Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oikawa, Kenichi; Sato, Hirotaka*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Su, Y. H.; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Hasemi, Hiroyuki
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012013_1 - 012013_6, 2023/10
Oikawa, Kenichi; Harjo, S.; Pham, A. H.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Morito, Shigekazu*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oba, Takuya*; Ito, Masakazu*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011062_1 - 011062_6, 2021/03
Parker, J. D.*; Harada, Masahide; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Nakatani, Takeshi; Oikawa, Kenichi; Segawa, Mariko; Shinohara, Takenao; et al.
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.102 - 107, 2020/05
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Nakatani, Takeshi; Segawa, Mariko; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Oi, Motoki; Harada, Masahide; Iikura, Hiroshi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(4), p.043302_1 - 043302_20, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:96.48(Instruments & Instrumentation) He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Instruments & Instrumentation)Oikawa, Kenichi; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Omae, Kazuma*; Pham, A.*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Harjo, S.; et al.
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.207 - 213, 2020/02
 He
He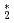 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.76(Physics, Applied)Teshigawara, Makoto; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke*; Ichikawa, Go*; Takata, Shinichi; Mishima, Kenji*; Harada, Masahide; Oi, Motoki; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Kai, Tetsuya; Kawamura, Seiko; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 929, p.113 - 120, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:86.05(Instruments & Instrumentation)A nano-diamond is an attractive neutron reflection material below cold neutron energy. The total neutron cross section of a nano-diamond was derived from a neutron transmission measurement over the neutron energy range of 0.2 meV to 100 meV because total neutron cross section data were not available. The total cross section of a nano-diamond with particle size of approximately 5 nm increased with a decrease in neutron energy to 0.2 meV. It was approximately two orders of magnitude larger than that of graphite at 0.2 meV. The contribution of inelastic scattering to the total cross section was to be shown negligible small at neutron energies of 1.2, 1.5, 1.9, 2.6, and 5.9 meV in the inelastic neutron scattering measurement. Moreover, small-angle neutron scattering measurements of the nano-diamond showed a large scattering cross section in the forward direction for low neutron energies.
Hiroi, Kosuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Parker, J. D.*; Su, Y. H.; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kai, Tetsuya; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.146 - 151, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.82(Physics, Condensed Matter)Kai, Tetsuya; Sato, Setsuo*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Segawa, Mariko; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oikawa, Kenichi; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.496 - 500, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.36(Physics, Condensed Matter)Segawa, Mariko; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kai, Tetsuya; Shinohara, Takenao; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; Nakatani, Takeshi; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 22, p.011028_1 - 011028_8, 2018/11
Hiroi, Kosuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Parker, J. D.*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Su, Y. H.; Kai, Tetsuya; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 22, p.011030_1 - 011030_7, 2018/11
Kai, Tetsuya; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Hiraga, Fujio*; Oi, Motoki; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(3), p.283 - 289, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Hirotaka*; Shiota, Yoshinori*; Morooka, Satoshi; Todaka, Yoshikazu*; Adachi, Nozomu*; Sadamatsu, Sunao*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Zhang, S.*; Su, Y. H.; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 50(6), p.1601 - 1610, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:79.13(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)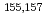 Gd
GdMizuyama, Kazuhito; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hasemi, Hiroyuki*; Kino, Koichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.11042_1 - 11042_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)Gadolinium has been used as neutron-absorbing material in a thermal reactor since 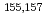 have large thermal neutron capture cross sections. Nevertheless, there is a discrepancy between RPI data and JENDL-4.0 data for
have large thermal neutron capture cross sections. Nevertheless, there is a discrepancy between RPI data and JENDL-4.0 data for  Gd. The criticality in the reactor is very sensitive to the capture cross section. The RPI data made the criticality of Gd-loaded thermal systems in ICSBEP overestimated. Recently, the neutron capture cross sections of
Gd. The criticality in the reactor is very sensitive to the capture cross section. The RPI data made the criticality of Gd-loaded thermal systems in ICSBEP overestimated. Recently, the neutron capture cross sections of 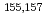 Gd were measured by the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method using the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI) in the J-PARC/MLF. The pulsed neutron beam from the Japan Spallation Neutron Source (JSNS) was used with a double-bunch structure in this measurement, since the incident proton beam is normally delivered in a double-bunch scheme in the J-PARC. In addition to this, it is necessary to take into account the energy resolution of the pulsed neutron beam at the JSNS for the accurate derivation of resolved resonance parameters. In this study, using the least-squares multilevel R-matrix code REFIT modified to include the double bunch structure and the resolution function for the ANNRI, we fitted the calculated capture cross sections of
Gd were measured by the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method using the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI) in the J-PARC/MLF. The pulsed neutron beam from the Japan Spallation Neutron Source (JSNS) was used with a double-bunch structure in this measurement, since the incident proton beam is normally delivered in a double-bunch scheme in the J-PARC. In addition to this, it is necessary to take into account the energy resolution of the pulsed neutron beam at the JSNS for the accurate derivation of resolved resonance parameters. In this study, using the least-squares multilevel R-matrix code REFIT modified to include the double bunch structure and the resolution function for the ANNRI, we fitted the calculated capture cross sections of 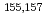 Gd to the experimental data at the ANNRI. We derived the resonance parameters for some low-lying resonances of the two Gd isotopes.
Gd to the experimental data at the ANNRI. We derived the resonance parameters for some low-lying resonances of the two Gd isotopes.
Kai, Tetsuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Segawa, Mariko; Nakatani, Takeshi; Oikawa, Kenichi; et al.
Physics Procedia, 88, p.306 - 313, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:85.09(Instruments & Instrumentation)Su, Y. H.; Oikawa, Kenichi; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gong, W.; Zhang, S. Y.*; Parker, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Procedia, 88, p.42 - 49, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:85.09(Instruments & Instrumentation)Seki, Yoshichika; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Yashiro, Wataru*; Momose, Atsushi*; Kato, Kosuke*; Kato, Hidemi*; Sadeghilaridjani, M.*; Otake, Yoshie*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 86(4), p.044001_1 - 044001_5, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:66.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)For the effective phase imaging at pulsed neutron sources, we have designed and developed the multi-colored Talbot-Lau interferometer which works at several wavelengths. At the Energy Resolved Neutron Imaging System RADEN in J-PARC, we demonstrated its operation by observing the visibilities of moire fringes derived from different wavelengths (0.25, 0.50, and 0.75 nm). We also investigated the variation of moire fringes dependent on the wavelength resolution from 18% to 50% and showed the advantage of pulsed beams. At the central wavelength of 0.5 nm, we have succeeded in interferometric imaging for the samples of metal rods made of aluminum, lead, and copper. An absorption grating as an analyzer was fabricated by imprinting of metallic glass for the first time, and showed a clear moire fringe with the high visibility of 68% and a well-controlled shape in comparison with previous ones fabricated by oblique evaporation of gadolinium.
Oikawa, Kenichi; Su, Y. H.; Tomota, Yo*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Zhang, S.*; Parker, J. D.*; Sato, Hirotaka*; et al.
Physics Procedia, 88, p.34 - 41, 2017/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:89.08(Instruments & Instrumentation)Time of flight Bragg edge transmission (BET) imaging was adopted to the plastically bent plates of a ferritic steel and a duplex stainless steel, and the obtained results were validated using neutron diffraction method and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) observations. The BET imaging results of texture distribution and phase volume fractions showed good agreements with those obtained by neutron diffraction and EBSD. The crystallite size evaluation using extinction correction was succeeded by the RITS code where Sabine's primary extinction function was applied, however, the crystallite size was not obtained by the Rietveld refinement where the same function was used for the evaluation. In this study, we comparatively reinvestigate the crystallite size and the dislocation density of the plastically bent steel plates by the use of Pawley analysis on the diffraction data and grain analysis on EBSD data.
Su, Y. H.; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harjo, S.; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Zhang, S.*; Parker, J. D.*; Sato, Hirotaka*; et al.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 675, p.19 - 31, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:72.59(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)