Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Zhang, L.*; Held, A.*; Ser a, D.*; Klemm, O.*
a, D.*; Klemm, O.*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.530 - 537, 2011/10
In order to investigate the transport of radioactive materials we have developed a one-dimensional numerical model that predicts the transfer of water, heat, and gaseous and particulate matters in atmosphere-soil-vegetation continuous system. The model calculates dry, wet and fog deposition of gaseous and particulate matters onto vegetation, taken into account the dependency of plant species such as leaf shape and leaf surface area. As a result of performance tests of the model under various environmental conditions, the model predicted the observed temporal changes in heat, water and CO fluxes over vegetative and non-vegetative surface, and temperature, water content, and CO
fluxes over vegetative and non-vegetative surface, and temperature, water content, and CO concentration in the soil under the temperate and arid climate. The model also reproduced observational data of mass fluxes of fog water and atmospheric gases such as ozone and
concentration in the soil under the temperate and arid climate. The model also reproduced observational data of mass fluxes of fog water and atmospheric gases such as ozone and 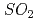 , and number flux of nano-sized aerosols over the vegetation.
, and number flux of nano-sized aerosols over the vegetation.
Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Wrzesinsky, T.*; Klemm, O.*; Eugster, W.*; Burkard, R.*
Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 47(8), p.2129 - 2146, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:57.93(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)A land surface model including cloud water deposition to vegetation was developed to better predict water exchanges between biosphere and atmosphere. High performance of our new model was confirmed and it provided a better prediction of measured cloud water flux than the commonly used model. Simple linear relationships between wind speed and deposition velocity (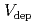 ) were found. Numerical experiments were performed to study the influences of leaf shapes (needle and broad leaves) and canopy structure (Leaf area index (LAI) and canopy height) on
) were found. Numerical experiments were performed to study the influences of leaf shapes (needle and broad leaves) and canopy structure (Leaf area index (LAI) and canopy height) on 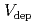 . Broad leaves with small sized leaves can capture larger amounts of cloud water than needle leaves. From the analyses of conductances at given Leaf Area Density (LAD), we found that trees whose LAD
. Broad leaves with small sized leaves can capture larger amounts of cloud water than needle leaves. From the analyses of conductances at given Leaf Area Density (LAD), we found that trees whose LAD 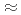 0.1 m
0.1 m m
m are the most efficient structures for cloud water deposition. A simple expression for the slope of
are the most efficient structures for cloud water deposition. A simple expression for the slope of 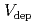 against LAD obtained from the experiments can be useful to predict cloud water deposition.
against LAD obtained from the experiments can be useful to predict cloud water deposition.
Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Wrzesinsky, T.*; Klemm, O.*; Eugster, W.*; Reto, B.*
no journal, ,
Several experiments focusing on cloud (fog) water deposition on the land surface suggest that cloud water plays an important role in water resource in arid and semi-arid areas. A one-dimensional vegetation model including the process of cloud water deposition on vegetation has been developed to better predict cloud water deposition on the vegetation. High performance of the model was confirmed by comparisons of calculated surface heat and cloud water fluxes over the forest with measurements acquired at the Norway spruce forest in the Waldstein, Germany. Numerical experiments to examine the dependence of cloud water deposition on the vegetation species and structures are performed using the presented model. The results showed that the differences of leaf shape and size have a large impact on cloud water deposition and cloud water deposition varies with the growth of vegetation and seasonal change of Leaf Area Index (LAI).
Katata, Genki; Held, A.*; Klemm, O.*; Nagai, Haruyasu
no journal, ,
Dry deposition process in a sophisticated multi-layer atmosphere-soil-vegetation model named SOLVEG was developed. Turbulent transfers in momentum, heat, cloud (fog) liquid water, water vapor, and carbon dioxide are solved in the SOLVEG model. The model takes into account the processes strongly related to dry deposition on vegetation such as stomata opening/closing and solar radiation transfers within canopy layers, in addition to photosynthesis, transpiration, and respiration processes. In this study, new schemes for dry deposition of gas and particulate matter were implemented in the model. Preliminary calculations were compared with measurements of ozone and particle number fluxes over the coniferous forest. Further modifications of the model are needed to estimate comprehensive acid deposition on vegetation via dry, wet and cloud deposition. The improved SOLVEG model may provide reference estimations for dry deposition monitoring in East Asia using simpler dry deposition models.
Katata, Genki; Klemm, O.*; Nagai, Haruyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Katata, Genki; Held, A.*; Nagai, Haruyasu; Klemm, O.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English