Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Seto, Hitoshi*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.1039 - 1054, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth rate (CGR) tests have been performed in simulated Boiling Water Reactor water conditions at  288
288 C on neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) at
C on neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) at  12-14 dpa. After the tests, the microstructures near the crack tip of the specimens are examined with scanning transmission electron microscope (FE-STEM). In comparison with a previous study at
12-14 dpa. After the tests, the microstructures near the crack tip of the specimens are examined with scanning transmission electron microscope (FE-STEM). In comparison with a previous study at 
 2 dpa, this result shows a less benefit of low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) conditions on CGR. A crack tip immersed over 1000 hours was filled with oxides, while almost no oxide film was observed near the crack front in the low-ECP conditions. In addition, a high density of deformation twins and dislocations were found near the fracture surface of the crack front. It is considered that both localized deformation and oxidation are possible dominant factors for the SCC growth in highly irradiated SSs.
2 dpa, this result shows a less benefit of low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) conditions on CGR. A crack tip immersed over 1000 hours was filled with oxides, while almost no oxide film was observed near the crack front in the low-ECP conditions. In addition, a high density of deformation twins and dislocations were found near the fracture surface of the crack front. It is considered that both localized deformation and oxidation are possible dominant factors for the SCC growth in highly irradiated SSs.
Kasahara, Shigeki; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 480, p.386 - 392, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper addresses influence of two different temperature profiles during startup periods in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor and a boiling water reactor upon microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel irradiated with neutrons to about 1 dpa and 3 dpa. Tensile tests at 290 C and Vickers hardness tests at room temperature were carried out, and their microstructures were observed by FEG-TEM. Influence of difference in the temperature profiles was observed obviously in interstitial cluster formation, in particular, growth of Frank loops. The influence was also found certainly in loss of strain hardening capacity and ductility, although the influence on the yield strength and the Vickers hardness was not clearly observed. As a result, Frank loops, which were observed in austenitic stainless steel irradiated at doses of 1 dpa or more, were considered to contribute to deformation of the austenitic stainless steel.
C and Vickers hardness tests at room temperature were carried out, and their microstructures were observed by FEG-TEM. Influence of difference in the temperature profiles was observed obviously in interstitial cluster formation, in particular, growth of Frank loops. The influence was also found certainly in loss of strain hardening capacity and ductility, although the influence on the yield strength and the Vickers hardness was not clearly observed. As a result, Frank loops, which were observed in austenitic stainless steel irradiated at doses of 1 dpa or more, were considered to contribute to deformation of the austenitic stainless steel.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 475, p.71 - 80, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:70.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To elucidate the mechanism of irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) in high-temperature water for neutron-irradiated austenitic stainless steels (SSs), the locally deformed structures, the oxide films formed on the deformed areas, and their correlation were investigated. Tensile specimens made of irradiated 316L SSs were strained 0.1%-2% at room temperature or at 563 K, and the surface structures and crystal misorientation among grains were evaluated. The strained specimens were immersed in high-temperature water, and the microstructures of the oxide films on the locally deformed areas were observed. The appearance of visible step structures on the specimens' surface depended on the neutron dose and the applied strain. The surface oxides were observed to be prone to increase in thickness around grain boundaries (GBs) with increasing neutron dose and increasing local strain at the GBs. No penetrative oxidation was observed along GBs or along surface steps.
Ito, Masayasu; Kawamata, Kazuo; Sozawa, Shizuo; Shibata, Akira; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Kodama, Mitsuhiro*
JAEA-Testing 2011-003, 22 Pages, 2011/06
In JMTR, beryllium metal is used for neutron reflector. However, the periodical exchange of the neutron reflector is necessary due to degradation of strength and swelling under neutron irradiation. So it is required to select the material that bears long term from the viewpoint of the utilization rate improvement and the radioactive waste decrease in JMTR. It is important to evaluate the characteristics of beryllium metals precisely. This report describes the preparation method of the sample and observation results by the transmission electron microscope that is being examined as a evaluation method of the beryllium metal.
Sawai, Tomotsugu; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Saito, Shigeru; Kikuchi, Kenji
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 356(1-3), p.118 - 121, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A type 316 stainless steel 316F and Ti-modified type 316 stainless steel JPCA irradiated in SINQ were examined using transmission electron microscopy. Estimated irradiation temperature for two 316F specimens were 250-300 C and that for the JPCA specimen was 255
C and that for the JPCA specimen was 255 C. Irradiation damage of these specimens is calculated to be about 10 dpa. Frank loops up to 30 nm and larger perfect loops up to 50 nm were observed in 316F irradiated at 300
C. Irradiation damage of these specimens is calculated to be about 10 dpa. Frank loops up to 30 nm and larger perfect loops up to 50 nm were observed in 316F irradiated at 300 C. Frank loops observed in JPCA is somewhat smaller, suggesting lower dislocation bias in JPCA.
C. Frank loops observed in JPCA is somewhat smaller, suggesting lower dislocation bias in JPCA.
Kitsunai, Yuji*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
In order to consider mechanism on irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC), oxide films on surface of locally deformed structure in irradiated stainless steel are investigated. The miniature tensile specimens are made of 316L stainless steels irradiated with neutrons in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). The specimens are strained up to 0.1-2%, and surface structure and crystal misorientation among grains are observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and electron backscattering diffraction (EBSD). As a result, visible step structure due to slip plane is appeared on the specimen surface, depending on the neutron fluence and the applied strain level. Furthermore, the data from EBSD suggests that the localization of strain occurred in the vicinity of grain boundaries. The visible step structure characterized from the viewpoints of the morphology and density, and the effects of neutron fluence and stain are discussed on the step structure are discussed.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Seto, Hitoshi*; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth tests in simulated BWR water conditions (at  563 K) were performed using neutron-irradiated specimens made of 316L stainless steels, and the oxide film properties and locally deformed structures near the crack tip have been investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). When electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) of the materials was lowered by deaeration and hydrogen injection into feed water, apparent suppression of oxidation inside the cracks was observed as well as suppression of the crack growth rate (CGR). In the presentation, the TEM results of the locally deformed structures along the cracks are also reported, and the relation among the CGR, oxide film properties, and locally deformed structures is discussed.
563 K) were performed using neutron-irradiated specimens made of 316L stainless steels, and the oxide film properties and locally deformed structures near the crack tip have been investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). When electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) of the materials was lowered by deaeration and hydrogen injection into feed water, apparent suppression of oxidation inside the cracks was observed as well as suppression of the crack growth rate (CGR). In the presentation, the TEM results of the locally deformed structures along the cracks are also reported, and the relation among the CGR, oxide film properties, and locally deformed structures is discussed.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hata, Kuniki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Seto, Hitoshi*; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
In order to investigate effects of environmental mitigation and water radiolysis caused by  -rays from radioactive material on irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior for highly irradiated material, crack growth tests in simulated BWR water conditions (at 563 K) are performed. The specimens made of 316L stainless steels are irradiated with neutrons up to
-rays from radioactive material on irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior for highly irradiated material, crack growth tests in simulated BWR water conditions (at 563 K) are performed. The specimens made of 316L stainless steels are irradiated with neutrons up to  12 dpa in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). One of the specimens is annealed at 973 K for 1 hour to show almost recovered mechanical and micro-chemical properties corresponding to the unirradiated material. For low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) condition, the crack growth rate (CGR) is suppressed by about one order of magnitude in high stress intensity factor (K) condition. This result indicates that environmental mitigation for crack growth can be found even under severe conditions on material and stress factors. The effects of water radiolysis on the CGRs are discussed.
12 dpa in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). One of the specimens is annealed at 973 K for 1 hour to show almost recovered mechanical and micro-chemical properties corresponding to the unirradiated material. For low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) condition, the crack growth rate (CGR) is suppressed by about one order of magnitude in high stress intensity factor (K) condition. This result indicates that environmental mitigation for crack growth can be found even under severe conditions on material and stress factors. The effects of water radiolysis on the CGRs are discussed.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Seto, Hitoshi*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth tests using compact tension (CT) specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) were performed in simulated BWR environments (at  288
288 C). Moreover, microstructures of deformed areas were observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM) after straining tensile specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L SSs. As a result, for lower neutron dose than
C). Moreover, microstructures of deformed areas were observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM) after straining tensile specimens made of neutron-irradiated 316L SSs. As a result, for lower neutron dose than 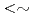 1.9 dpa, the crack growth rates (CGRs) show effective environmental mitigation and the deformed structures show tangling of dislocations. On the other hand, for higher neutron dose than
1.9 dpa, the crack growth rates (CGRs) show effective environmental mitigation and the deformed structures show tangling of dislocations. On the other hand, for higher neutron dose than 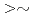 2.7 dpa, the CGRs show small environmental mitigation and the deformed structures consist mainly of dislocation channels. From the relationship between CGRs and deformed structures, mechanisms on IASCC growth will be discussed.
2.7 dpa, the CGRs show small environmental mitigation and the deformed structures consist mainly of dislocation channels. From the relationship between CGRs and deformed structures, mechanisms on IASCC growth will be discussed.
Kitsunai, Yuji*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Akihiro*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Sato, Ikken
no journal, ,
Several contaminant samples from 1F1 primary containment vessel are carefully observed by transmission electron microscope to find micro-scale uranium-containing particles in their chemical forms of U-rich c-(U,Zr)O and Zr-rich t-(Zr,U)O
and Zr-rich t-(Zr,U)O , which are also observed in fuel debris of TMI-2 and Chernobyl NPP-4.
, which are also observed in fuel debris of TMI-2 and Chernobyl NPP-4.
Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Chatani, Kazuhiro*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
Austenitic stainless steel irradiated with neutrons by using JMTR were examined to evaluate the effects of neutron flux and temperature history at the beginning of the irradiation on their mechanical properties. Specimens of SUS304 were irradiated under two different flux conditions up to a dose of 5 10
10 n/m
n/m . Neutron irradiation of SUS316L specimens up to 2
. Neutron irradiation of SUS316L specimens up to 2 10
10 n/m
n/m was performed under the condition of so-called conventional temperature control, which used to be adopted in JMTR. The comparison of 0.2% proof stress obtained from the specimens suggests that the neutron flux and the temperature history does not remarkably influence the mechanical properties of the irradiated stainless steel.
was performed under the condition of so-called conventional temperature control, which used to be adopted in JMTR. The comparison of 0.2% proof stress obtained from the specimens suggests that the neutron flux and the temperature history does not remarkably influence the mechanical properties of the irradiated stainless steel.
Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*
no journal, ,
According to existing data of slow strain rate tensile (SSRT) test under high temperature water conditions, which simulated BWR primary coolant environment, low carbon stainless steel, which was irradiated with neutrons up to about 3 dpa in BWR core, shows susceptibility of Irradiation associated stress corrosion cracking (IASCC). On the other hand, the stainless steel irradiated by using the JMTR did not show IASCC susceptibility, regardless of neutron fluence. To investigate this different result about IASCC susceptibility, the JMTR operated to simulate temperature history at start-up of BWR, and a tensile specimen of SUS316L was irradiated up to about 3 dpa under the condition. After that, the specimen was examined by SSRT test to evaluate IASCC susceptibility. The result of fracture surface observation after the SSRT test indicated that the specimen fractured by Inter-granular mode and was evaluated to be susceptible to IASCC. In the comparison of the data of IASCC sensitivity by the JMTR irradiated materials, which did not show IASCC susceptibility, the difference of them was suggested to attribute to different temperature histories at the start of irradiation. The relationship between IASCC susceptibility and the parameters obtained from tensile tests was discussed, in consideration of the difference of the tensile parameters which are suffered from the irradiation condition under the different temperature history during the start period of the irradiation.