Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
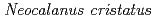 (Copepoda) from a deep sediment-trap; Abundance and implications for ecological and biogeochemical studies
(Copepoda) from a deep sediment-trap; Abundance and implications for ecological and biogeochemical studiesIkenoue, Takahito*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Honda, Makio*; Kitamura, Minoru*; Mino, Yoshihisa*; Narita, Hisashi*; Kobayashi, Takuya
Frontiers in Marine Science (Internet), 9, p.884320_1 - 884320_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)We studied seasonal variations of the mesozooplankton swimmer community collected by a sediment trap moored at 873 m in the Kuroshio & Oyashio Transition region off the east coast of Japan from 5 August 2011 to 23 June 2013. The total flux of mesozooplankton swimmers varied between 0 and 11.1 individuals m-2 d-1, with a mean of 3.1 individuals m-2 d-1 during the sampling period. Among the Copepoda, Neocalanus cristatus was the most dominant taxon. The species composition of the swimmers closely reflected the mid-depth mesozooplankton of the Oyashio region. The fluxes of Neocalanus species reflected ontogenetic vertical migration, but may have been overestimates of active fluxes if they included dormant individuals that accidentally entered the sediment trap.
 Sr in cattle bone and tooth samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Sr in cattle bone and tooth samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryKoarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 36(8), p.1678 - 1682, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:55.72(Chemistry, Analytical)Rapid analysis of  Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. Therefore, the ICP-MS method can be rapid and useful procedure of
Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. Therefore, the ICP-MS method can be rapid and useful procedure of  Sr in small bone and tooth samples derived from terrestrial animals.
Sr in small bone and tooth samples derived from terrestrial animals.
 As
As
Taen, Toshihiro*; Yagyuda, Hidenori*; Nakajima, Yasuyuki*; Tamegai, Tsuyoshi*; Okayasu, Satoru; Kitamura, Hisashi*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Laviano, F.*; Ghigo, G.*
Physica C, 484, p.62 - 65, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.16(Physics, Applied)We report effects of particle energy on physical properties of Co-doped BaFe As
As in the case of Xe and Au irradiations. The irradiation-induced suppression of
in the case of Xe and Au irradiations. The irradiation-induced suppression of 
 is found to be related with several factors, such as defect structures and the thickness of the crystal. Heavy-ion irradiation induces enhancement of critical current density
is found to be related with several factors, such as defect structures and the thickness of the crystal. Heavy-ion irradiation induces enhancement of critical current density 
 , and a weak dip in the hysteresis loop. The fish-tail effect is completely suppressed by a modest density of defects. The enhancement of
, and a weak dip in the hysteresis loop. The fish-tail effect is completely suppressed by a modest density of defects. The enhancement of 
 is closely related to the defect structure. Namely, splayed structure in columnar defects, inevitably introduced at lower energies, results in a strong enhancement of
is closely related to the defect structure. Namely, splayed structure in columnar defects, inevitably introduced at lower energies, results in a strong enhancement of 
 by forced entanglement of vortices.
by forced entanglement of vortices.
Tamegai, Tsuyoshi*; Taen, Toshihiro*; Yagyuda, Hidenori*; Tsuchiya, Yuji*; Mohan, S.*; Taniguchi, Tomotaka*; Nakajima, Yasuyuki*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sasase, Masato*; Kitamura, Hisashi*; et al.
Superconductor Science and Technology, 25(8), p.084008_1 - 084008_14, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:85 Percentile:93.2(Physics, Applied)Various kinds of energetic particles are irradiated into iron-based superconductors, and their effects on the critical current density 
 and vortex dynamics have been systematically studied. It is found that
and vortex dynamics have been systematically studied. It is found that 
 is enhanced and vortex dynamics is strongly suppressed by energetic particles having a sufficient energy deposition rate, similar to the case of high temperature cuprate superconductors. The enhancement of
is enhanced and vortex dynamics is strongly suppressed by energetic particles having a sufficient energy deposition rate, similar to the case of high temperature cuprate superconductors. The enhancement of 
 , in general, persists up to much higher irradiation doses than in cuprates. However, details of the effect of irradiation depend on the kind of ion species and their energies. Even with the same ions and energies, the effect is not universal for different kinds of iron-based superconductors. The correlated nature of defects created by heavy-ion irradiation is confirmed by the angular dependence of irreversible magnetization.
, in general, persists up to much higher irradiation doses than in cuprates. However, details of the effect of irradiation depend on the kind of ion species and their energies. Even with the same ions and energies, the effect is not universal for different kinds of iron-based superconductors. The correlated nature of defects created by heavy-ion irradiation is confirmed by the angular dependence of irreversible magnetization.
Tamegai, Tsuyoshi*; Taen, Toshihiro*; Yagyuda, Hidenori*; Nakajima, Yasuyuki*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sasase, Masato*; Kitamura, Hisashi*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Kambara, Tadashi*; Kanai, Yasuyuki*
Physica C, 471, p.777 - 780, 2011/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.25(Physics, Applied)Magnetic relaxations in Ba(Fe Co
Co )
) As
As before and after swift particle irradiations are measured. The normalized relaxation rate S shows a clear suppression in a pristine sample at low fields below the self-field. Heavy-ion irradiations suppress these anomalies considerably, although there still remain weak features depending on ion species and/or energies. In a proton irradiated sample, the low-field anomaly of S survives although it is smeared compared with that in a pristine sample. All these results indicate that the low-field anomaly of S is suppressed by defects, and correlated defects have stronger effects.
before and after swift particle irradiations are measured. The normalized relaxation rate S shows a clear suppression in a pristine sample at low fields below the self-field. Heavy-ion irradiations suppress these anomalies considerably, although there still remain weak features depending on ion species and/or energies. In a proton irradiated sample, the low-field anomaly of S survives although it is smeared compared with that in a pristine sample. All these results indicate that the low-field anomaly of S is suppressed by defects, and correlated defects have stronger effects.
 As
As with columnar defects introduced by heavy-Ion irradiation
with columnar defects introduced by heavy-Ion irradiationNakajima, Yasuyuki*; Tsuchiya, Yuji*; Taen, Toshihiro*; Yagyuda, Hidenori*; Tamegai, Tsuyoshi*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sasase, Masato*; Kitamura, Hisashi*; Murakami, Takeshi*
Physica C, 470(20), p.1103 - 1105, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.17(Physics, Applied)We report the formation of columnar defects in Co-doped BaFe As
As single crystals with different heavy ion irradiations. The formation of columnar defects by 200 MeV Au ion irradiation is confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and their density is about 40% of the irradiation dose. Magneto-optical imaging and bulk magnetization measurements reveal that the critical current density
single crystals with different heavy ion irradiations. The formation of columnar defects by 200 MeV Au ion irradiation is confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and their density is about 40% of the irradiation dose. Magneto-optical imaging and bulk magnetization measurements reveal that the critical current density 
 is enhanced in the 200 MeV Au and 800 MeV Xe ion irradiated samples while
is enhanced in the 200 MeV Au and 800 MeV Xe ion irradiated samples while 
 is unchanged in the 200 MeV Ni ion irradiated sample. We also find that vortex creep rates are strongly suppressed by the columnar defects. We compare the effect of heavy-ion irradiation into Co-doped BaFe
is unchanged in the 200 MeV Ni ion irradiated sample. We also find that vortex creep rates are strongly suppressed by the columnar defects. We compare the effect of heavy-ion irradiation into Co-doped BaFe As
As and cuprate superconductors.
and cuprate superconductors.
Koarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Fujiwara, Kenso; Ono, Takumi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have investigated incorporation of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in teeth of cattle and otoliths of fish. Specific activity of
Cs in teeth of cattle and otoliths of fish. Specific activity of  Sr in the dentin tissue was higher than that in the enamel tissue. The result shows change of
Sr in the dentin tissue was higher than that in the enamel tissue. The result shows change of  Sr incorporation in cattle even within a tooth. Concentrations of stable Sr and Cs were 94 ppm and 3 ppb. Distributions of stable Sr and Cs were uniform in the otolith of fish. If distribution of
Sr incorporation in cattle even within a tooth. Concentrations of stable Sr and Cs were 94 ppm and 3 ppb. Distributions of stable Sr and Cs were uniform in the otolith of fish. If distribution of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in the otolith was measured, change of
Cs in the otolith was measured, change of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs incorporation into the fish would be found. These findings suggest that distribution patterns of
Cs incorporation into the fish would be found. These findings suggest that distribution patterns of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in the environment could be estimated from distribution of the radionuclides in the tooth and otolith.
Cs in the environment could be estimated from distribution of the radionuclides in the tooth and otolith.
Koarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Terashima, Motoki; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; et al.
no journal, ,
We demonstrated a method of  Sr measurement in small pieces of hard tissues with radioactivity measurement or ICP-MS measurement. Interference elements of the measurements were removed by chemical separation. We could determine
Sr measurement in small pieces of hard tissues with radioactivity measurement or ICP-MS measurement. Interference elements of the measurements were removed by chemical separation. We could determine  Sr in 0.1 g of hard tissues by radioactivity measurement method and ICP-MS method. Limit of detection of the ICP-MS method was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. The ICP-MS method is adequate method for distribution analysis of
Sr in 0.1 g of hard tissues by radioactivity measurement method and ICP-MS method. Limit of detection of the ICP-MS method was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. The ICP-MS method is adequate method for distribution analysis of  Sr in the hard tissues.
Sr in the hard tissues.
 Sr in trace amount of bone; Application of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Sr in trace amount of bone; Application of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryKoarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
Rapid analysis of  Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. Therefore, the ICP-MS method can be rapid and useful procedure of
Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. Therefore, the ICP-MS method can be rapid and useful procedure of  Sr in small bone and tooth samples derived from terrestrial animals.
Sr in small bone and tooth samples derived from terrestrial animals.
Koarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
Rapid analysis of  Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. The ICP-MS method was improved by ICP-MS/MS and oxygen-ammonia mixed gas reaction.
Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. The ICP-MS method was improved by ICP-MS/MS and oxygen-ammonia mixed gas reaction.