Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1301 - 1312, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:62.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/08
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Aoi, Nori*; Azaiez, F.*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Kimura, Atsushi; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:44.13(Physics, Nuclear)Ma, F.; Kopecky, S.*; Alaerts, G.*; Harada, Hideo; Heyse, J.*; Kitatani, Fumito; Noguere, G.*; Paradela, C.*; 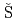 alamon, L.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
alamon, L.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 35(3), p.478 - 488, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.67(Chemistry, Analytical) scintillation detector equipped with specially-designed shield for neutron resonance capture analysis
scintillation detector equipped with specially-designed shield for neutron resonance capture analysisTsuchiya, Harufumi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 932, p.16 - 26, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.42(Instruments & Instrumentation)Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM 60th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/07
Nakamura, Shoji; Kitatani, Fumito; Kimura, Atsushi; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.493 - 502, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross-section( )and resonance integral(I
)and resonance integral(I ) were measured for the
) were measured for the  Np(n,
Np(n, )
) Np reaction by an activation method. A method with a Gadolinium filter, which is similar to the Cadmium difference method, was used to measure the
Np reaction by an activation method. A method with a Gadolinium filter, which is similar to the Cadmium difference method, was used to measure the  with paying attention to the first resonance at 0.489 eV of
with paying attention to the first resonance at 0.489 eV of  Np, and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as a cut-off energy. Neptunium-237 samples were irradiated at the pneumatic tube of the Kyoto University Research Reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as monitors to determine thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A
Np, and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as a cut-off energy. Neptunium-237 samples were irradiated at the pneumatic tube of the Kyoto University Research Reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as monitors to determine thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A  -ray spectroscopy was used to measure activities of
-ray spectroscopy was used to measure activities of  Np,
Np,  Np and neutron monitors. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the
Np and neutron monitors. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the  and I
and I values were derived as 186.9
values were derived as 186.9 6.2 barn, and 1009
6.2 barn, and 1009 90 barn, respectively.
90 barn, respectively.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Ma, F.; Kitatani, Fumito; Paradella, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Proceedings of 41st ESARDA Annual Meeting (Internet), p.374 - 377, 2019/05
Kitatani, Fumito; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Toh, Yosuke; Hori, Junichi*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Takahashi, Yoshiyuki*; Nakajima, Ken*
KURRI Progress Report 2017, P. 99, 2018/08
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Toh, Yosuke; Paradela, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Proceedings of INMM 59th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/07
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 59th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Maeda, Makoto; Toh, Yosuke; Kureta, Masatoshi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 13(Sp.1), p.2406004_1 - 2406004_4, 2018/02
Recently, it has become important in the field of nuclear nonproliferation and nuclear security to quantify nuclear materials (NMs) of uranium and plutonium in nuclear fuel using a non-destructive assay (NDA) technique. Currently, there is no reliable NDA system to apply to nuclear fuels such as spent fuel, fuel debris and next generation fuel for nuclear transmutation. Accordingly, development of NDA techniques for quantification of NMs in those fuels is an urgent issue. Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is one candidate that is applicable to the quantification of NMs. Utilizing pulsed neutron beams, NRTA analyzes the content of a sample by measuring neutron beams that are transmitted from the sample. It is one of the reliable NDA methods that are based on a neutron time-of-flight technique for accurately evaluating nuclear data such as total cross sections and resonance parameters. A present NRTA system generally requires a large electron linear accelerator to produce intense neutron beams. Therefore this is not so easy to apply to various facilities that are used to measure NMs. Given this situation, a compact NRTA system would be required for practical applications of a method to quantify NMs in various samples. In order to realize a compact NRTA system, we consider two types of system: one uses a D-T neutron generator with pulse width of 10  sec and the other a small electron linac with pulse width of 1
sec and the other a small electron linac with pulse width of 1  sec Assuming each system is applied to measurements of NMs in spent fuel, numerical calculations were carried out and the results showed that the pulse widths of neutron beam largely affect the NRTA measurements. In this presentation, we will talk about the NRTA technique and give a schematic design of a compact NRTA system. Then, comparing calculation results for a D-T tube with those for a small electron linac, we especially discuss how the pulse widths of neutron beams to be used for NRTA affect the measurement of NMs in nuclear fuel.
sec Assuming each system is applied to measurements of NMs in spent fuel, numerical calculations were carried out and the results showed that the pulse widths of neutron beam largely affect the NRTA measurements. In this presentation, we will talk about the NRTA technique and give a schematic design of a compact NRTA system. Then, comparing calculation results for a D-T tube with those for a small electron linac, we especially discuss how the pulse widths of neutron beams to be used for NRTA affect the measurement of NMs in nuclear fuel.
Paradela, C.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.09002_1 - 09002_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:97.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kitatani, Fumito; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takamine, Jun; Hori, Junichi*; Sano, Tadafumi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.09032_1 - 09032_3, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Seya, Michio; et al.
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.684 - 693, 2017/00

 -ray spectrometer for detecting
-ray spectrometer for detecting  B in debris of melted nuclear fuel
B in debris of melted nuclear fuelKoizumi, Mitsuo; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; Mondelaers, W.*; Paradela, C.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 837, p.153 - 160, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kunieda, Satoshi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Minato, Futoshi; Okamoto, Tsutomu; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Kitatani, Fumito; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.41 - 46, 2016/09
Neutron- and proton-induced cross-section data are required in a wide energy range beyond 20 MeV, for the design of accelerator applications. New evaluations are performed with recent knowledge in the optical and pre-equilibrium model calculations. We also evaluated cross-sections for p+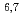 Li and p+
Li and p+ Be which have been highly requested from a medical field. The present high-energy nuclear data library, JENDL-4.0/HE, includes evaluated cross-sections for incident neutrons and protons up to 200 MeV (for about 130 nuclei). We overview substantial features of the library, i.e., (1) systematic evaluation with CCONE code, (2) challenges for evaluations of light nuclei and (3) inheritance of JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/HE-2007. In this talk, we also focus on the results of benchmark calculation for neutronics to show performance of the present library.
Be which have been highly requested from a medical field. The present high-energy nuclear data library, JENDL-4.0/HE, includes evaluated cross-sections for incident neutrons and protons up to 200 MeV (for about 130 nuclei). We overview substantial features of the library, i.e., (1) systematic evaluation with CCONE code, (2) challenges for evaluations of light nuclei and (3) inheritance of JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/HE-2007. In this talk, we also focus on the results of benchmark calculation for neutronics to show performance of the present library.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/07
From a viewpoint of nuclear safeguards and nuclear security, it has recently become important to develop a non-destructive assay (NDA) system that accurately determines the amount of special nuclear materials (SNMs) in various samples such as spent fuels, next generation MA-Pu fuels and fuel debris. One candidate of those NDA techniques is neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). It relies on a neutron time-of-flight measurement and is a well-established method to apply for the accurate evaluations of nuclear data, including total cross sections and resonance parameters. The potential of NRTA to quantify SNM in complex materials has been already demonstrated by performing NRTA measurement at IRMM/GELINA under collaboration of JAEA and JRC. However, a present NRTA system usually has a large electron accelerator facility to generate intense neutrons, whereas this is very difficult to apply to various facilities that need to measure SNM. Therefore a compact NRTA system would be required for practical applications of quantifying SNM in a variety of samples. In order to realize a compact NRTA system, we are developing a prototype with a D-T neutron generator that has a pulse width of 10  s and an average maximum neutron yield ranging from
s and an average maximum neutron yield ranging from 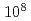 n/s to
n/s to 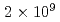 n/s. Numerical calculations were used to optimize the system performance to quantify SNM and MA in spent and MA-Pu fuels. In this presentation, those numerical calculation results, together with a brief description of the prototype, are presented. In addition, we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system equipped with a neutron source with a shorter pulse width (ex. 100 ns) and a more intense neutron yield.
n/s. Numerical calculations were used to optimize the system performance to quantify SNM and MA in spent and MA-Pu fuels. In this presentation, those numerical calculation results, together with a brief description of the prototype, are presented. In addition, we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system equipped with a neutron source with a shorter pulse width (ex. 100 ns) and a more intense neutron yield.
 Se(
Se( , n) cross section and the evaluation of uncertainty of
, n) cross section and the evaluation of uncertainty of  Se(n,
Se(n,  ) cross section
) cross sectionKitatani, Fumito
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (114), p.44 - 49, 2016/06
no abstracts in English
 Se(
Se( , n) cross section and uncertainty evaluation of the
, n) cross section and uncertainty evaluation of the  Se(n,
Se(n,  ) cross section
) cross sectionKitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Goko, Shinji*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Kawakatsu*; Igashira, Masayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(4), p.475 - 485, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)