shielding experiment, started on 2007, as collaborative research with Fermilab using high energy proton accelerators, the measurement of reaction rate distributions in the antiproton target station has been carried out. Reaction rates were measured with activation method. Using the reaction rate data, neutron spectra at each measurement position were deduced by means of nonlinear least square method; a shape of the neutron spectrum between 5 and 100 MeV was expressed as a fitting function with 5 fitting parameters, whose values were determined at a minimum of 
 values for the reaction rates. In the presentation, systematics of the variation of neutron spectra in the shield will be discussed.
values for the reaction rates. In the presentation, systematics of the variation of neutron spectra in the shield will be discussed.
Nakashima, Hiroshi; Mokhov, N.*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Leveling, A.*; Boehnlein, D.*; Vaziri, K.*; Sanami, Toshiya*; et al.
no journal, ,
Several multi-purpose high-energy radiation transport codes are used in many research fields such as high-energy physics as well as accelerator facility shielding designs. The codes are benchmarked against experimental data on a regular basis. To promote this to a higher level and to a hardly explored field of neutron radiation induced by energetic muons, a JASMIN collaboration (Japanese-American Study of Muon Interaction and Neutron detection), has been created with several Laboratories and Universities of Japan and U.S.A. The collaboration has performed a series of experiments at the Pbar target station and NuMI facility at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, using irradiation of targets with 120 GeV protons for antiproton and neutrino production. This paper reviews recent activities and results.