Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kimuro, Shingo; Taneichi, Yayoi; Iwata, Hajime; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kitamura, Akira; Tachi, Yukio; Tanaka, Takeru*; Hirano, Kana*; Hieda, Manami*; Miyabe, Shunsuke*; et al.
Journal of Solution Chemistry, 53(6), p.854 - 868, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical) (cr) at 318 K in the presence of iron
(cr) at 318 K in the presence of ironYoshida, Yasushi*; Kitamura, Akira; Shibutani, Sanae*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.900 - 910, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) O
O decomposition at the U
decomposition at the U O
O surface in bicarbonate solution
surface in bicarbonate solutionMcGrady, J.; Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kitamura, Akira; Kimuro, Shingo
RSC Advances (Internet), 11(46), p.28940 - 28948, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.90(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kitamura, Akira
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-020, 164 Pages, 2021/03
Part of JAEA's Thermodynamic Database (JAEA-TDB) for solubility and speciation of radionuclides (JAEA-TDB-RN) for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes has been updated with subsuming the database for geochemical calculations (JAEA-TDB-GC). This report has focused to update JAEA-TDB-RN after selecting change in standard Gibbs free energy of formation (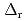
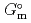 ), change in standard enthalpy change of formation (
), change in standard enthalpy change of formation (


 ), standard molar entropy (
), standard molar entropy (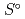
 ) and, heat capacity (
) and, heat capacity (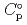 ), change in standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (
), change in standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (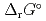
 ), change in standard enthalpy change of reaction (
), change in standard enthalpy change of reaction (
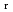


 ) and standard entropy change of reaction (
) and standard entropy change of reaction (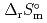 ) as well as logarithm of equilibrium constant (log
) as well as logarithm of equilibrium constant (log
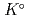 ) at standard state. The extent of selection of these thermodynamic data enables to evaluate solubility and speciation of radionuclides at temperatures other than 298.15 K. Furthermore, the latest thermodynamic data for iron which have been critically reviewed, selected and compiled by the Nuclear Energy Agency within Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) have been accepted. Most of previously selected log
) at standard state. The extent of selection of these thermodynamic data enables to evaluate solubility and speciation of radionuclides at temperatures other than 298.15 K. Furthermore, the latest thermodynamic data for iron which have been critically reviewed, selected and compiled by the Nuclear Energy Agency within Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) have been accepted. Most of previously selected log
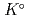 have been refined to confirm internal consistency with JAEA-TDB-GC. Text files of the updated JAEA-TDB have been provided for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
have been refined to confirm internal consistency with JAEA-TDB-GC. Text files of the updated JAEA-TDB have been provided for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
Kitamura, Akira; Yoshida, Yasushi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 327(2), p.839 - 845, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.71(Chemistry, Analytical)Thermodynamic data for radium for radioactive waste management have been predicted using an electrostatic model and correlation with the ionic radii of the alkaline earth metals. Estimation of the standard Gibbs free energy of formation and standard molar entropy of aqueous radium species and compounds has been based on such approaches as extrapolation of the thermodynamic properties of strontium and barium, and use of a model of ion pair formation. The predicted thermodynamic data for radium have been compared with previously reported values.
Kitamura, Akira; Yoshida, Yasushi*; Goto, Takahiro*; Shibutani, Sanae*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(2), p.58 - 71, 2020/12
Evaluation and estimation of solubility values are required for a performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes. Selection of solubility-limiting solid phases (SSPs) that control the solubility of radionuclides is necessary for the evaluation and estimation of solubility values. The authors have developed a methodology for selection of the SSP through a calculation of saturation indices (SIs) using thermodynamic database to show a transparent procedure for the selection. Literature survey should be performed to confirm decision of the SSP from candidate SSPs which generally have larger SIs from realistic point of view for precipitation and solubility control. The authors have selected the SSPs for the elements of interest for the latest Japanese performance assessment in bentonite and cement porewaters after grouping various water compositions.
Kitamura, Akira; Akahori, Kuniaki; Nagata, Masanobu*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(2), p.83 - 93, 2020/12
Direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel (SNF) in deep underground repositories (hereafter "direct disposal") is a concept that disposal canisters stored fuel assemblies dispose without reprocessing. Behavior of radionuclide release from SNF must be different from that from vitrified glass. The present study established a methodology on determination of instant release fraction (IRF) of radionuclides from SNF, which is the one of the parameters on radionuclide release based on the latest safety assessment reports in other countries, especially for IRF values proportional to a fission gas release ratio (FGR). Recommended and maximum values of FGR have been estimated using the fuel performance code FEMAXI-7 after collecting FGR values on Japanese SNFs. Furthermore, recommended and maximum values of IRF for Japanese SNFs used in a pressurized water reactor (PWR) have been estimated using the presently obtained FGR values and experimentally obtained IRF values on foreign SNFs. The recommended and maximum IRF values obtained in the present study have been compared with those of the latest safety assessment reports in other countries.
Kitamura, Akira
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(1), p.23 - 28, 2020/01
, 62(1), p.23 - 28, 2020/01
Thermodynamic databases (TDBs) for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level waste and TRU waste have been developed to predict solubility and speciation of radionuclides in groundwater in some countries including Japan. The present manuscript briefly describes current status of development of the TDB organized by the Nuclear Energy Agency within the Organisation of Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) and the TDBs in some countries including Japan.
 -isosaccharinic acid
-isosaccharinic acidKobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 138, p.151 - 158, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:23.66(Thermodynamics)The effect of  -isosaccharinic acid (ISA) on the solubility and redox of tetravalent and hexavalent uranium (U(IV), U(VI)) was investigated in the hydrogen ion concentration (pH
-isosaccharinic acid (ISA) on the solubility and redox of tetravalent and hexavalent uranium (U(IV), U(VI)) was investigated in the hydrogen ion concentration (pH ) range of 6
) range of 6 13 and at total ISA concentration ([ISA]
13 and at total ISA concentration ([ISA]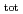 ) = 10
) = 10
 10
10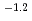 mol/dm
mol/dm . The dependence of U(IV) solubility on pH
. The dependence of U(IV) solubility on pH and [ISA]
and [ISA]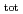 suggested the existence of U(OH)
suggested the existence of U(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 as a dominant species within the investigated pH
as a dominant species within the investigated pH range of 6
range of 6 12. For the U(VI)-ISA system, UO
12. For the U(VI)-ISA system, UO (OH)
(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 was suggested as a dominant species at pH
was suggested as a dominant species at pH 7
7 13. The formation constants of the U(IV)-ISA and U(VI)-ISA complexes were determined by least-squares fitting of the solubility data. The solubility of U(IV) and U(VI) in the presence of ISA and its effect on the redox behavior were thermodynamically interpreted based on the obtained constants.
13. The formation constants of the U(IV)-ISA and U(VI)-ISA complexes were determined by least-squares fitting of the solubility data. The solubility of U(IV) and U(VI) in the presence of ISA and its effect on the redox behavior were thermodynamically interpreted based on the obtained constants.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:99.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
 -UO
-UO
 -CO
-CO
 system and integration with JAEA's thermodynamic database for geochemical calculations
system and integration with JAEA's thermodynamic database for geochemical calculationsKitamura, Akira
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-018, 103 Pages, 2019/03
The latest available thermodynamic data were critically reviewed and the selected values were included into the JAEA-TDB for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes. This critical review specifically addressed thermodynamic data for (1) a zirconium-hydroxide system through comparison of thermodynamic data selected by the Nuclear Energy Agency within the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA), (2) complexation of metal ions with isosaccharinic acid based on the latest review papers. Furthermore, the author performed (3) tentative selection of thermodynamic data on ternary complexes among alkaline-earth metal, uranyl and carbonate ions, and (4) integration with the latest version of JAEA's thermodynamic database for geochemical calculations. The internal consistency of the selected data was checked by the author. Text files of the updated and integrated thermodynamic database have been prepared for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
 addition on water durability of FeO-Fe
addition on water durability of FeO-Fe O
O -P
-P O
O glasses
glassesKitamura, Naoto*; Nomura, Akira*; Saito, Akira*; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Amamoto, Ippei; Takebe, Hiromichi*
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 126(11), p.948 - 951, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:23.20(Materials Science, Ceramics)We studied compositional dependence of water durability of Zr(IV) containing FeO-Fe O
O -P
-P O
O glasses systems, which can apply to immobilize nuclear waste of Zr isotope. Stabilized film with interference fringe on the surface improves better water durability after immersion tests for BaO and ZrO
glasses systems, which can apply to immobilize nuclear waste of Zr isotope. Stabilized film with interference fringe on the surface improves better water durability after immersion tests for BaO and ZrO coexisting glasses without fracture. On the other hand, microcrystalline ZrP
coexisting glasses without fracture. On the other hand, microcrystalline ZrP O
O was detected in the glass matrix when more than 1 mol% of ZrO
was detected in the glass matrix when more than 1 mol% of ZrO incorporated. The effect of impregnated ZrP
incorporated. The effect of impregnated ZrP O
O crystal on the structure was discussed based on the phosphate structure analyzed by Raman spectra. Formation of Q
crystal on the structure was discussed based on the phosphate structure analyzed by Raman spectra. Formation of Q and Q
and Q units, which contribute to water durability in the glass, are due to preferential precipitation of ZrP
units, which contribute to water durability in the glass, are due to preferential precipitation of ZrP O
O crystal.
crystal.
Rai, D.*; Yui, Mikazu; Kitamura, Akira
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.19 - 26, 2018/11
The objectives of this presentation are (1) to describe the solubility method, (2) to list desirable criteria of the solubility method so that the reader can recognize which studies have been done in a way that yields quality information, (3) to present an example of how to use the evaluation criteria, and (4) to provide a few examples of future research needs where the solubility method is ideally suited and the other methods are unsuitable for these investigations.
 (am) solubility at 25
(am) solubility at 25 C in the Ca
C in the Ca -Na
-Na -H
-H -Cl
-Cl -OH
-OH -H
-H O system; A Critical review
O system; A Critical reviewRai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Altmaier, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Journal of Solution Chemistry, 47(5), p.855 - 891, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:10.90(Chemistry, Physical)We have critically reviewed experimental data for Zr hydrolysis constant values for formation of several mononuclear and polynuclear species and a solubility product value for ZrO (am). We have determined new/revised values for the formation constants of Zr(OH)
(am). We have determined new/revised values for the formation constants of Zr(OH)
 , Zr(OH)
, Zr(OH) (aq), Zr(OH)
(aq), Zr(OH)
 , Zr(OH)
, Zr(OH)
 and Ca
and Ca Zr(OH)
Zr(OH)
 , and the solubility product for ZrO
, and the solubility product for ZrO (am) after the critical review.
(am) after the critical review.
Rai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 114, p.135 - 143, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:20.39(Thermodynamics)Isosaccharinic acid is a cellulose degradation product that can form in low-level nuclear waste repositories and is known to form strong complexes with many elements, including actinides, disposed of in these repositories. We (1) reviewed the available data for deprotonation and lactonisation constants of isosaccharinic acid, and the isosaccharinate binding constants for Ca, Fe(III), Th, U(IV), U(VI), Np(IV), Pu(IV), and Am(III), (2) summarized complexation constant values for predicting actinide behavior in geologic repositories in the presence of isosaccharinate, and (3) outlined additional studies to acquire reliable thermodynamic data where the available data are inadequate.
 and spent fuel; A Review
and spent fuel; A ReviewKitamura, Akira; Akahori, Kuniaki*
Advances in Materials Science for Environmental and Energy Technologies, 6, p.133 - 144, 2017/10
The Japanese geological disposal program has started researching disposal of spent nuclear fuel (SF) in deep geological strata as an alternative management option other reprocessing followed by vitrification and geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. One of the key parameters for SF disposal other than the disposal of high-level radioactive waste is the fuel dissolution rate. Carbonate concentration in the simulated water composition with contact to SF after canister breaching in the Japanese SF disposal system is around 10 mol dm
mol dm , which is one order of magnitude larger than those in some countries in Europe. The SF dissolution rate will be depend on carbonate concentration due to promoting oxidative dissolution of SF by formation of carbonate complexes of uranium(VI). For evaluation of reliable SF dissolution rate in the Japanese SF disposal system as an alternative management option, effect of carbonate concentration on dissolution rate of UO
, which is one order of magnitude larger than those in some countries in Europe. The SF dissolution rate will be depend on carbonate concentration due to promoting oxidative dissolution of SF by formation of carbonate complexes of uranium(VI). For evaluation of reliable SF dissolution rate in the Japanese SF disposal system as an alternative management option, effect of carbonate concentration on dissolution rate of UO and spent fuel has been reviewed.
and spent fuel has been reviewed.
 (am) in the aqueous K
(am) in the aqueous K - HCO
- HCO
 - CO
- CO
 - OH
- OH - H
- H O system
O systemRai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Rosso, K.*
Radiochimica Acta, 105(8), p.637 - 647, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.58(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Solubility of HfO (am) was determined as a function of KHCO
(am) was determined as a function of KHCO concentrations ranging from 0.001 mol.kg
concentrations ranging from 0.001 mol.kg to 0.1 mol.kg
to 0.1 mol.kg . The solubility of HfO
. The solubility of HfO (am) increased dramatically with the increase in KHCO
(am) increased dramatically with the increase in KHCO concentrations, indicating that Hf(IV) makes strong complexes with carbonate. Thermodynamic equilibrium constants for the formation of Hf-carbonate complexes were determined using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The dramatic increase in Hf concentrations with the increase in KHCO
concentrations, indicating that Hf(IV) makes strong complexes with carbonate. Thermodynamic equilibrium constants for the formation of Hf-carbonate complexes were determined using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The dramatic increase in Hf concentrations with the increase in KHCO concentrations can best be described by the formation of Hf(OH-)
concentrations can best be described by the formation of Hf(OH-) (CO
(CO )
)
 and Hf(CO
and Hf(CO )
)
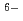 . The log
. The log K
K values for the reactions [Hf
values for the reactions [Hf + 2 CO
+ 2 CO
 +2 OH
+2 OH
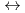 Hf(OH)
Hf(OH) (CO
(CO )
)
 ] and [Hf
] and [Hf + 5 CO
+ 5 CO

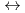 Hf(CO
Hf(CO )
)
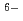 ], based on the SIT model, were determined to be 44.53
], based on the SIT model, were determined to be 44.53  0.46 and 41.53
0.46 and 41.53  0.46, respectively.
0.46, respectively.
Kobayashi, Taishi*; Teshima, Takeshi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(2), p.233 - 241, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)Zr solubility in the presence of gluconic acid (GLU) and isosaccharinic acid (ISA) was investigated as a function of hydrogen ion concentration (pH ) and the total concentration of GLU or ISA. The dependence of the increase in Zr solubility on the pH
) and the total concentration of GLU or ISA. The dependence of the increase in Zr solubility on the pH and GLU concentration suggested the existence of Zr(OH)
and GLU concentration suggested the existence of Zr(OH) (GLU)
(GLU)
 in the neutral pH region and Zr(OH)
in the neutral pH region and Zr(OH) (GLU)(GLU
(GLU)(GLU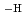 )
) in the alkaline pH region above pH
in the alkaline pH region above pH 10 as the dominant species in the presence of 10
10 as the dominant species in the presence of 10 - 10
- 10 mol/dm
mol/dm (M) GLU. In the presence of ISA, the dominant species Zr(OH)
(M) GLU. In the presence of ISA, the dominant species Zr(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 and Zr(OH)
and Zr(OH) (ISA)(ISA
(ISA)(ISA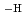 )
) were proposed to occur in the neutral and alkaline pH regions, similar to those found in the presence of GLU. From X-ray diffraction analysis, the solubility-limiting solid phase in the presence of GLU and ISA was considered to be Zr(OH)
were proposed to occur in the neutral and alkaline pH regions, similar to those found in the presence of GLU. From X-ray diffraction analysis, the solubility-limiting solid phase in the presence of GLU and ISA was considered to be Zr(OH) (am). The formation constants of the Zr gluconate and isosaccharinate complexes were determined by least squares fitting analysis of the solubility data, and the obtained values were discussed in comparison with those of tetravalent actinides.
(am). The formation constants of the Zr gluconate and isosaccharinate complexes were determined by least squares fitting analysis of the solubility data, and the obtained values were discussed in comparison with those of tetravalent actinides.
 (cr)
(cr)Rai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Rosso, K. M.*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Radiochimica Acta, 104(8), p.583 - 592, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.07(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Solubility studies were conducted with HfO (cr) solid as a function of acid concentrations. These studies involved (1) using two different amounts of the solid phase, (2) acid washing the bulk solid phase, (3) preheating the solid phase to 1400
(cr) solid as a function of acid concentrations. These studies involved (1) using two different amounts of the solid phase, (2) acid washing the bulk solid phase, (3) preheating the solid phase to 1400  C, and (4) heating amorphous HfO
C, and (4) heating amorphous HfO (am) suspensions to 90
(am) suspensions to 90  C to ascertain whether the HfO
C to ascertain whether the HfO (am) converts to HfO
(am) converts to HfO (cr) and to determine the solubility from the oversaturation direction. Based on the results of these treatments it is concluded that the HfO
(cr) and to determine the solubility from the oversaturation direction. Based on the results of these treatments it is concluded that the HfO (cr) contains a small fraction of less crystalline, but not amorphous, material [HfO
(cr) contains a small fraction of less crystalline, but not amorphous, material [HfO (lcr)] and this, rather than the HfO
(lcr)] and this, rather than the HfO (cr), is the solubility-controlling phase in the range of experimental variables investigated in this study. The solubility data are interpreted using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The log
(cr), is the solubility-controlling phase in the range of experimental variables investigated in this study. The solubility data are interpreted using both the Pitzer and SIT models. The log of the solubility product of HfO
of the solubility product of HfO (cr) is estimated. The observation of a small fraction of less crystalline higher solubility material is consistent with the general picture that mineral surfaces are often structurally and/or imperfect leading to a higher solubility than the bulk crystalline solid. This study stresses the urgent need, during interpretation of solubility data, of taking precautions to make certain that the observed solubility behavior for sparingly-soluble solids is assigned to the proper solid phase.
(cr) is estimated. The observation of a small fraction of less crystalline higher solubility material is consistent with the general picture that mineral surfaces are often structurally and/or imperfect leading to a higher solubility than the bulk crystalline solid. This study stresses the urgent need, during interpretation of solubility data, of taking precautions to make certain that the observed solubility behavior for sparingly-soluble solids is assigned to the proper solid phase.
Kitamura, Akira; Chikazawa, Takahiro*; Akahori, Kuniaki*; Tachi, Yukio
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 23(1), p.55 - 72, 2016/06
The Japanese geological disposal program has started researching disposal of spent nuclear fuel (SF) in deep geological strata (hereafter "direct disposal of SF") as an alternative management option other reprocessing followed by vitrification and geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. We conducted literature survey of dissolution rate of SF matrix and constructing materials (e.g. zircaloy cladding and control rods) selected in safety assessment reports for direct disposal of SF in Europe and United States. We also investigated basis of release rate determination and assignment of uncertainties in the safety assessment reports. Furthermore, we summarized major conclusions proposed by some European projects governed by European Commission. It was found that determined release rates are fairly similar to each other due to use of similar literature data in all countries of interest. It was also found that the determined release rates were including conservativeness because it was difficult to assign uncertainties quantitatively. It is expected that these findings are useful as fundamental information for determination of the release rates for the safety assessment of Japanese SF disposal system.